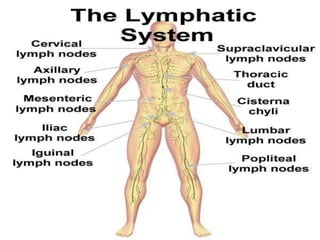
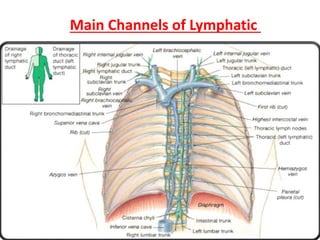
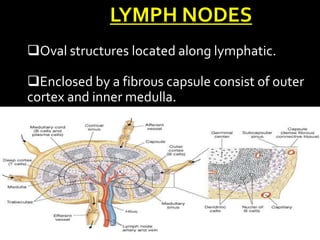
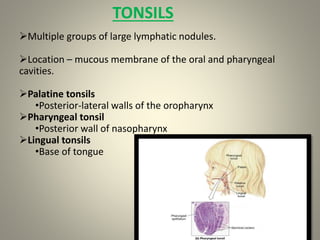
The document outlines the components and functions of the lymphatic system, which includes lymph fluid, lymphatic vessels, and lymph nodes. Key functions include returning tissue fluid to the bloodstream, transporting fats, and providing immune defense through various organs such as the spleen and thymus. It details the structure and function of lymph nodes, tonsils, the spleen, and the thymus gland in supporting the body's immune response.