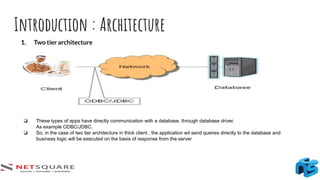
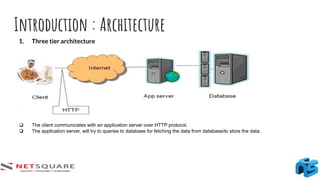
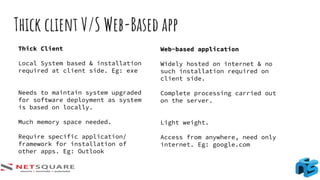
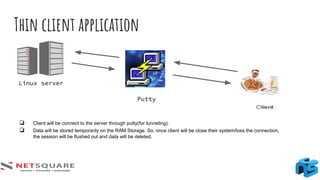
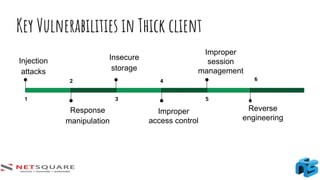
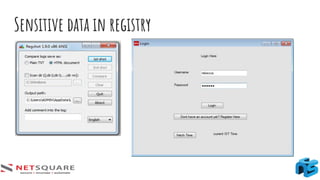
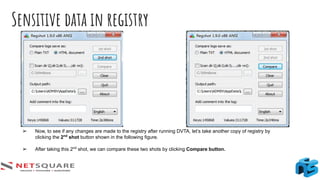
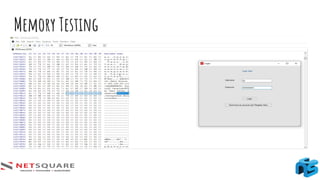
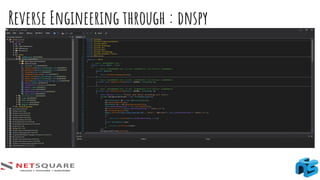
The document provides an introduction to thick client applications, distinguishing them from thin client and web applications, and detailing their architecture. It covers key vulnerabilities, testing methodologies, and tools for testing thick clients, including dynamic, local storage, and memory testing. Additional insights include the importance of monitoring sensitive data in local storage and registry, and techniques for reverse engineering thick client applications.