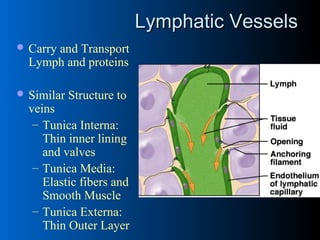
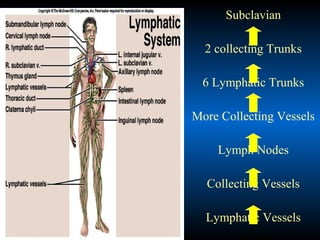
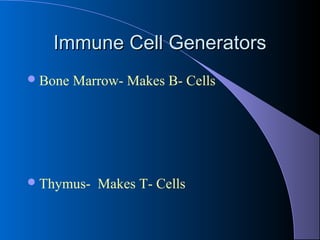
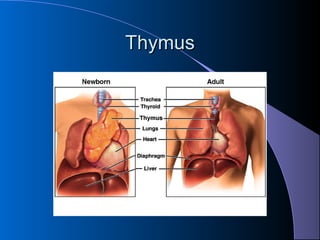
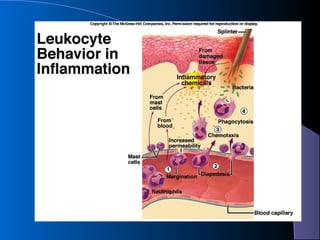
The lymphatic system absorbs excess fluid from tissues and returns it to the circulatory system. It also plays a role in immunity. The lymphatic system is made up of lymph, lymphatic tissue including lymph nodes and spleen, and lymphatic vessels. During inflammation, chemical messengers are released that increase blood flow and permeability, causing redness and swelling. Leukocytes migrate to the inflamed area to phagocytose and destroy pathogens and recruit more immune cells.