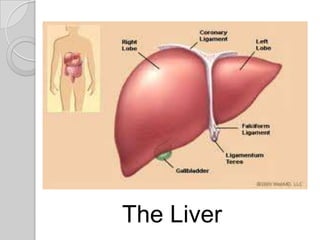
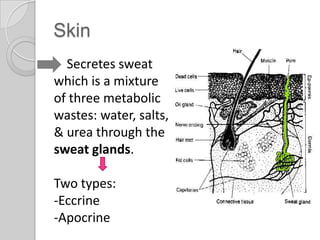
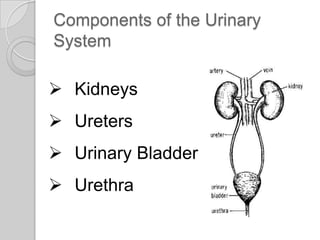
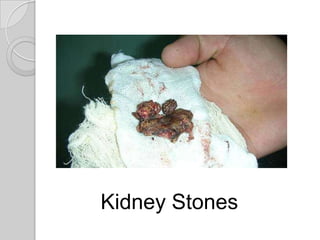
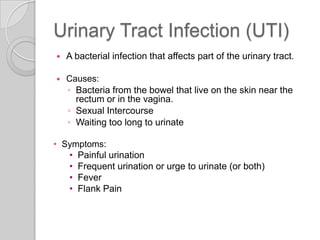
The excretory system removes waste from the body through various organs. It maintains homeostasis by filtering out metabolic waste like carbon dioxide, urea, and salts through the lungs, liver, skin, and urinary system. The kidneys filter blood to form urine via nephrons. Urine is transported by the ureters to the bladder and then exits through the urethra. Common diseases include kidney stones, urinary tract infections, athlete's foot, and bladder cancer.