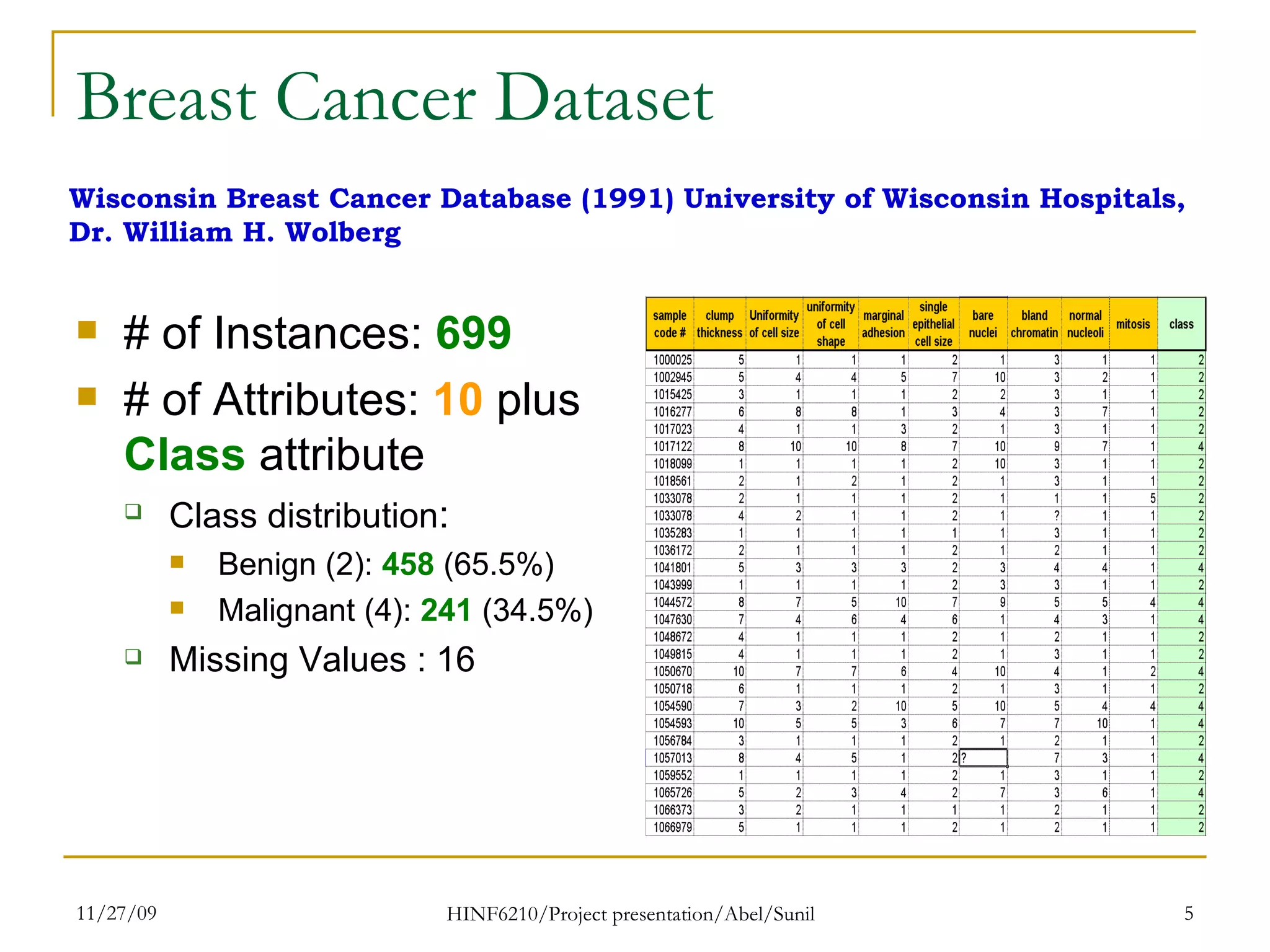
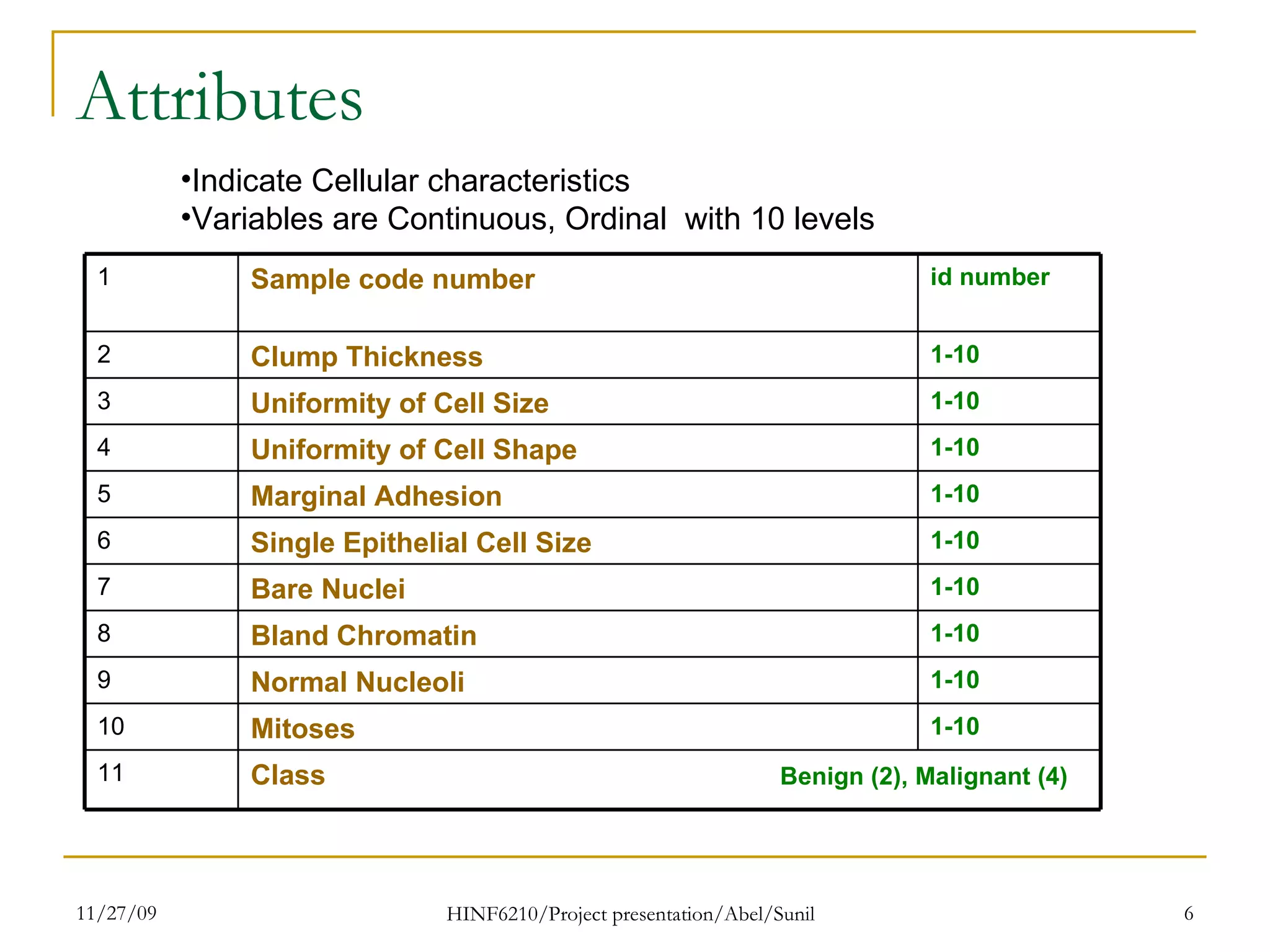
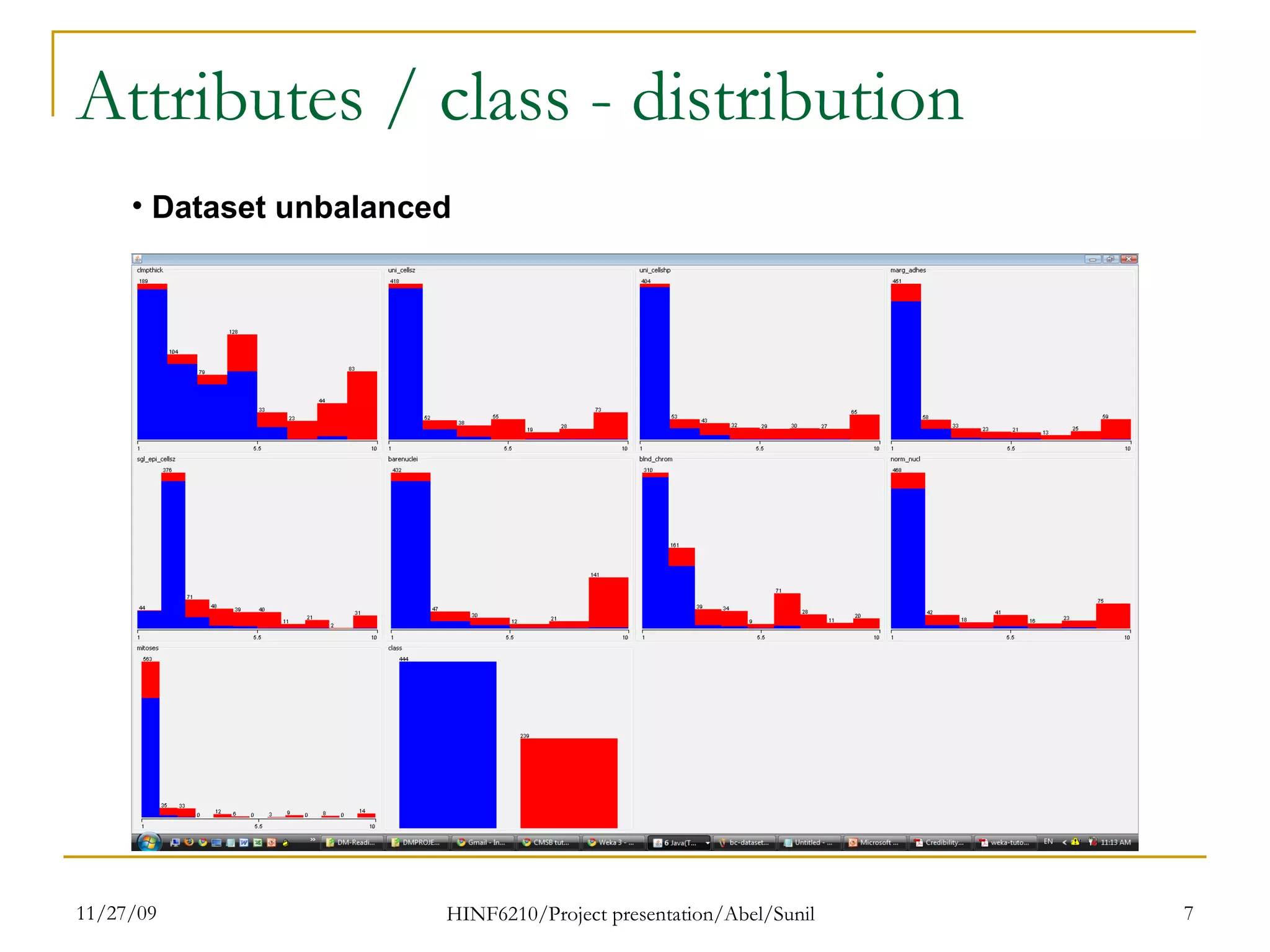
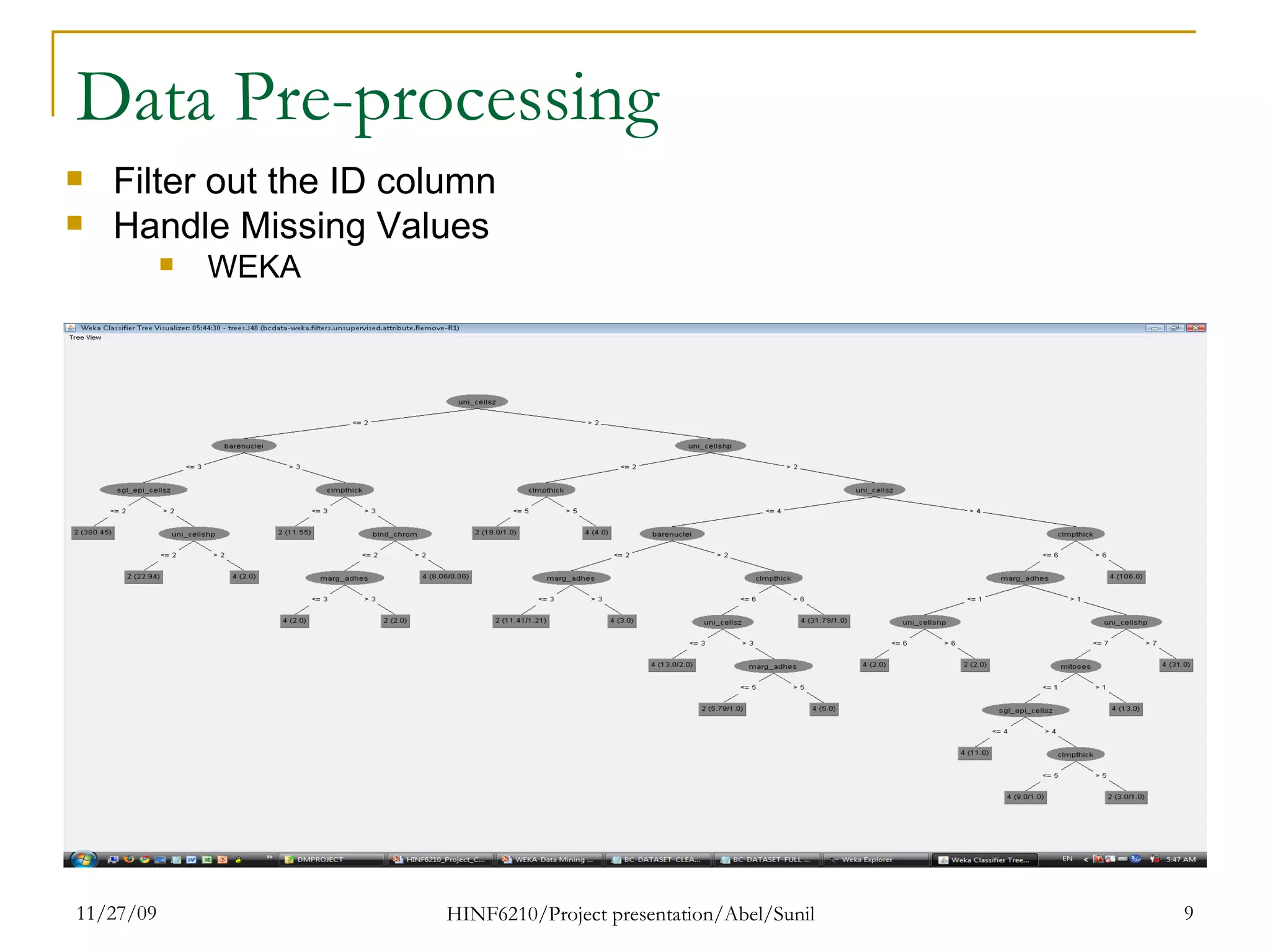
