Diabetes mellitus
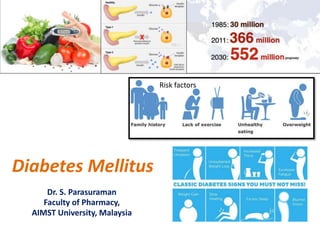
- 1. Diabetes Mellitus Dr. S. Parasuraman Faculty of Pharmacy, AIMST University, Malaysia Risk factors
- 2. World Health Day 2016 7 April
- 3. Diabetes Mellitus • As per the WHO, diabetes mellitus (DM) is defined as a hetrogeneous metabolic disorder characterised by common feature of chronic hyperglycaemia with disturbance of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism. • Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas dose not produce enough insulin or the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Uncontrolled diabetes may lead to serious damage to many body systems, especially the nervous and blood vessels.
- 4. DM – Facts sheet June, 2016 by WHO • The number of people with diabetes has risen from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014. • Global prevalence of diabetes among adults over 18 years of age has raisin from 4.7% in 1980 to 8.5% in 2014. • Diabetes is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke and lower limb amputation. • In 2012 an estimated 1.5 million deaths were directly caused by diabetes and another 2.2 million deaths were attributable to high glucose. • Healthy diet, regular physical activity, maintaining normal body weight and avoiding tobacco use are way to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
- 5. Etiologic Classification of DM Type Sub-type Type 1 Diabetes mellitus (10%) Type IA DM: Immune- mediated Type IB DM: Idiopathic Type 2 Diabetes mellitus (80%) Other specific types of diabetes (10%) • Genetic defect of β-cell function due to mutations in various enzymes • Genetic defect in insulin action • Endocrinopathies • Drug- or chemical-induced • Infections • Uncommon forms of immune-mediated DM (stiff man syndrome, anti-insulin receptor antibodies) • Other genetic syndromes (e.g. Down's syndrome, Klinefelter's syndrome, Turner's syndrome) Gestational diabetes mellitus
- 6. Type 1 Diabetes mellitus • Type 1 DM occurs commonly in patients under 30 years of age, autoimmune destruction of β-cells can occur at any age.
- 7. Type 2 Diabetes mellitus • It constitutes about 80% cases of DM. • Type 2 DM earlier called non-insulin-dependent, or maturity-onset diabetes (MOD). • Type 2 DM predominantly affects older individuals, it is now known that it also occurs in obese adolescent children.
- 8. Major Risk Factors for Type 2 DDM • Family history of type 2 DM • Obesity • Habitual physical inactivity • Race and ethnicity (Blacks, Asians, Pacific Islanders) • Previous identification of impaired fasting glucose or impaired • glucose tolerance • History of gestational DM or delivery of baby heavier than 4 kg • Hypertension • Dyslipidaemia (HDL level < 35 mg/dl or triglycerides > 250 mg/dl) • Polycystic ovary disease and acanthosis nigricans • History of vascular disease
- 9. Gestational DM • About 4% pregnant women develop DM due to metabolic changes during pregnancy. • They revert back to normal glycaemia after delivery, these women are prone to develop DM later in their life.
- 10. Pathogenesis • Depending upon etiology of DM, hyperglycaemia may result from the following: – Reduced insulin secretion – Decreased glucose use by the body – Increased glucose production.
- 11. Normal Insulin Metabolism A: Pathway of normal insulin synthesis and release in β-cells of pancreatic islets. B: Chain of events in action of insulin on target cell.
- 12. Type 1 Diabetes mellitus
- 13. Type 1 Diabetes mellitus • It constitutes about 10% cases of DM. • Type 1 DM earlier called Insulin-dependent, or juvenile- onset diabetes. • It is called insulin dependent DM (IDDM) because it was known that these patients have absolute requirement for insulin replacement as treatment. • Subtype 1A (immune-mediated) DM characterised by autoimmune destruction of β-cells which usually leads to insulin deficiency. • Subtype 1B (idiopathic) DM characterised by insulin deficiency with tendency to develop ketosis but these patients are negative for autoimmune markers.
- 14. Pathogenesis of Type 1 DM • Type 1 DM is destruction of β-cell mass, usually leading to absolute insulin deficiency. • Genetic susceptibility: Type 1A DM involves inheritance of multiple genes to confer susceptibility to the disorder [identical twins- has chances of 50% development of Type1A DM to second twin; genetic predisposition to type 1A DM have the susceptibility gene located in the HLA region of chromosome 6 (MHC class II region), particularly HLA DR3, HLA DR4 and HLA DQ locus]. Short arm Long arm
- 15. Pathogenesis of Type 1 DM • Autoimmune factors: Immunologic abnormalities such as • presence of islet cell antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and insulin • insulitis [occurrence of lymphocytic infiltrate in and around the pancreatic islets] • selective destruction of βcells • role of T cell-mediated autoimmunity • role of other autoimmune diseases [20% of Type 1 DM associated with Graves’ disease, Addison’s disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, pernicious and anaemia] • Immunosuppressive therapy
- 16. Pathogenesis of Type I DM • Environmental factors: Certain viral (mumps, measles, coxsackie B virus, cytomegalovirus and infectious mononucleosis), chemicals (alloxan, streptozotocin and pentamidine) dietary proteins (bovine milk proteins) share antigenic properties with human cell surface proteins and trigger the immune attack on β-cells by a process of molecular mimicry [β-cells act as autoantigens and activate CD4+ T lymphocytes].
