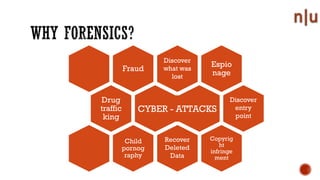
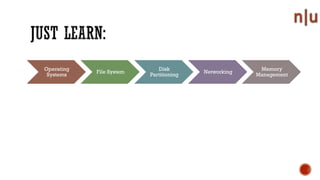
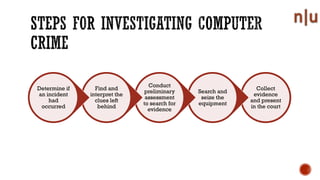
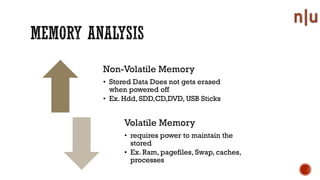
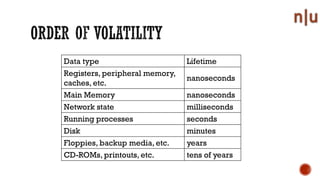
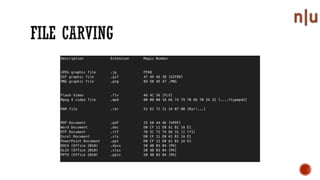
This document provides an overview of digital forensics and related topics. It discusses autopsy procedures, computer forensics, memory analysis, volatile vs. non-volatile memory, encryption and steganography techniques, network analysis, challenges in the field, terms used, and how to become a forensics expert. Anti-forensics methods like encryption and data hiding are also covered.