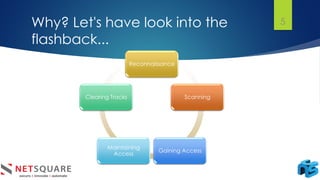
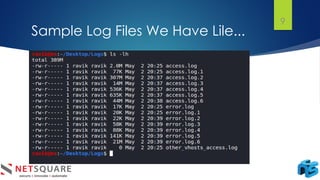
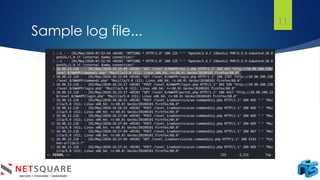
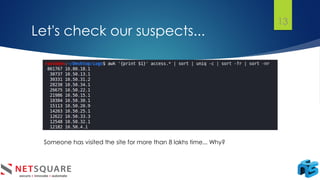
The document discusses log analysis and its components, including the importance of audit trail records for mitigating risks and meeting compliance regulations. It outlines how logs are generated, the various tools available for analysis, and some key use cases such as responding to data breaches and troubleshooting systems. Additionally, it differentiates between log monitoring and log analysis, emphasizing the latter's role in detecting intrusions.