- 17. Type 2 Diabetes mellitus
- 18. Pathogenesis of Type 2 DM • Genetic factors: No definite and consistent genes have been identified for the development of type 2 DM. Multifactorial inheritance is the most important factor in development of type 2 DM. • Constitutional factors: Certain environmental factors such as obesity, hypertension, and level of physical activity play contributory role and modulate the phenotyping of the disease. • Insulin resistance: One of the most prominent metabolic features of type 2 DM is the lack of responsiveness of peripheral tissues to insulin, especially of the skeletal muscle and liver. Obesity, in particular, is strongly associated with insulin resistance and hence type 2 DM.
- 19. Pathogenesis of Type 2 DM • Insulin resistance:.
- 20. • Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance plays a major pathogenic role in the development of the metabolic syndrome, which may include any or all of the following: • Hyperinsulinemia • Type 2 diabetes or glucose intolerance • Central obesity • Hypertension • Dyslipidemia that includes high triglyceride levels • Low HDL-C level and small, dense low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles • Hypercoagulability characterized by an increased plasminogen activator inhibitor–1 (PAI-1) level Pathogenesis of Type 2 DM
- 21. Pathogenesis of Type 2 DM • Impaired insulin secretion: Hyperinsulinaemia, failure of β- cell function, glucose toxicity and lipotoxicity are worsen the islet cell function. • Increased hepatic glucose synthesis: Increased hepatic synthesis of glucose which contributes to hyperglycaemia.
- 22. Complications of diabetes mellitus • Acute Metabolic Complications – Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic Nonketotic Coma (HHS) – Hypoglycaemia • Late Systemic Complications – Atherosclerosis – Diabetic microangiopathy – Diabetic nephropathy – Diabetic neuropathy – Diabetic retinopathy – Infections
- 23. Diagnosis of diabetes • Urine testing (Benedict’s qualitative test, Tests for ketone bodies [Ketonuria]) • Single blood sugar estimation (O-toluidine, Somogyi- Nelson and glucose oxidase] • Oral glucose tolerance test • Other tests (Glycosylated haemoglobin [HbA1C], Glycated albumin, extended GTT, intravenous GTT, cortisone-primed GTT, insulin assay, proinsulin assay, C-peptide assay, islet autoantibodies, screening for diabetes-associated complications)
- 24. Diagnosis of diabetes Diagnosis of Diabetes by Oral GTT (as per American Diabetes Association, 2007). Plasma Glucose Value Diagnosis FASTING (FOR > 8 HOURS) VALUE Below 100 mg/dl (< 5.6 mmol/L) Normal fasting value 100-125 mg/dl (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) Impaired fasting glucose (IFG) 126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/L) or more Diabetes mellitus TWO-HOUR AFTER 75 GM ORAL GLUCOSE LOAD < 140 mg/dl (< 7.8 mmol/L) Normal post-prandial GTT 140-199 mg/dl (7.8-11.1 mmol/L) Impaired post-prandial glucose tolerance 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/L) or more Diabetes mellitus RANDOM VALUE 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/L) or more Diabetes mellitus in a symptomatic patient
Editor's Notes
- Read more: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/
- Synthesis: pre-proinsulin which is single-chain 86-amino acid precursor polypeptide Proinsulin Further cleavage of proinsulin gives rise to A (21 amino acids) and B (30 amino acids) chains of insulin, linked together by connecting segment called C-peptide. Release: Hyperglycaemia (glucose level more than 70 mg/dl or above 3.9 mmol/L) stimulates transport into β-cells of a glucose transporter, GLUT2. glucokinase Metabolism of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate by glycolysis generates ATP inhibition of ATP-sensitive K+ channel on the cell membrane and opening up of calcium channel with resultant influx of calcium, which stimulates insulin release. Action: Half of insulin secreted from β-cells into portal vein is degraded in the liver while the remaining half enters the systemic circulation for action on the target cells
- Ketosis: Raised levels of ketone bodies in the body, associated with abnormal fat metabolism and diabetes mellitus.
- Cyclosporin A may cause Type 1 DM
- Cyclosporin A may casue Type 1 DM Enteroviruses may enhace Type 1 DM
- Cyclosporin A may casue Type 1 DM Enteroviruses may enhace Type 1 DM
- Available in: http://openmindstate.com/2016/05/29/4-ways-activate-weight-loss-hormones/ http://goodfoodeating.com/4321/what-is-insulin-resistance/
- Available in http://www.mangomannutrition.com/the-causes-of-insulin-resistance-in-type-1-diabetes-type-2-diabetes-and-prediabetes/
- Cyclosporin A may casue Type 1 DM Enteroviruses may enhace Type 1 DM
