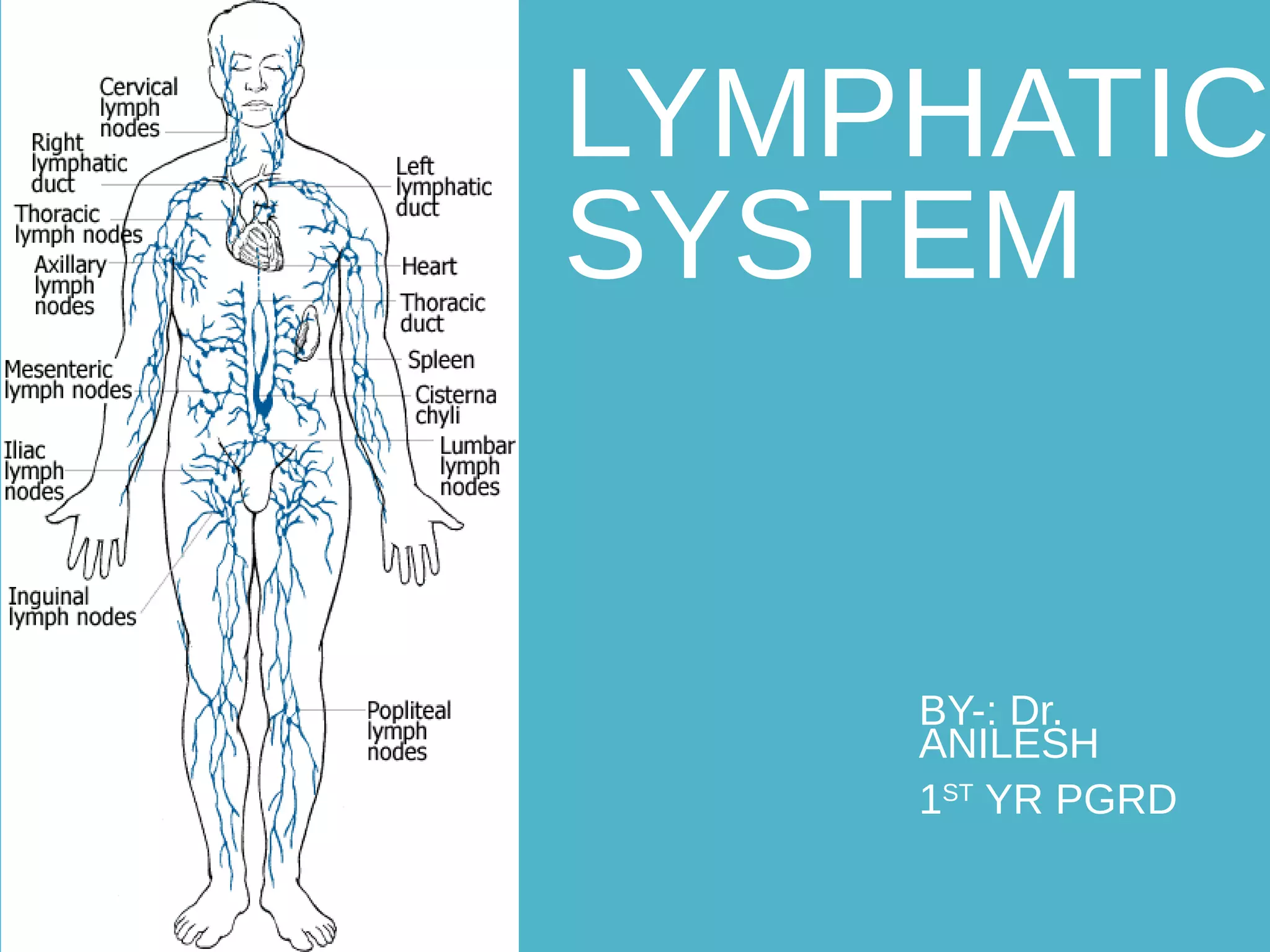
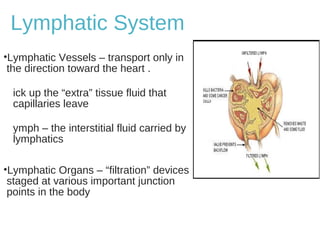
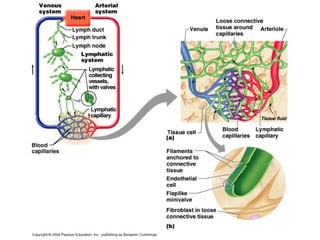
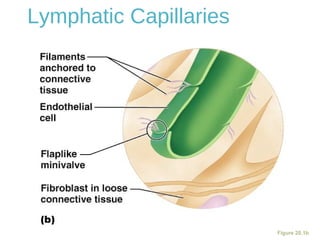
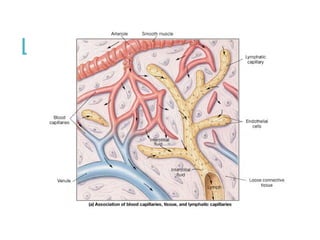
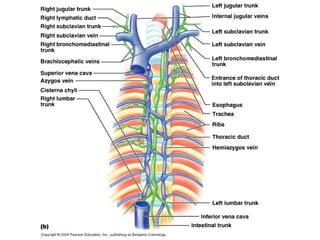
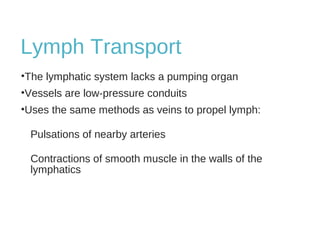
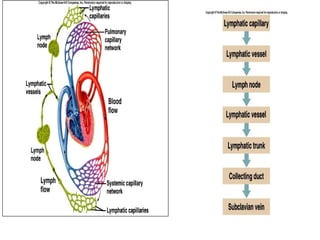
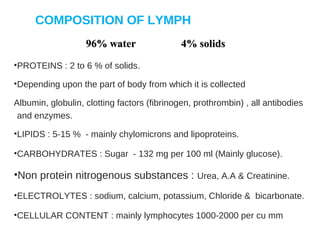
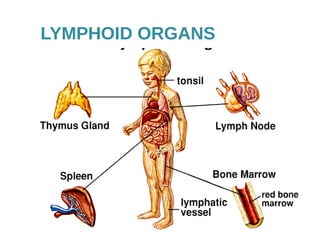
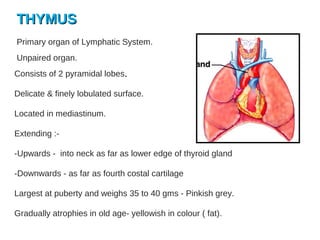
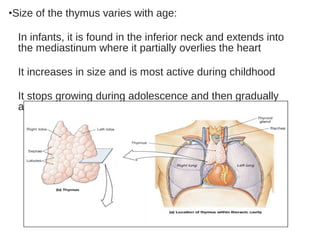
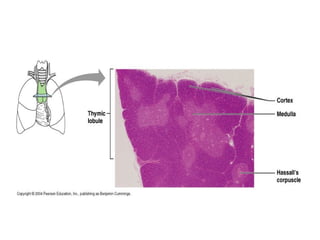
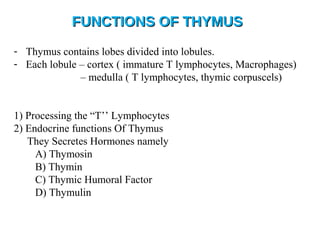
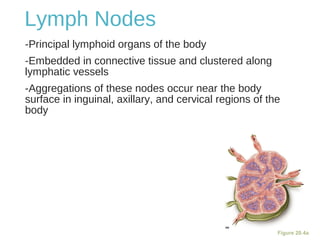
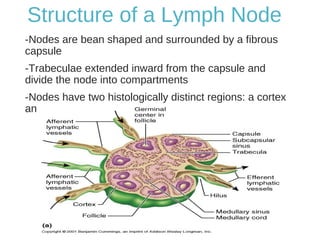
