Lipoproteins
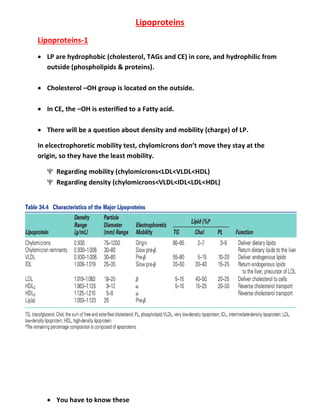
- 1. Lipoproteins Lipoproteins-1 LP are hydrophobic (cholesterol, TAGs and CE) in core, and hydrophilic from outside (phospholipids & proteins). Cholesterol –OH group is located on the outside. In CE, the –OH is esterified to a Fatty acid. There will be a question about density and mobility (charge) of LP. In elcectrophoretic mobility test, chylomicrons don’t move they stay at the origin, so they have the least mobility. Regarding mobility (chylomicrons<LDL<VLDL<HDL) Regarding density (chylomicrons<VLDL<IDL<LDL<HDL) You have to know these
- 2. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Chylomicrons are synthesized from the exogenous lipoprotein pathway. What are the major apolipoproteins of the chylomicrons 1-apo B48 2-apo CII 3-apo E What does apo-CII do? ............................................. ans. It activates LPL Once LPL is activated, 1- It hydrolyzes chylomicrons. 2- Releases free fatty acids from core TAGs to be –stored in adipose tissue and mammary cells or -oxidized in muscle cells After the chylomicrons are hydrolyzed by LPL, apoCII is now lost. -apoCII is not really lost. It will be given back to the HDL. Then the chylomicrons are now called chylomicron remnants They lost apoCII They lost most of their core TAGs Rich in CE
- 3. Chylomicron remnants are taken up by the liver by receptor-mediated endocystosis. (Through the binding of apoE to its receptor on liver cells), where they will be degraded by lysosomes. Important to note that; ApoB48 is added to the chylomicrons in the intestinal mucosa (nascent chylomicron) ApoCII and apoE are transferred from HDL to LDL. (mature chylomicron) (Fig.25.3) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- You should know why VLDL is formed... (Due to excess carbs in body which are converted to TAGs endogenously that along with cholesterol and CE and apoB100 will form nascent VLDL. Nascent VLDL-->endogenously synthesized TAGs +cholesterol & CE +apoB100 Mature VLDL-->endogenous TAGs +cholesterol & CE +apoB100 +apoCII +apoE After activation of LPL by apoCII and release of most of the TAGs, VLDL is now called IDL or VLDL remnants. IDL then transfers apoE back to the HDL IDL now will have mainly 2 fates. It can be endocytosed and degraded by the liver. Or further digested by hepatic TG lipase (HTGL) to form LDL (Fig..18) What does HTGL do??................................ Ans. It degrades the TAGs remaining in the IDL converting it to LDL. LDL is rich in cholesterol and CE. 60% goes back to liver (receptor-mediated endocytosis by apoB100) 40% goes to extrahepatic tissues such as adrenal cortex and gonads where LDL cholesterol is used synthesize steroid hormones. (Fig.34.18) High intracellular cholesterol concentration induces the storage of cholesterol, and inhibits the expression of LDL receptors.
- 4. Where can we find LDL receptors?? ………………… ans. Mainly on the membrane of liver cells, adrenal cortex cells, and gonadal cells LDL receptors contain a unique clathrin protein, once the LDL-receptor complex is endocytosed to the inside of the cell in a vesicle, this vesicle fuses with lysosomes and its contents are freed up. CEs are hydrolyzed to free cholesterol but once the degradation process ends, all the free cholesterol molecules are re-esterified by ACAT to be trapped within the cell. Lipoprotein receptors can recognize both apoB100 and apoE. Any mutation in the LDL receptor gene can result in hypercholesterolemia. When LDL receptors in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues become saturated due excess LDL particles, the excess LDL can oxidized and taken up scavenger receptors on macrophages present near the endothelial cells of arteries. 1) And after taking certain amount of oxLDL, they will be called foam cells. 2) Foam cells induce migration of SMCs from media layer to intima layer. And SMCs will start uptaking oxLDL and become foam cells. 3) This will initiate the cascade of atherosclerosis. Lipoproteins-2 3 ways to synthesize HDL Synthesize a nascent HDL by liver and intestines similar in its main structure to the other lipoproteins but it has specific apoproteins (AI, AII, CI, CII) mainly. Budding of apoproteins from chylomicrons and VLDL particles as they are digested by LPL. Free apoAI can acquire cholesterol and phospholipids from other LP and from cell membranes forming a nascent HDL within the circulation. Nascent HDL has a hollow core with very low levels of CE and TAGs, and outer shell with free cholesterol and phospholipids. Fig.18.22
- 5. Once this core gets filled with CE and the outer shell acquires more cholesterol and phospholipids (from cells lining the blood vessels), the nascent HDL is now called mature HDL that now has a distinct globular shape. (No enzymes used).. What is reverse cholesterol transport?.............. 1. HDL picks up cholesterol from cell membranes. 2. This cholesterol is converted to CE in the HDL by the LCAT reaction. 3. HDL transfers CE to the liver by binding to specific receptor on hepatocytes SR-B1 (mentioned later) through the apoAI. Cholesterol from cell membranes to HDL 1. Cells contain the protein ABC1 (ATP-binding cassette protein 1) which uses ATP hydrolysis to move cholesterol from the inner leaflet of the membrane to the outer leaflet. 2. Cholesterol particles then move out of the cell membrane and enter the HDL. 3. Cholesterol as a hydrophobic molecule must be trapped in the HDL so it will be converted to CE by the enzyme (lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase) LCAT (synthesized in liver), LCAT catalyzes the transfer of a fatty acid from the 2-position of lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) in the phospholipid shell of the HDL to the 3- hydroxyl group of cholesterol, forming a cholesterol ester. HDL is considered as a vasculoprotective particle. Receptors of HDL on hepatocytes are apoE receptor and Scavenger receptors (SR-B1). ApoE is found only on hepatocytes but SR-B1 is found in many cell types, and since HDL is widely utilized by many cell types, SR-B1 is considered to be the primary mean to uptake and clear HDL particles. We mentioned one fate of cholesterol and CE of the HDL by being returned back to the liver.
- 6. Another fate is that, HDL can transfer CE to VLDL and chylomicrons in exchange for triacylglycerol (TG). The cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) mediates this exchange. ₰ Mature HDL= HDL3 ₰ After reverse cholesterol transport =HDL2 (atherogenic protective form) ₰ After exchanging CE for TAGs with VLDL and chylomicrons = HDL3 regenerated ₰ After hepatic lipase removing the TAGs from it= HDL2 ………. Fig.2.2 (summary of HDL cycle)
- 9. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- 12. -THE END-
- 13. References Marks’ Basic Medical Biochemistry: A Clinical Approach Fourth Edition Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry, Twenty-Sixth Edition Koolman, Color Atlas of Biochemistry, 2nd edition © 2005 Thieme Usage subject to terms and conditions of license. All right preserved. Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry 5th Edition Lehninger principles of biochemistry 4th Edition. Done by// Aly Ahmed Barakat 4th year MD student in OMC
