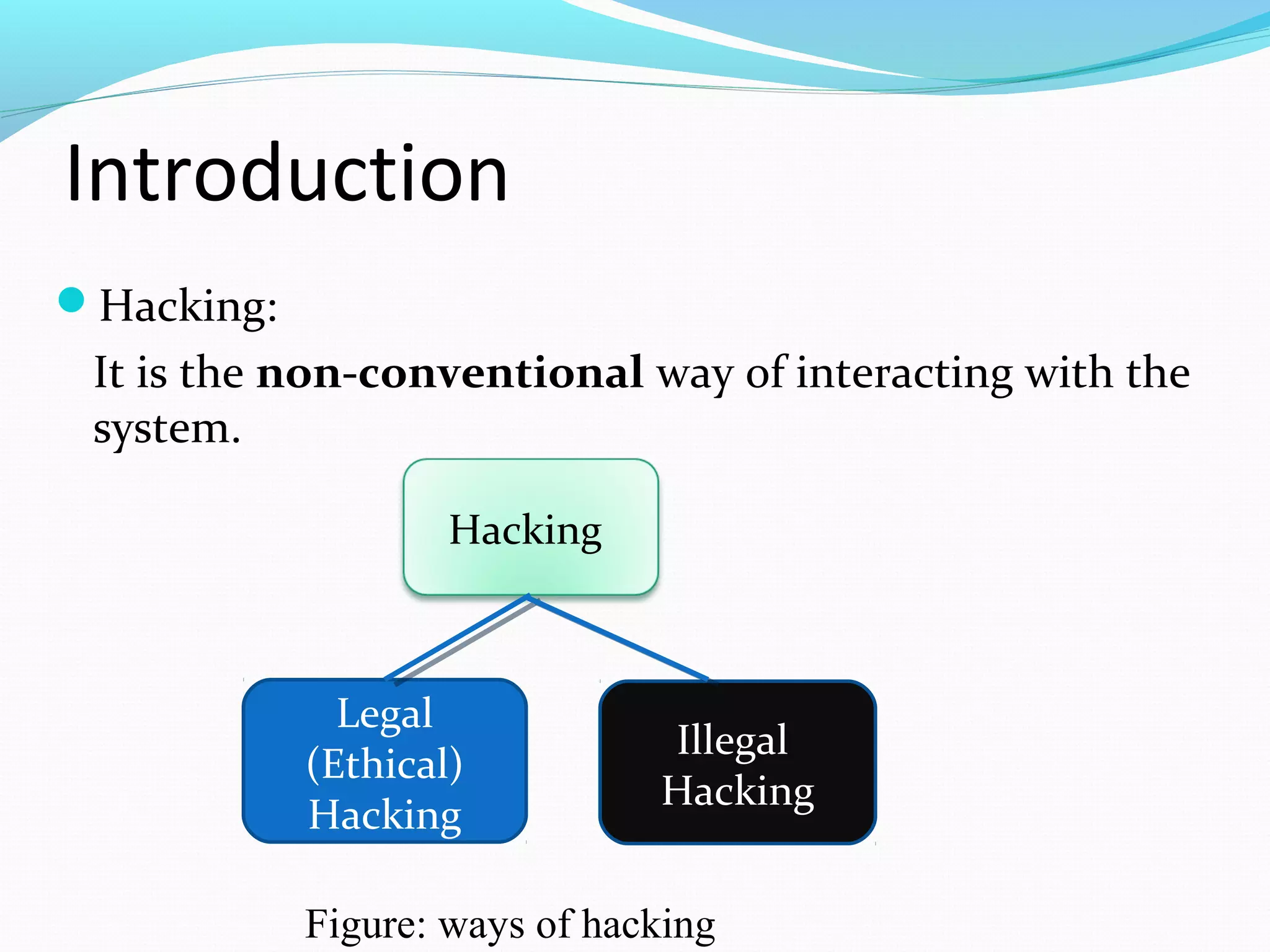
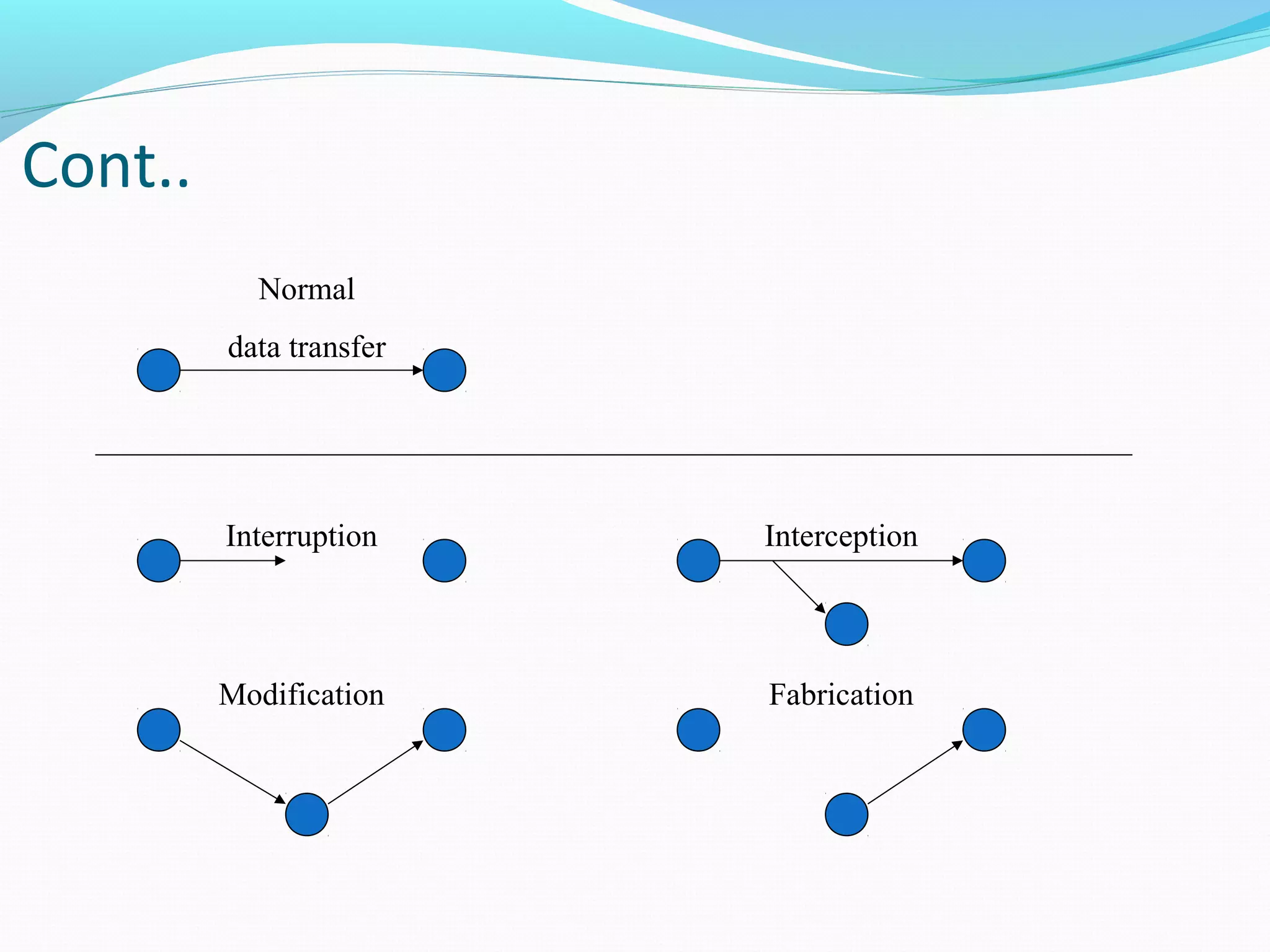
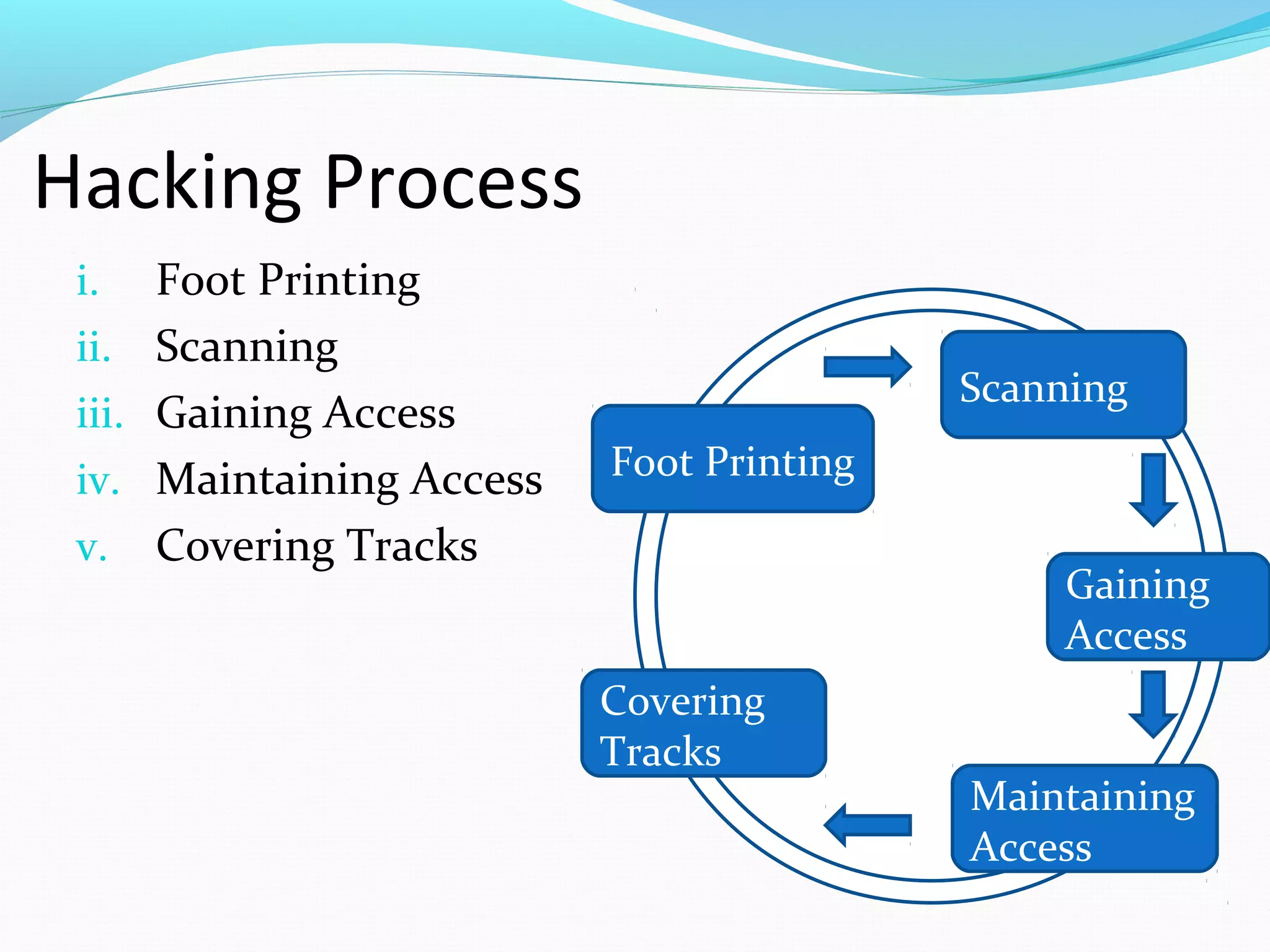
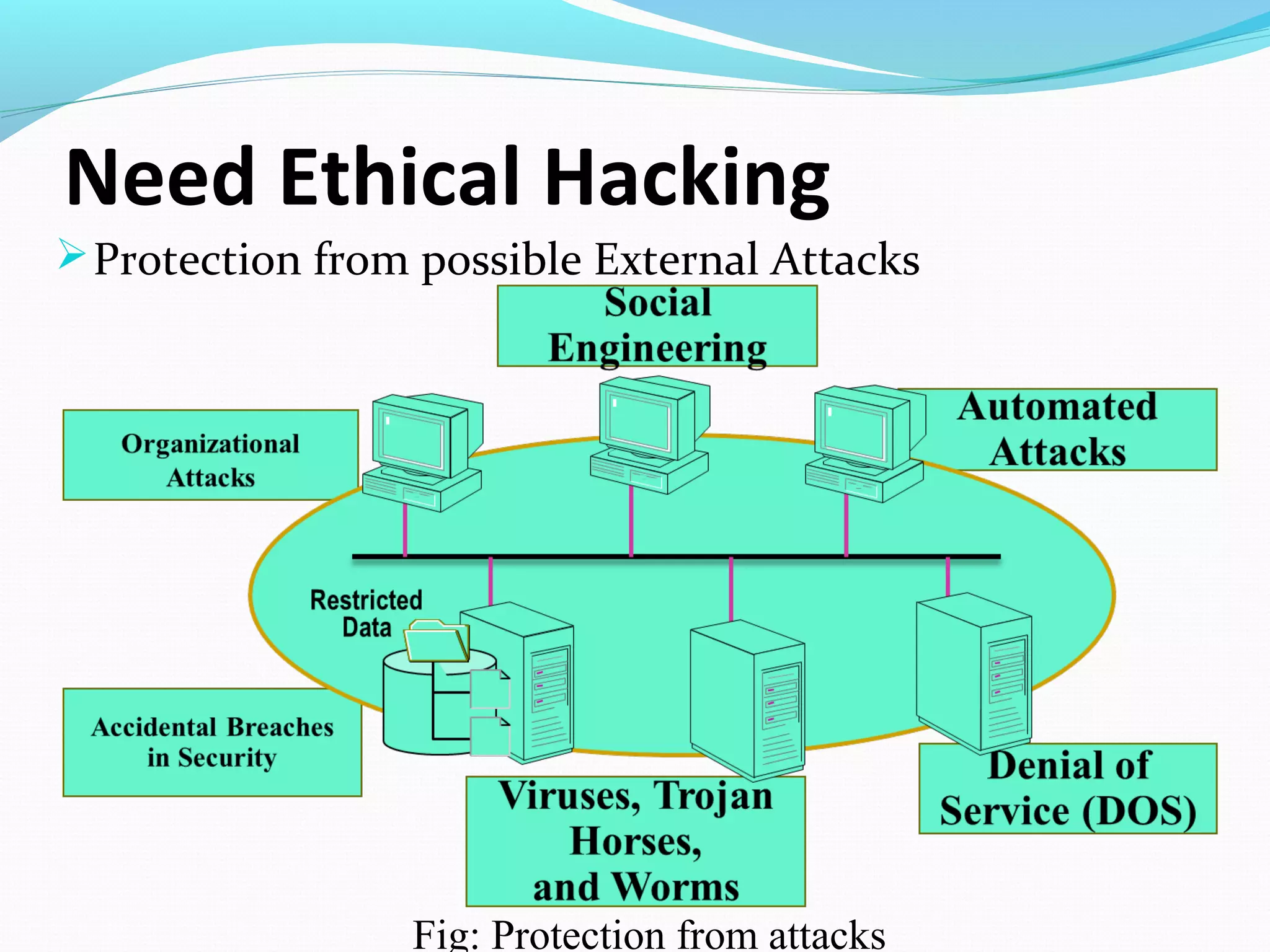
This document discusses ethical hacking and defines it as assessing a system's security vulnerabilities from the perspective of a hacker for legitimate purposes like security testing, with the owner's consent and without malicious intent. It outlines the types of hackers (black hat, white hat, grey hat), hacking process (footprinting, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, covering tracks), why ethical hacking is needed (to protect from external attacks), and its advantages (finding security holes, preventing attacks) and disadvantages (requires trustworthy professionals which can be expensive).












![References:
[1] Ethical Hacking and Systems Defense: National
CyberWatch Center Edition by Sean-Philip
Oriyano,Edition: 1st/2016.
[2] www.wikipedia.com
[3] https://www.simplilearn.com/roles-of-ethical-hacker-article
Accessed on 13/03/2018/6 :00 PM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ethicalhackingramchandra-r-180316181939/75/Ethical-hacking-17-2048.jpg)
