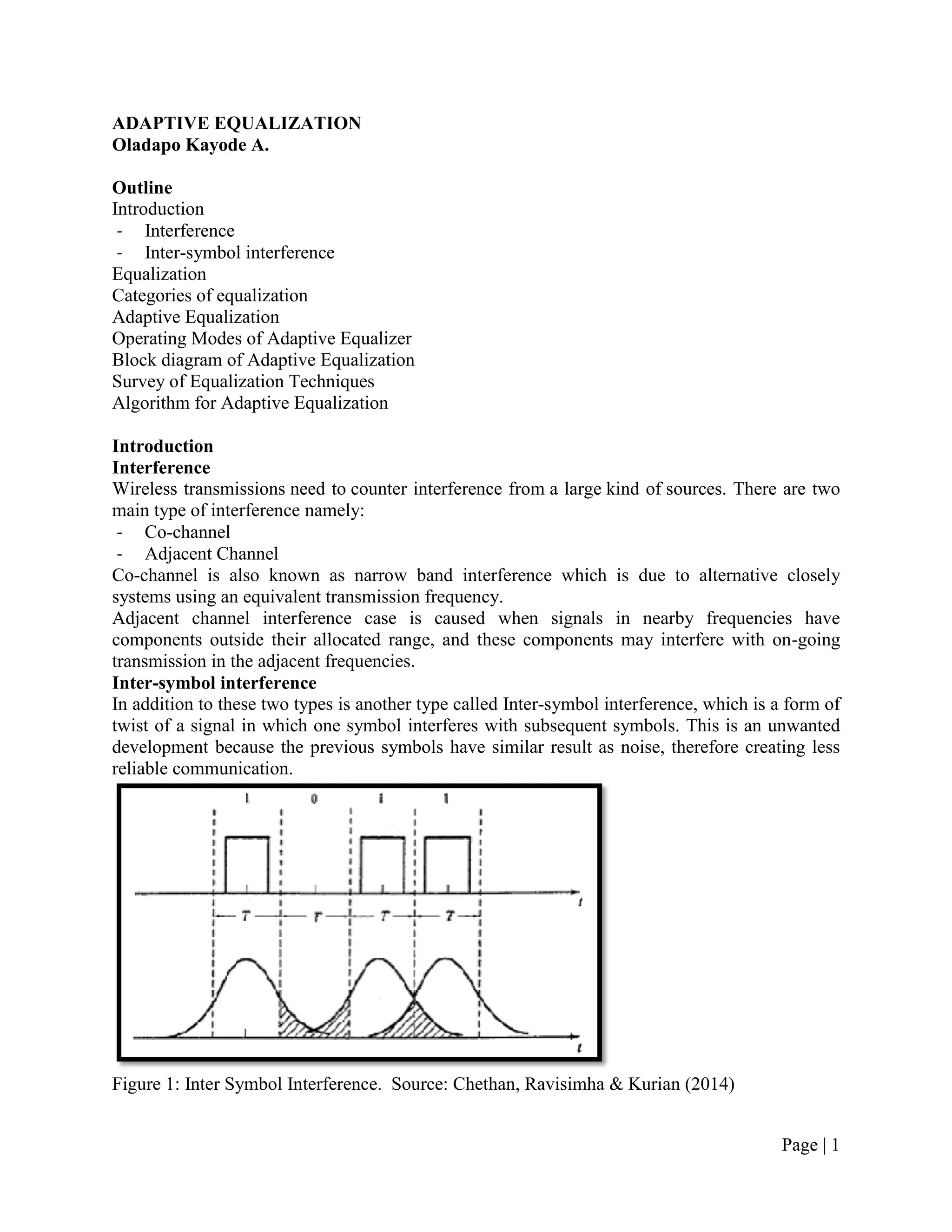
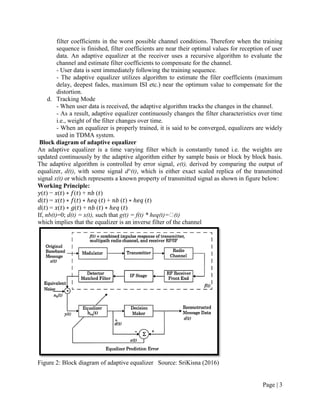
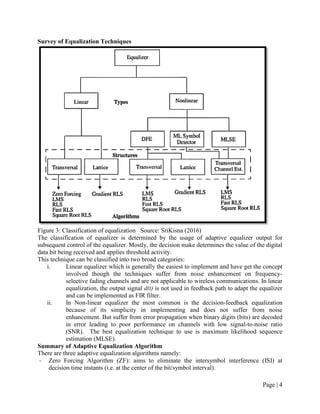
The document discusses adaptive equalization techniques used in wireless communications. It introduces inter-symbol interference as a major challenge for high-speed data transmission over mobile radio channels. Adaptive equalization aims to track time-varying channel characteristics and counteract inter-symbol interference. The techniques include decision-directed and training modes. Common adaptive equalization algorithms are zero forcing, least mean squares, and recursive least squares.