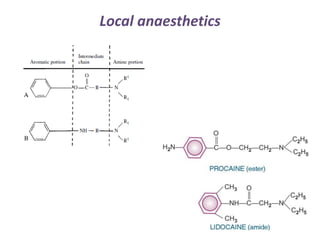
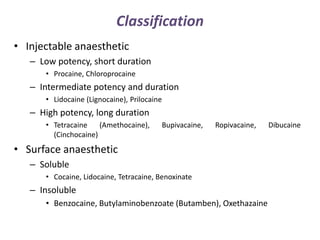
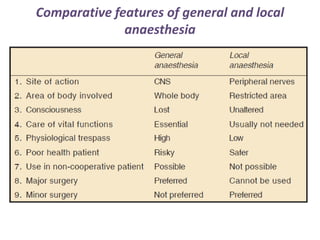
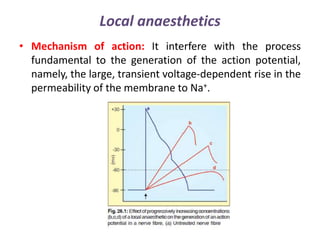
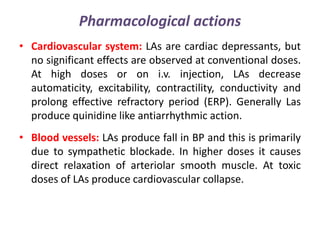
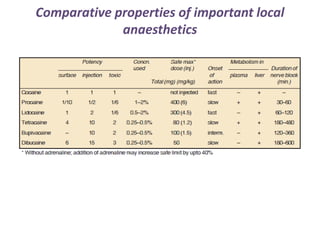
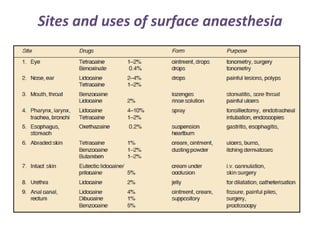
Local anesthetics are drugs that cause reversible loss of sensation, especially pain, in a restricted area of the body. They work by interfering with sodium channel function and action potential generation in neurons. Common local anesthetics include lidocaine, bupivacaine, and tetracaine. Adding vasoconstrictors like epinephrine prolongs the duration of anesthesia by slowing absorption from the injection site. Local anesthetics are used for surface anesthesia, injections, and spinal anesthesia. Adverse effects include central nervous system toxicity, cardiovascular effects, and allergic reactions at high doses.