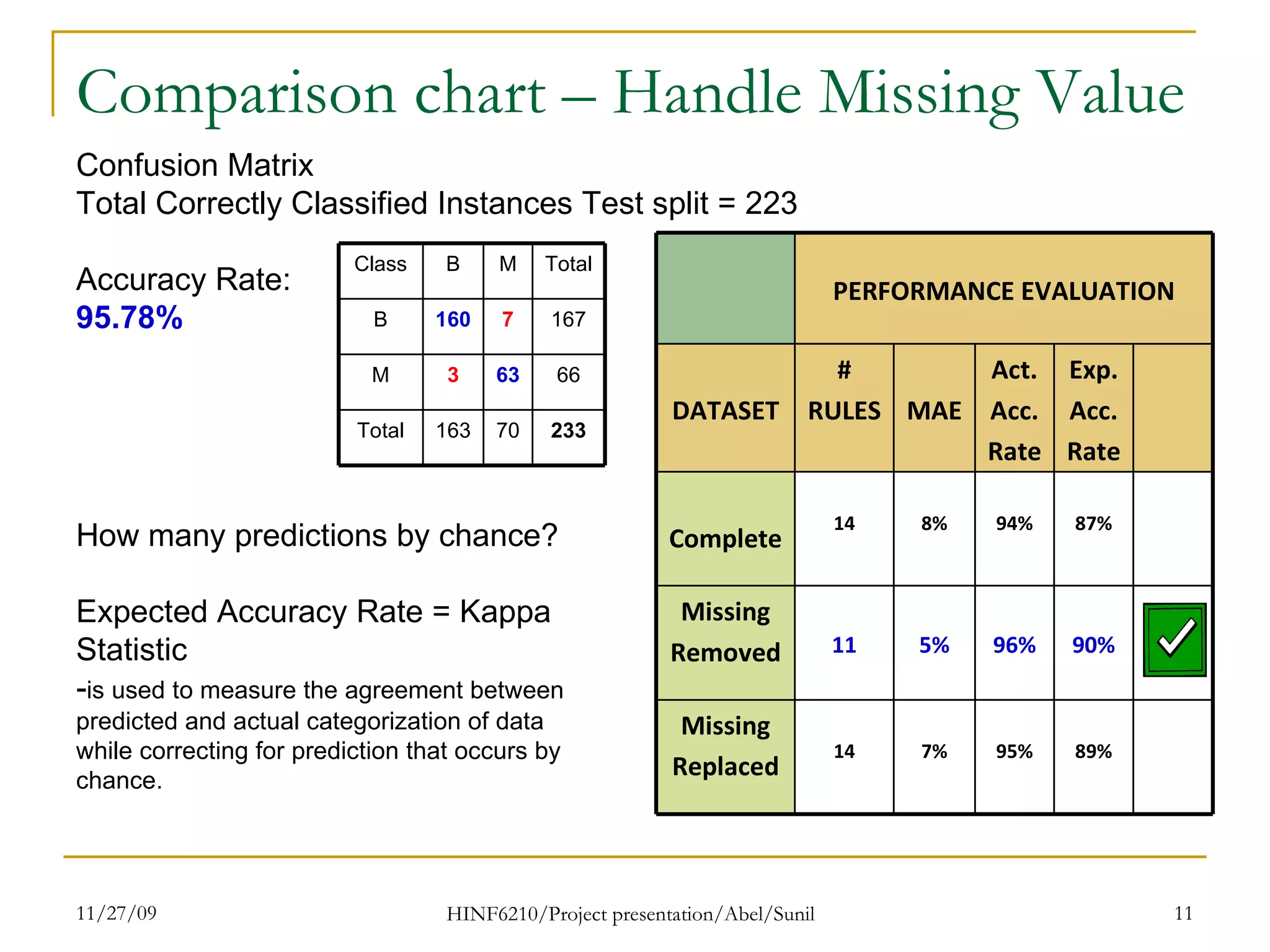
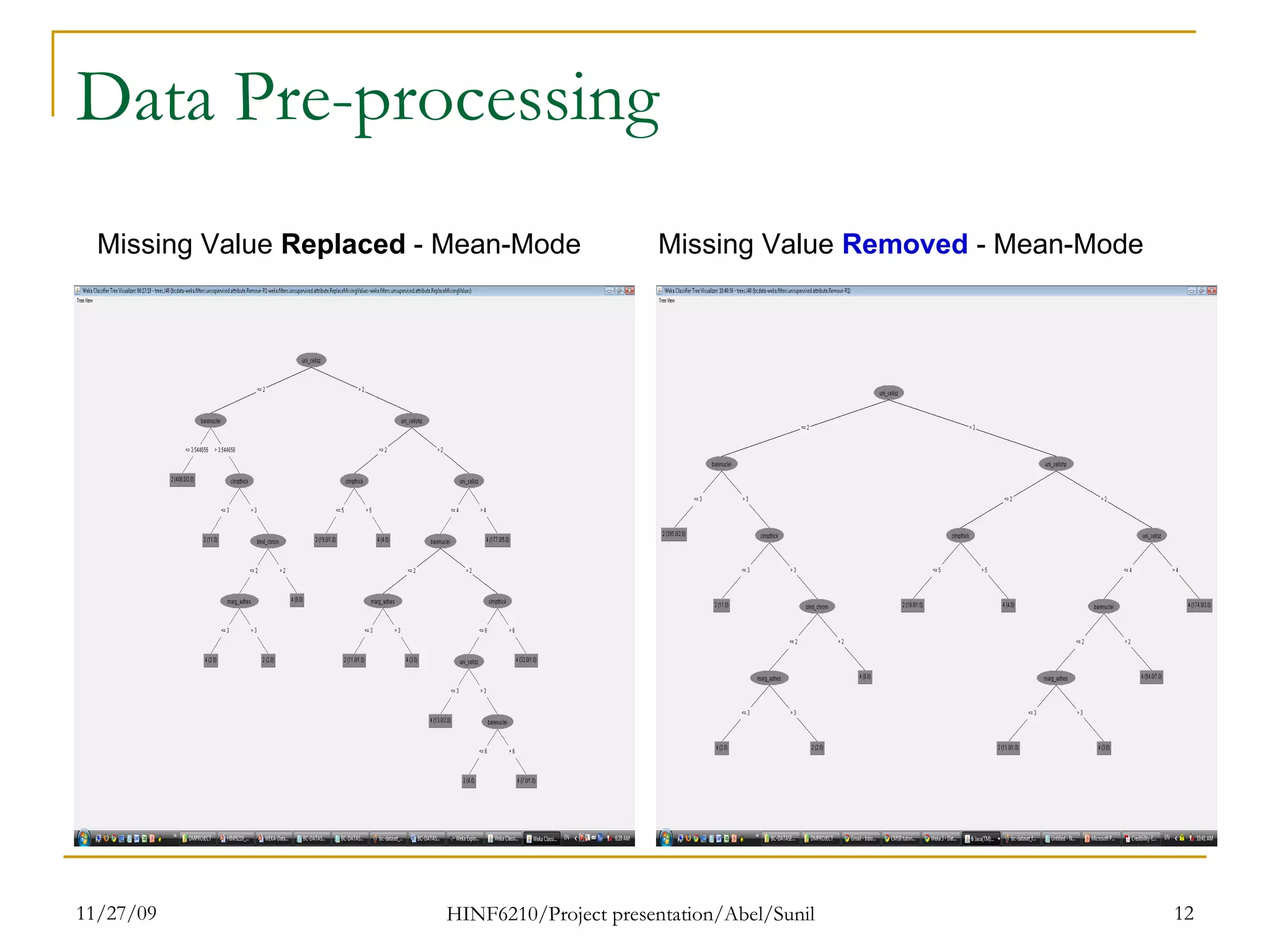
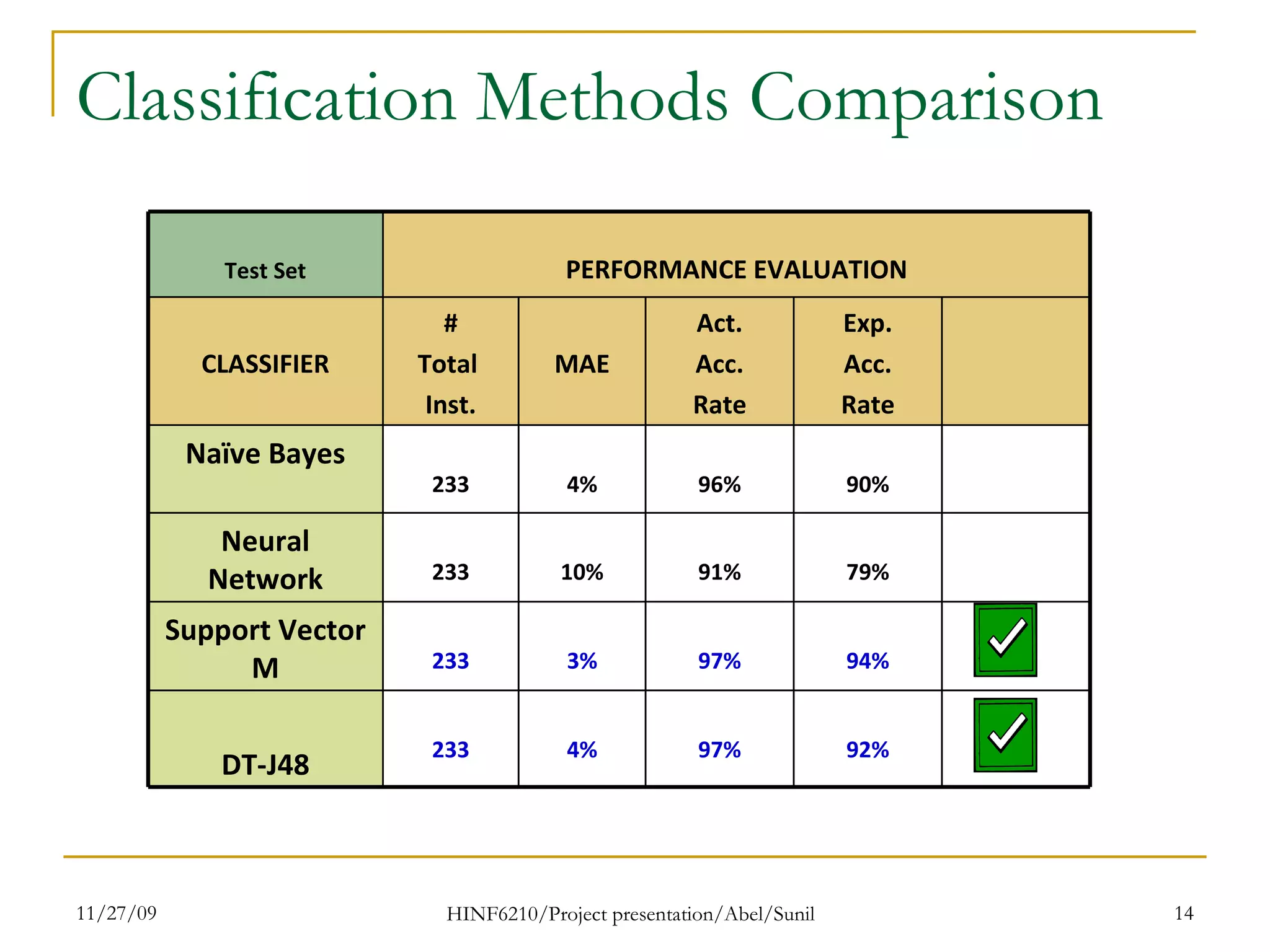
