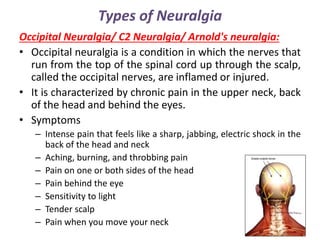
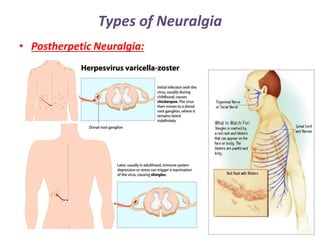
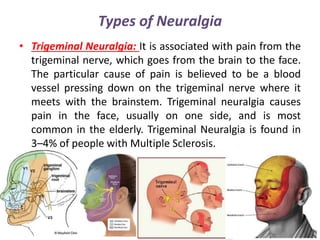
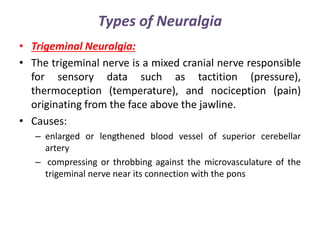
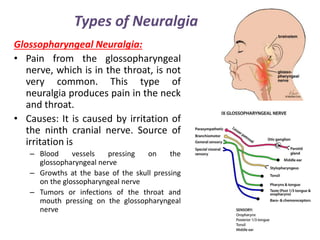
Neuralgia is a severe pain along damaged nerves, commonly in the face and neck, caused by various factors such as diabetes, infections, and trauma. Types of neuralgia include postherpetic, trigeminal, glossopharyngeal, swimmer's headache, and occipital neuralgia, each with specific causes and treatment options ranging from medications to surgical interventions. Effective treatment often involves controlling pain through medications, nerve blocks, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical procedures to relieve nerve pressure.






![Types of Neuralgia
Swimmer's headache, or supraorbital neuralgia or Goggle
Headache:
• .
Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2004 Oct; 17(4): 418–419. [PMC1200682]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralgia-160626135348/85/Neuralgia-13-320.jpg)