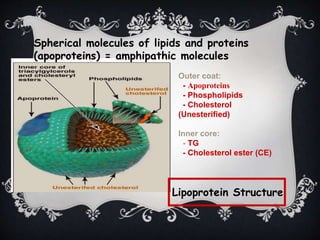
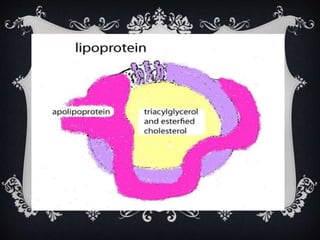
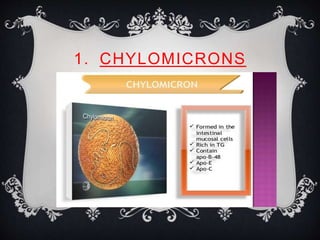
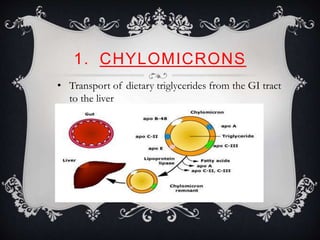
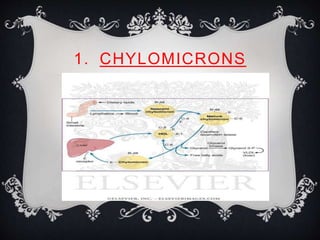
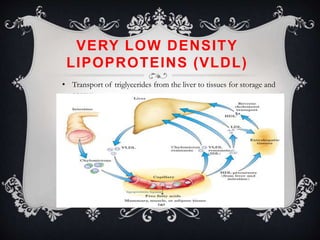
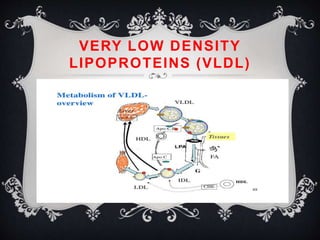
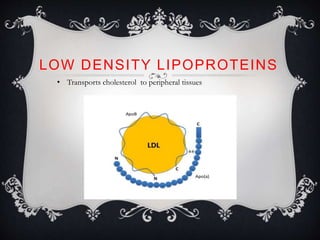
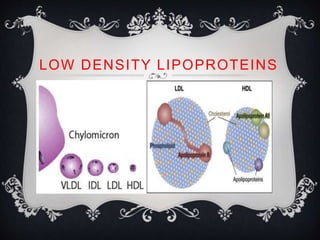
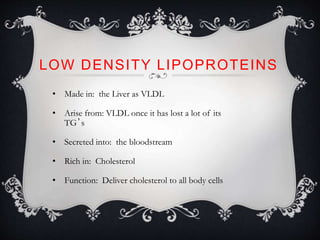
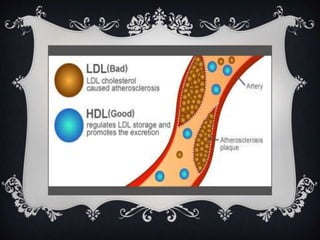
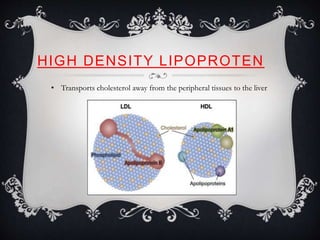
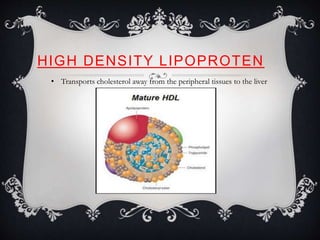
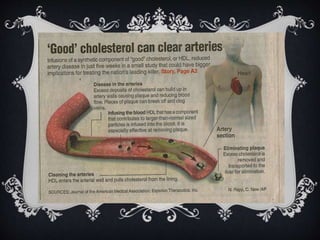
Lipoproteins are biochemical assemblies of proteins and lipids that enable the transportation of water-insoluble fats in the blood, playing a crucial role in preventing blockages that can lead to heart disease. Different types of lipoproteins, such as chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, and HDL, each have unique functions in transporting triglycerides and cholesterol throughout the body. Understanding lipoproteins is essential due to their relationship with heart health and disease.