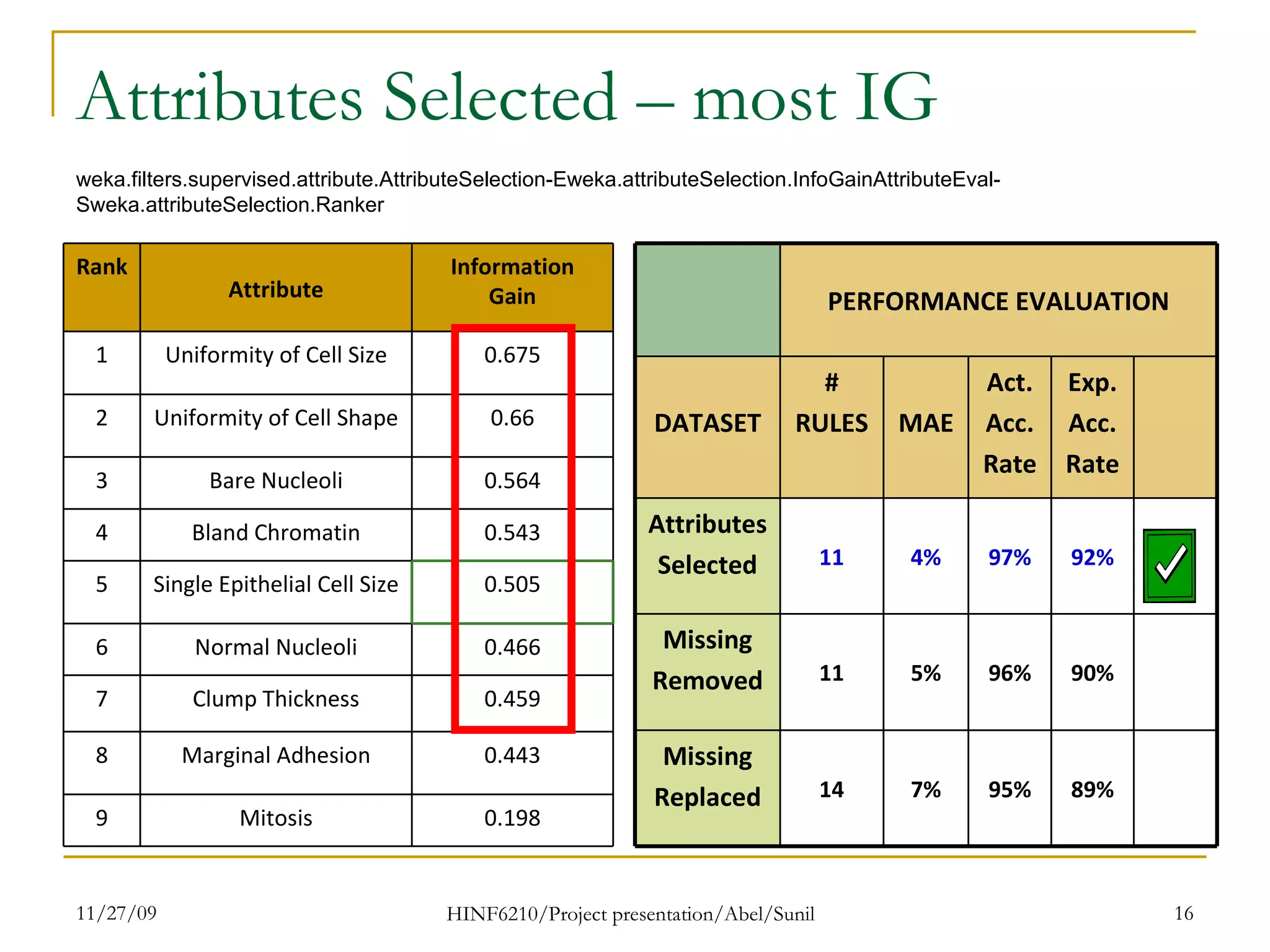
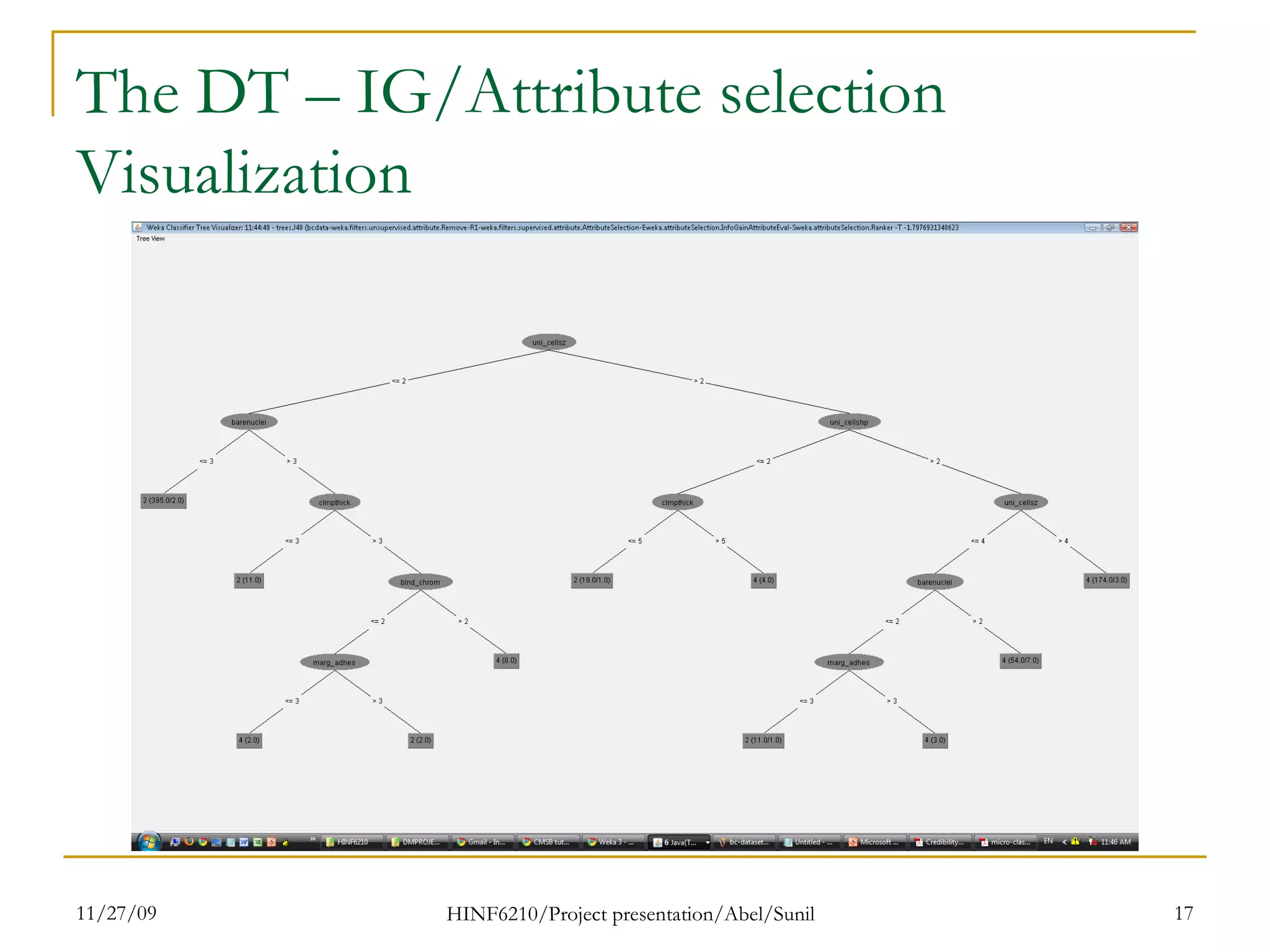
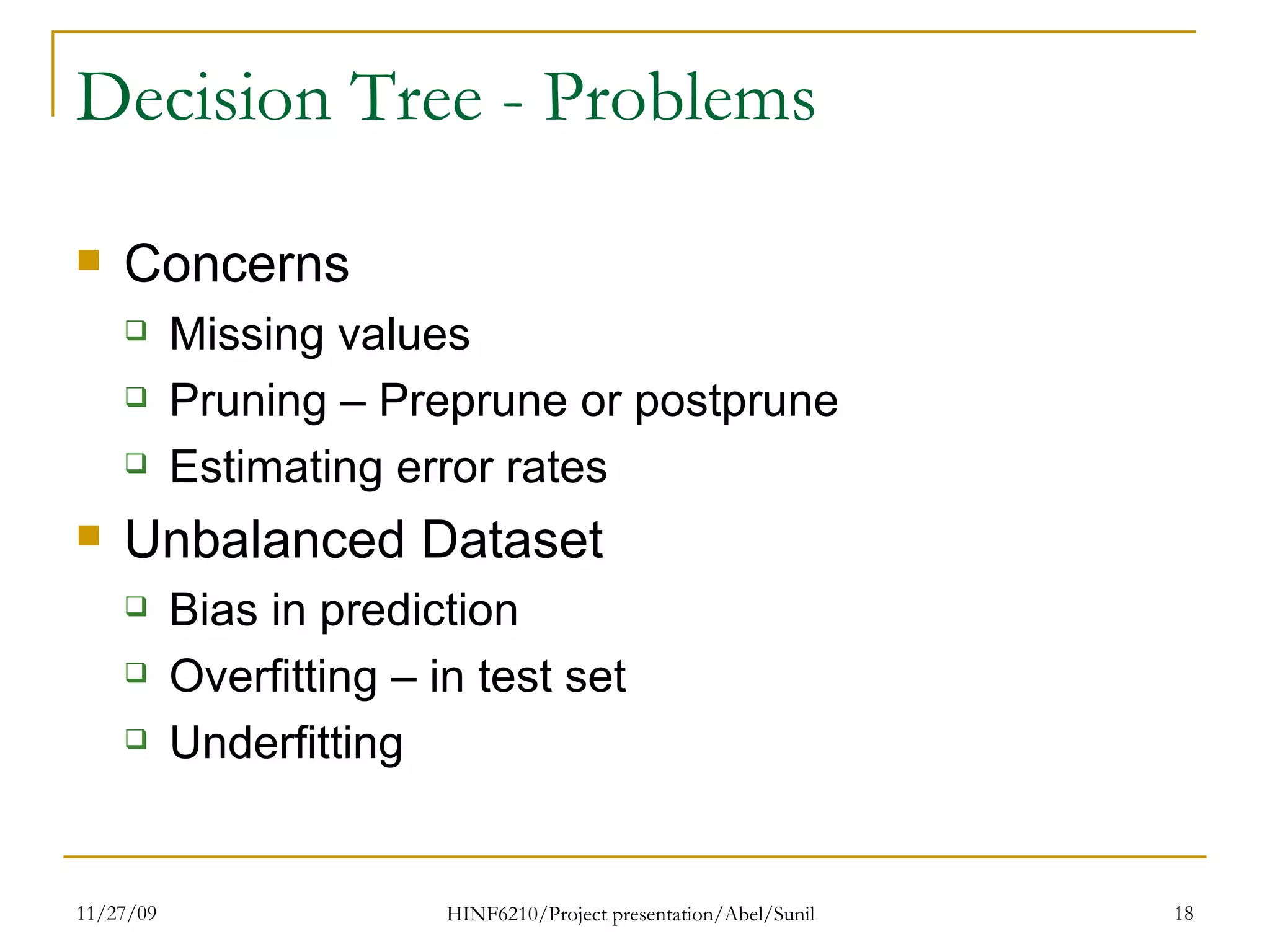
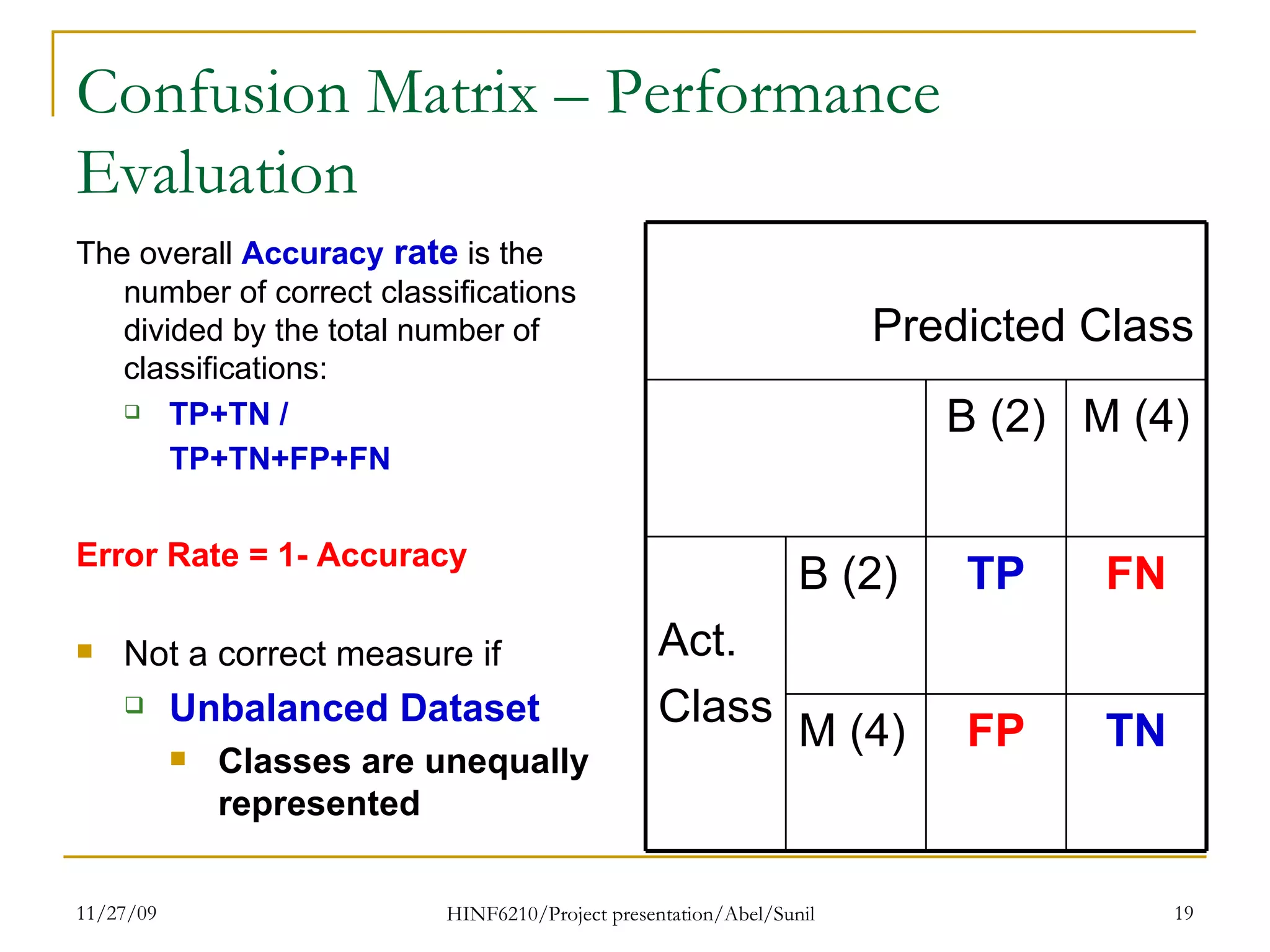