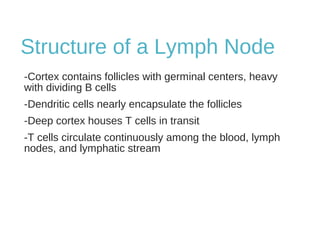
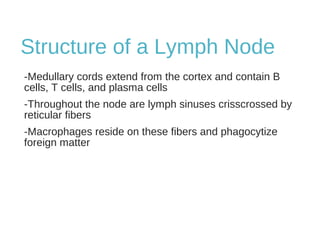
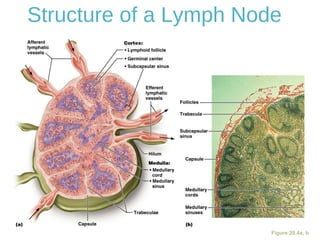
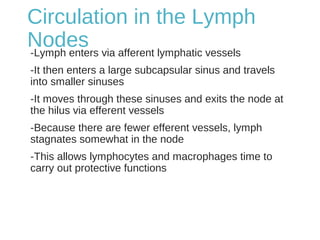
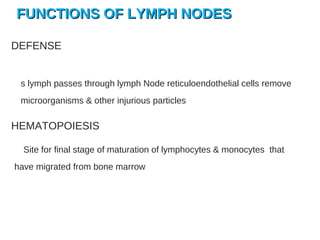
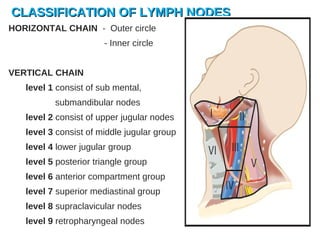
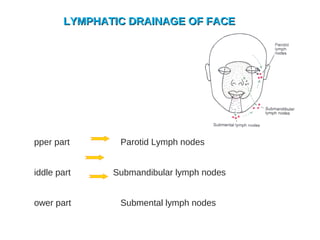
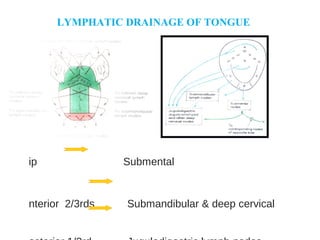
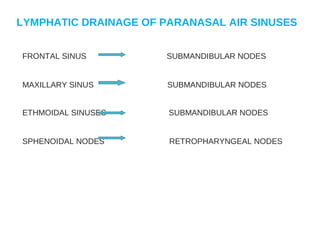
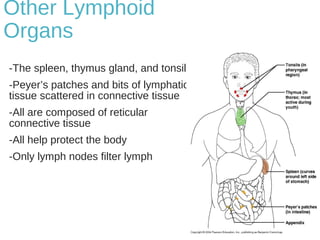
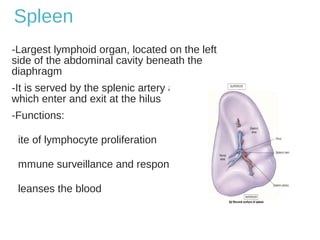
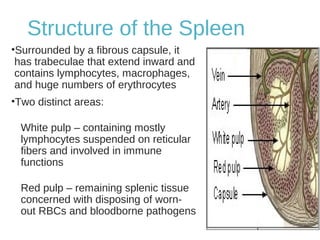
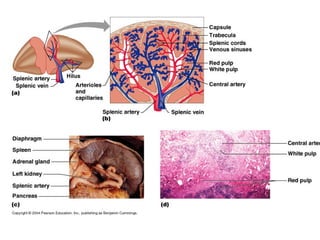
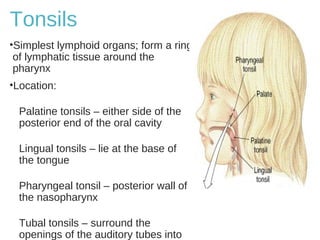
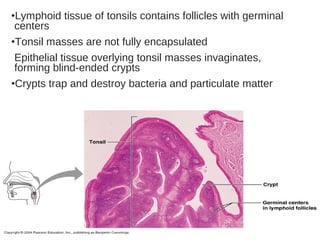
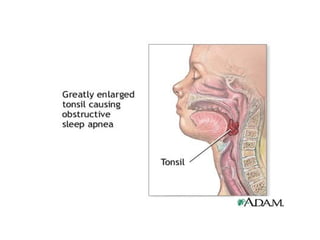
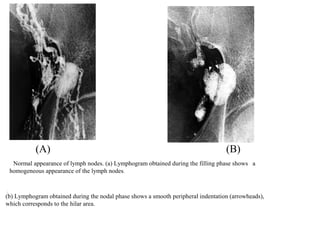
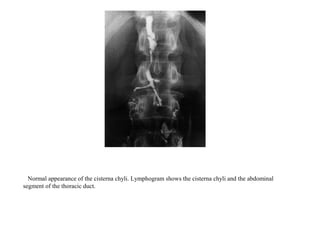
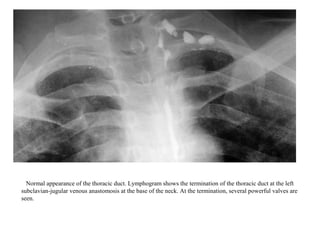
The lymphatic system transports lymph fluid and immune cells throughout the body. It is composed of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, the spleen, thymus, tonsils, adenoids, and bone marrow. Lymph fluid is collected from tissues by lymphatic capillaries and transported to lymph nodes where immune cells filter out pathogens and debris. The lymph then drains into the subclavian veins or thoracic duct to return to systemic circulation. Key functions of the lymphatic system include fluid homeostasis, absorption of fats from the intestine, and immune defense.