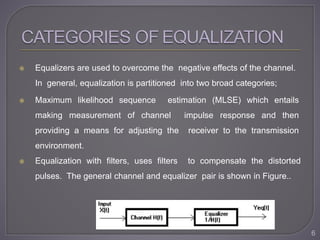
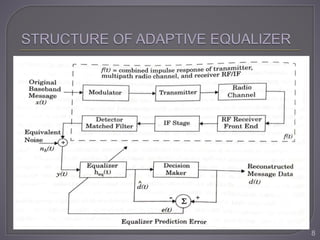
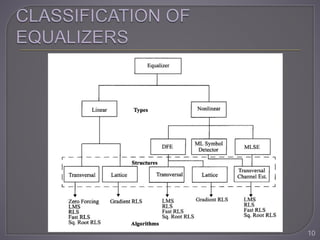
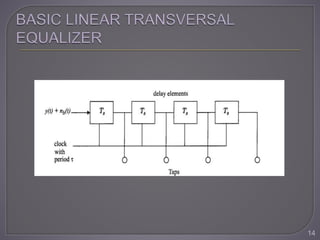
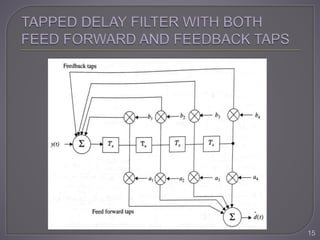
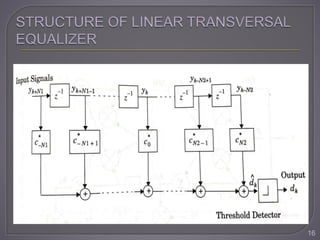
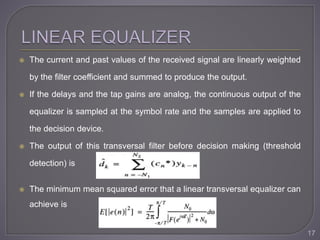
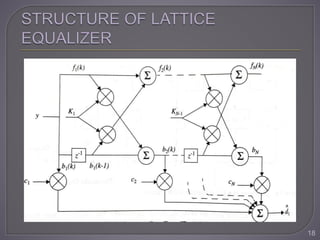
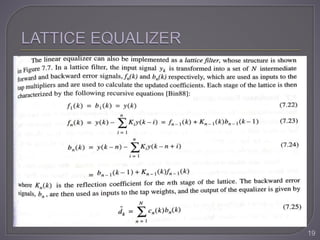
The document discusses equalization techniques in the context of electronics and communication engineering, highlighting their role in mitigating intersymbol interference (ISI) caused by multipath effects in time-dispersive channels. It categorizes equalizers into linear and nonlinear types, explaining adaptive equalizers' necessity due to the time-varying nature of mobile channels. Additionally, it covers various equalizer structures, their advantages, and the challenges faced by linear equalizers in channels with deep spectral nulls.