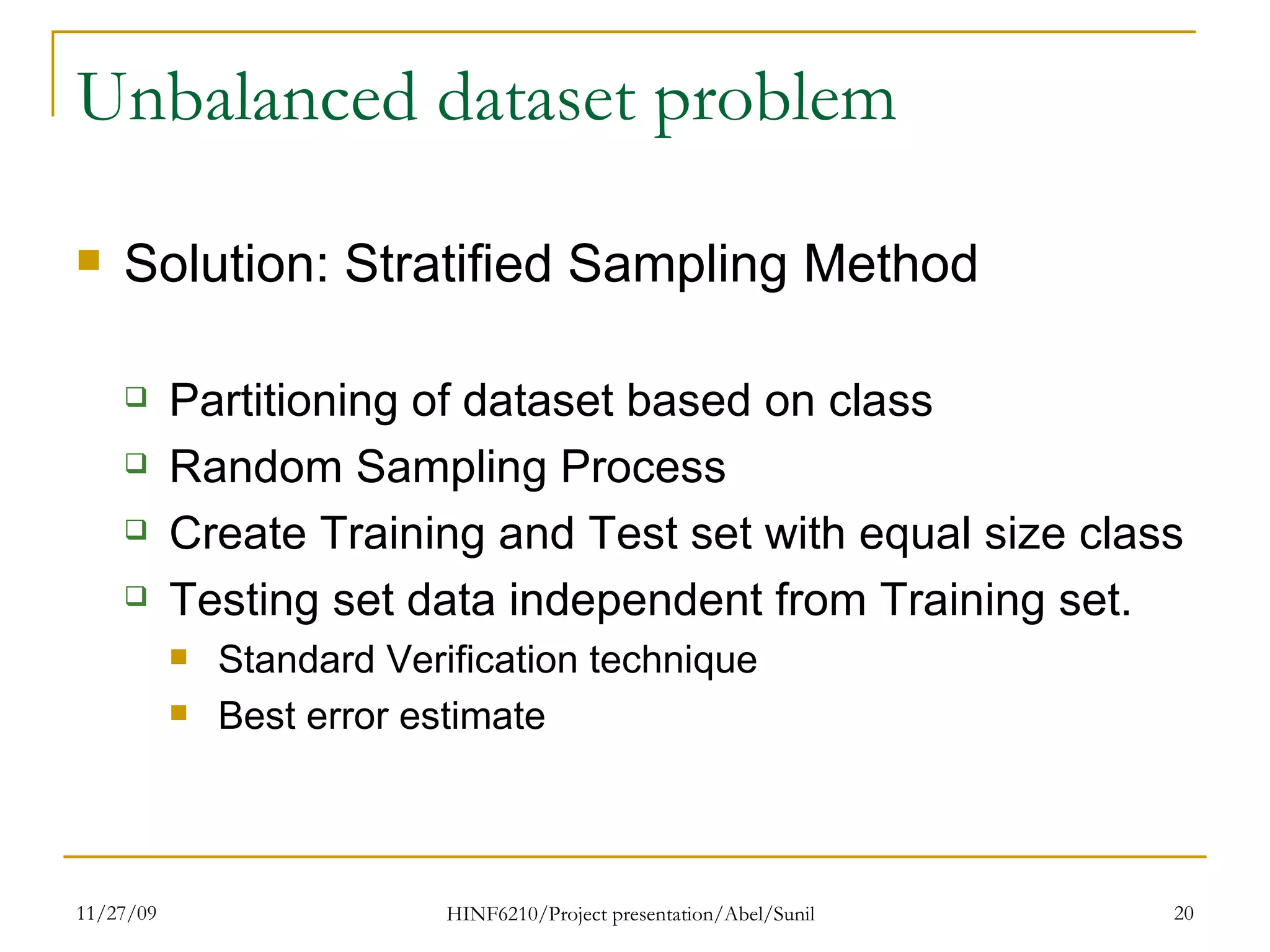
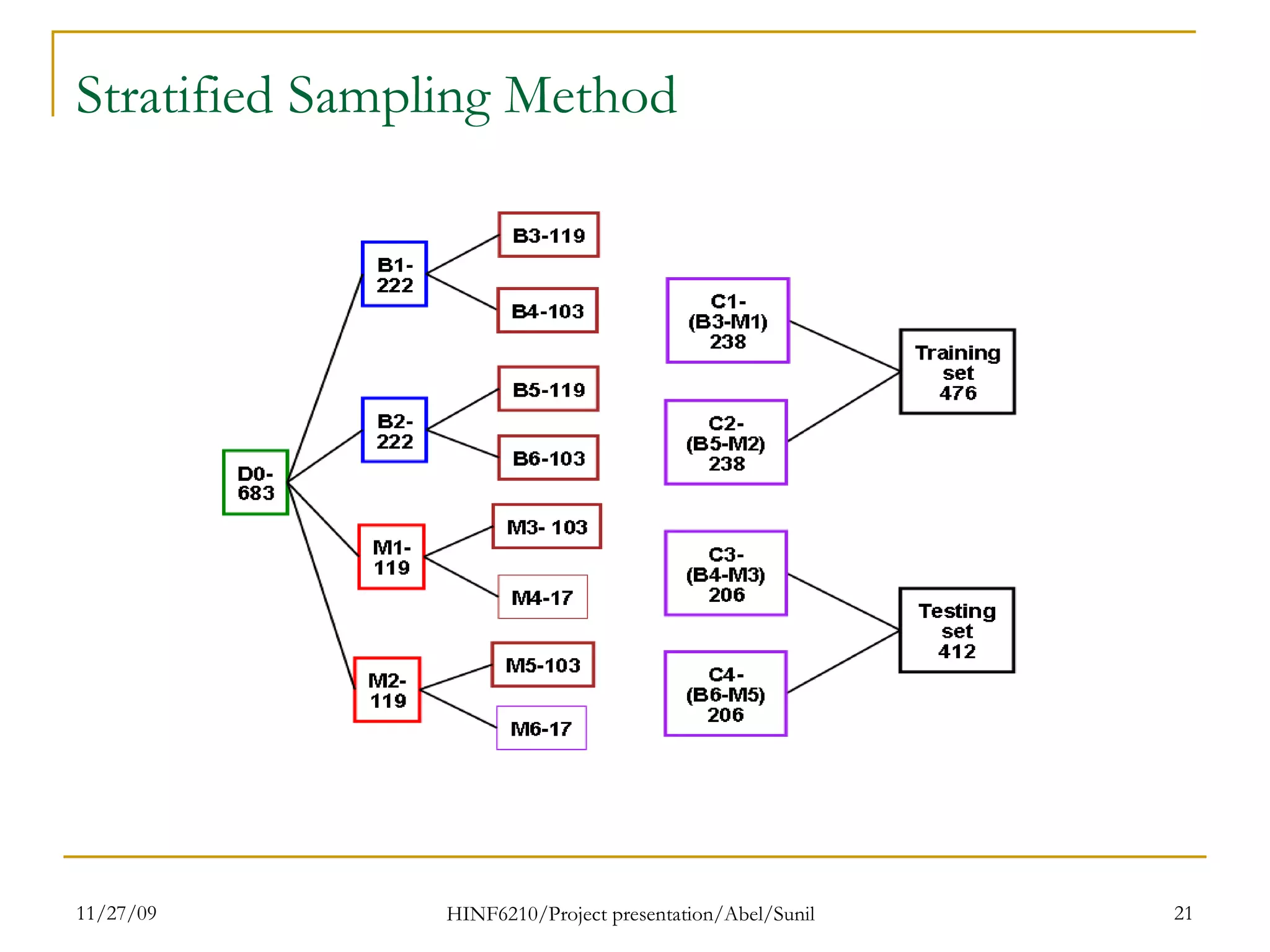
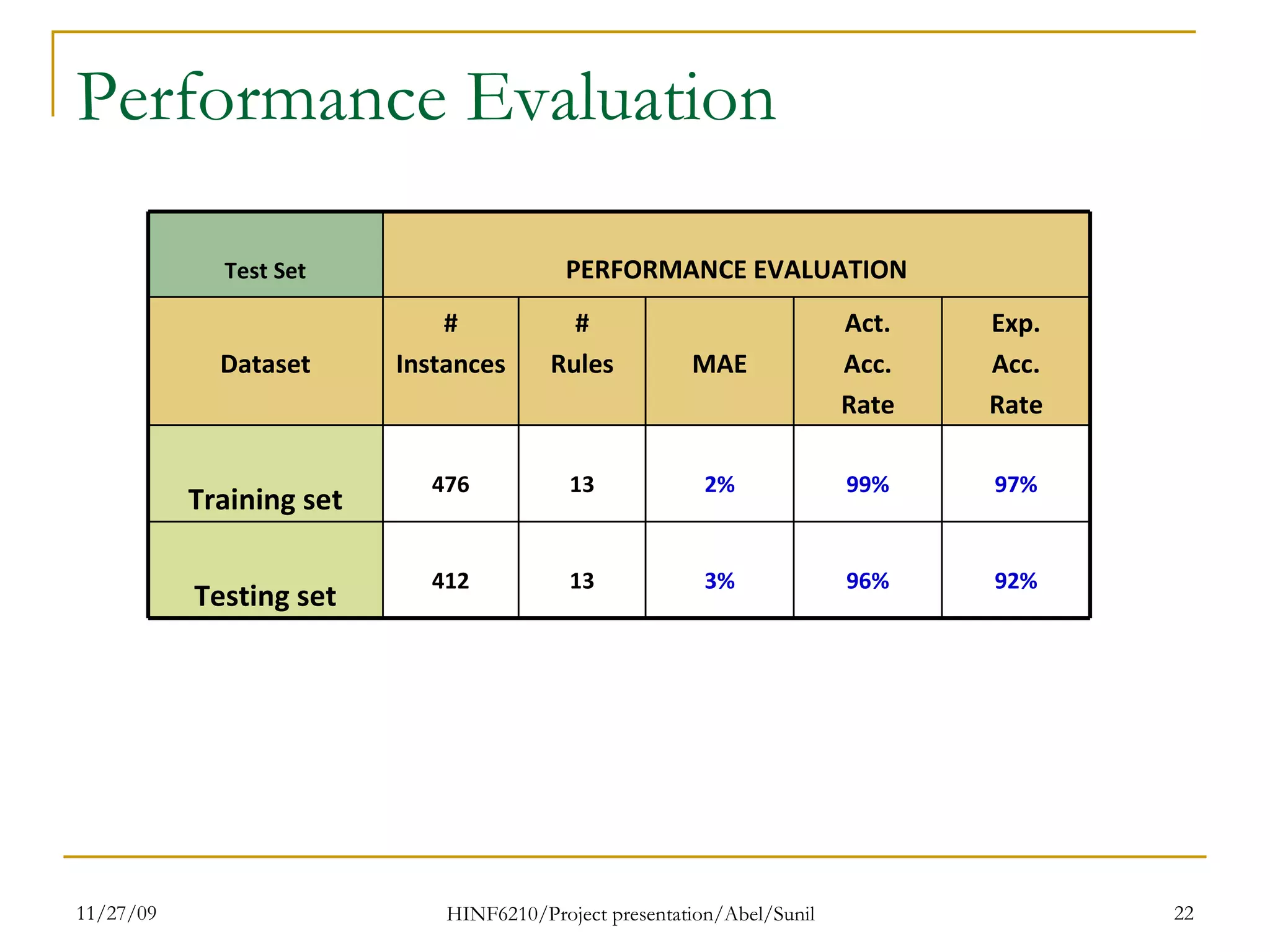
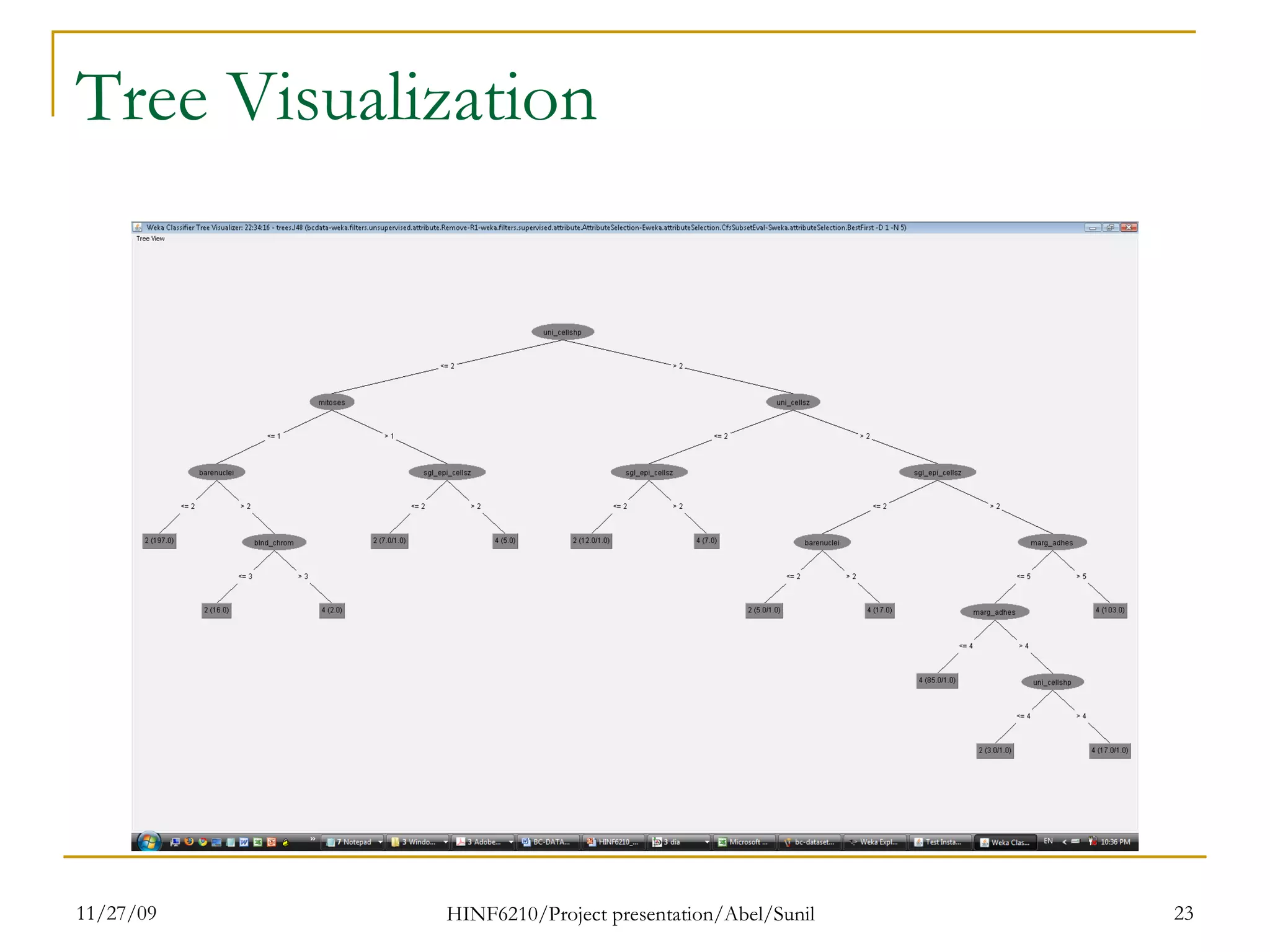
