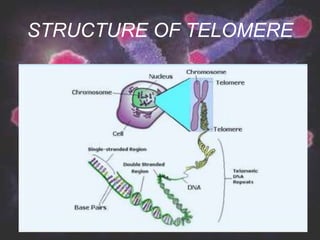
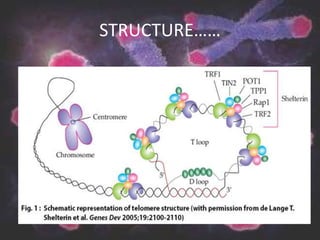
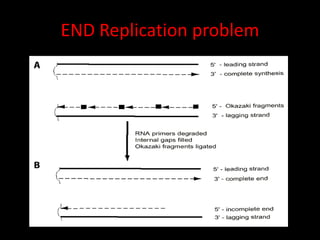
Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes that protect chromosomal integrity. Each cell division causes telomeres to shorten as DNA replication cannot fully copy chromosome ends. When telomeres become too short, cells stop dividing or die. Telomerase is an enzyme that adds telomeric DNA to chromosome ends and counteracts shortening. While most somatic cells lack telomerase, its presence allows cancer cells and germ cells to avoid replicative aging. Maintaining telomere length through telomerase overexpression is a hallmark of cancer cells and targeting this process may lead to new anticancer therapies.