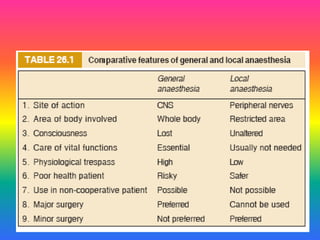
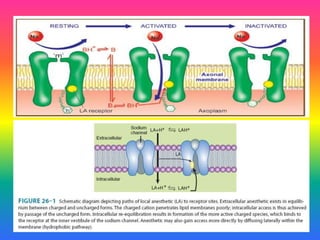
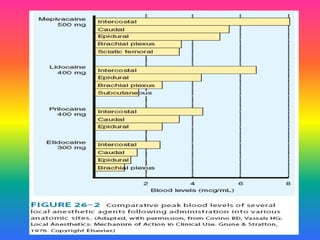
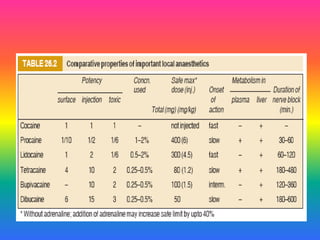
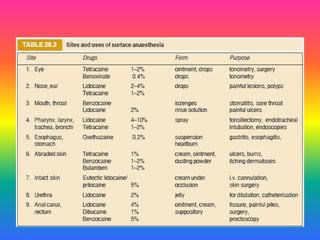
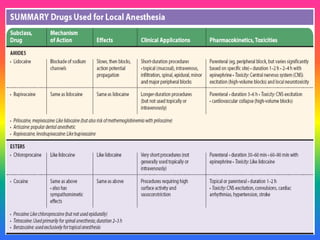
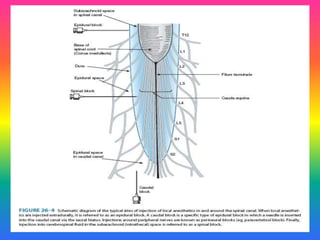
Local anaesthetics (LAs) are drugs that cause reversible loss of sensory perception in a localized area by blocking nerve impulses without structural damage. They can be classified into injectable and surface anaesthetics, with various examples like lidocaine and bupivacaine. LAs have distinct mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, and potential adverse effects, and are employed in various techniques such as infiltration and spinal anaesthesia.