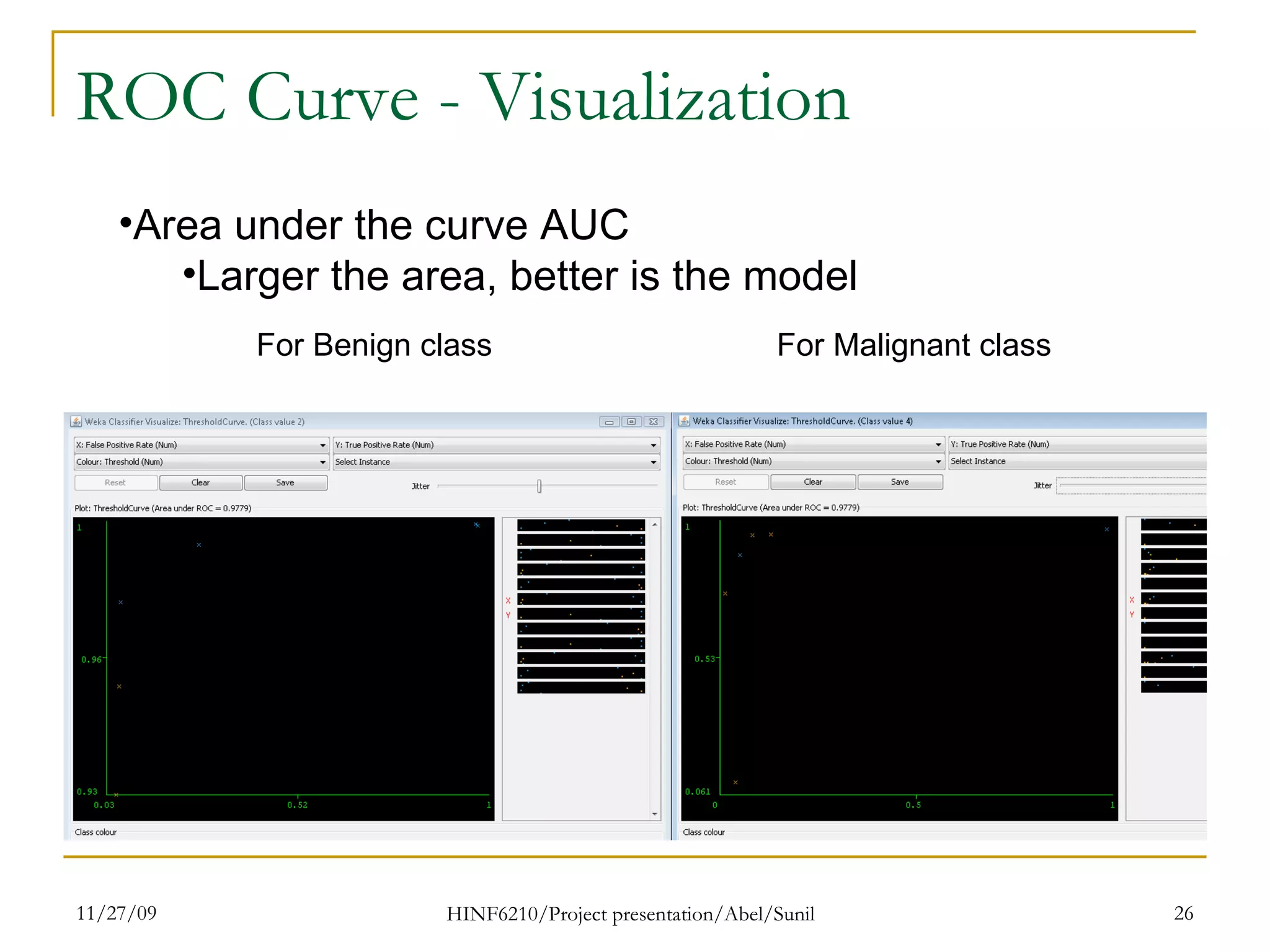
The document summarizes research on classifying breast cancer datasets using decision trees. The researchers used a Wisconsin breast cancer dataset containing 699 instances with 10 attributes plus a class attribute. They preprocessed the data to handle missing values, compared various classification methods, and achieved the best accuracy of 97% using decision trees with attribute selection. Issues addressed included unbalanced classes and future work proposed methods like clustering and multiple classifiers to further improve accuracy.