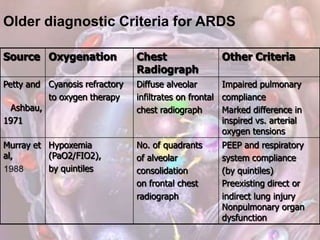
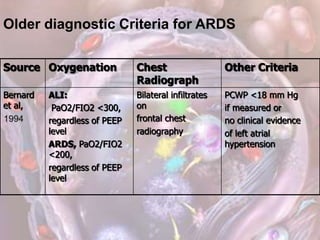
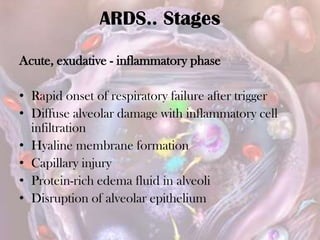
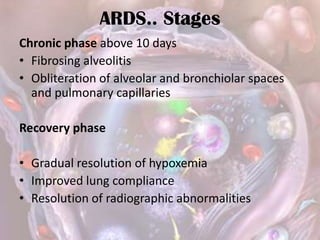
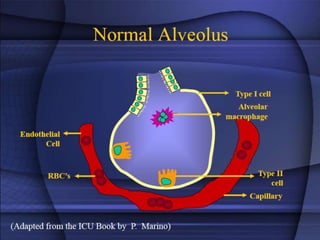
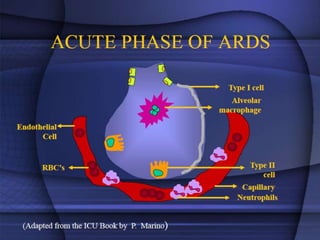
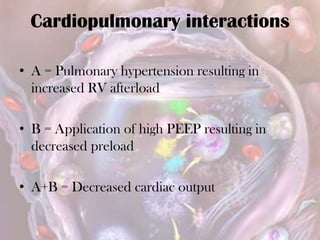
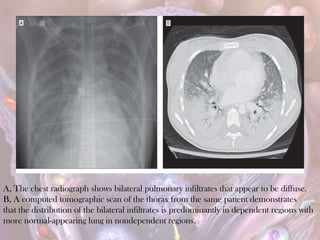
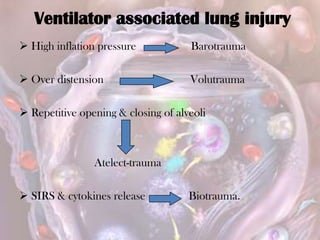
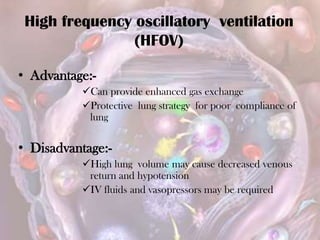
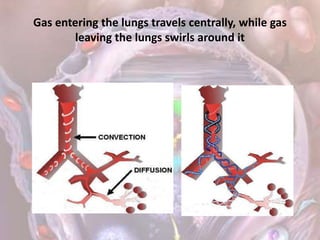
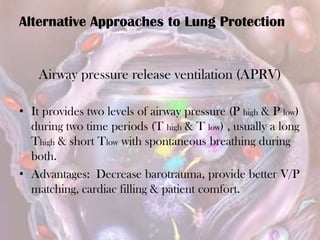
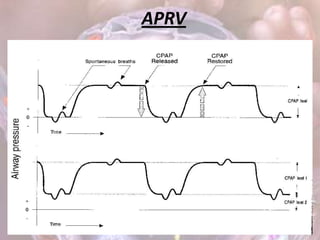
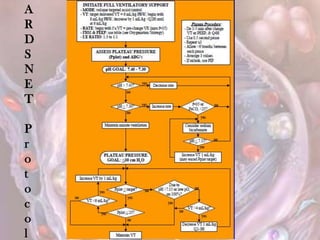
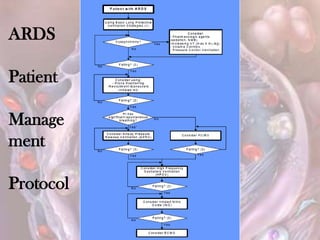
ARDS is defined by acute onset hypoxemia caused by bilateral lung infiltrates from non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema. The Berlin definition categorizes ARDS as mild, moderate, or severe based on oxygenation levels. Mechanical ventilation can worsen lung injury so strategies aim to limit tidal volumes and pressures while using PEEP to recruit alveoli. Additional techniques like prone positioning, inhaled nitric oxide, and alternative modes may help in severe cases but require more study.