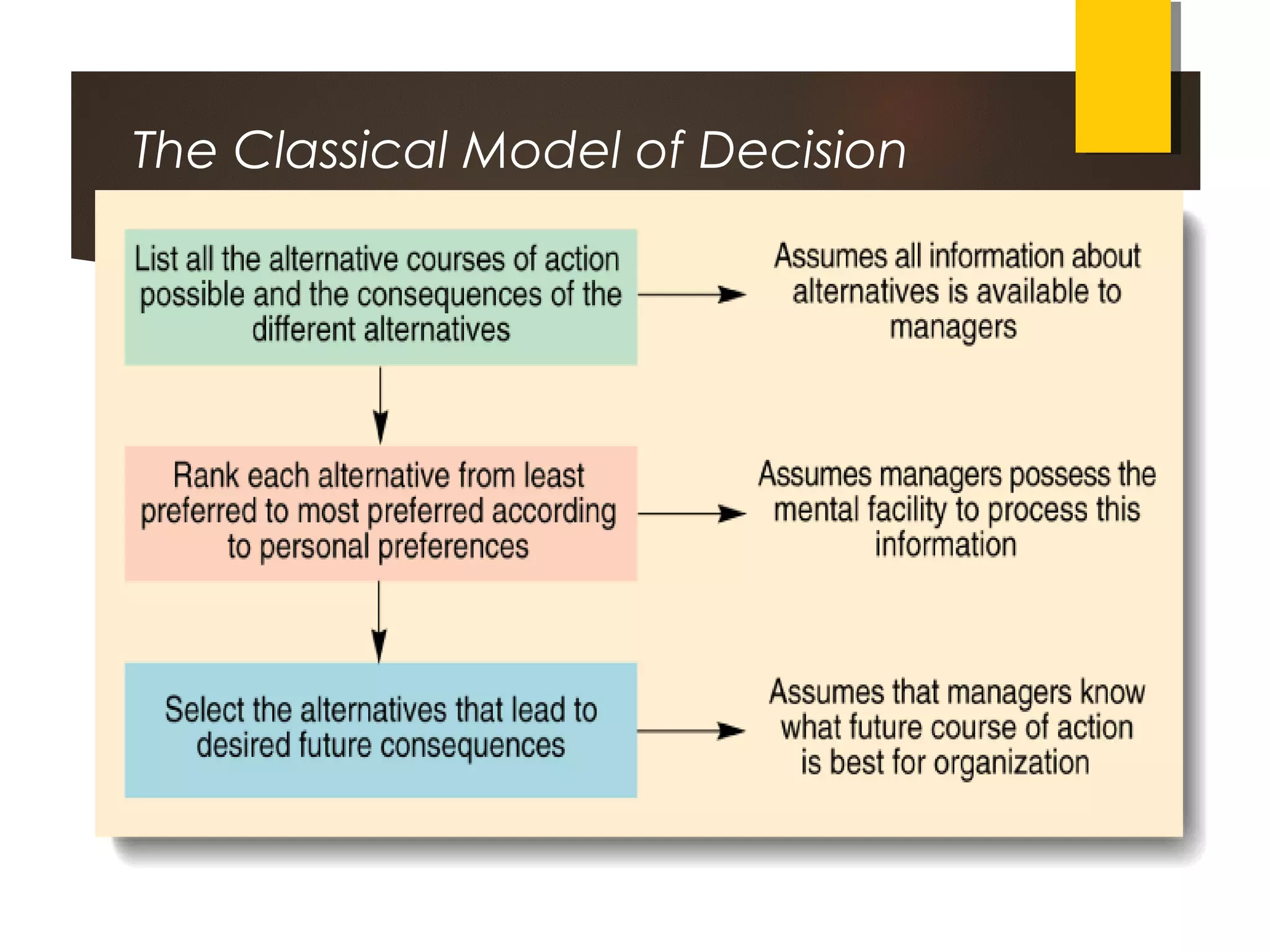
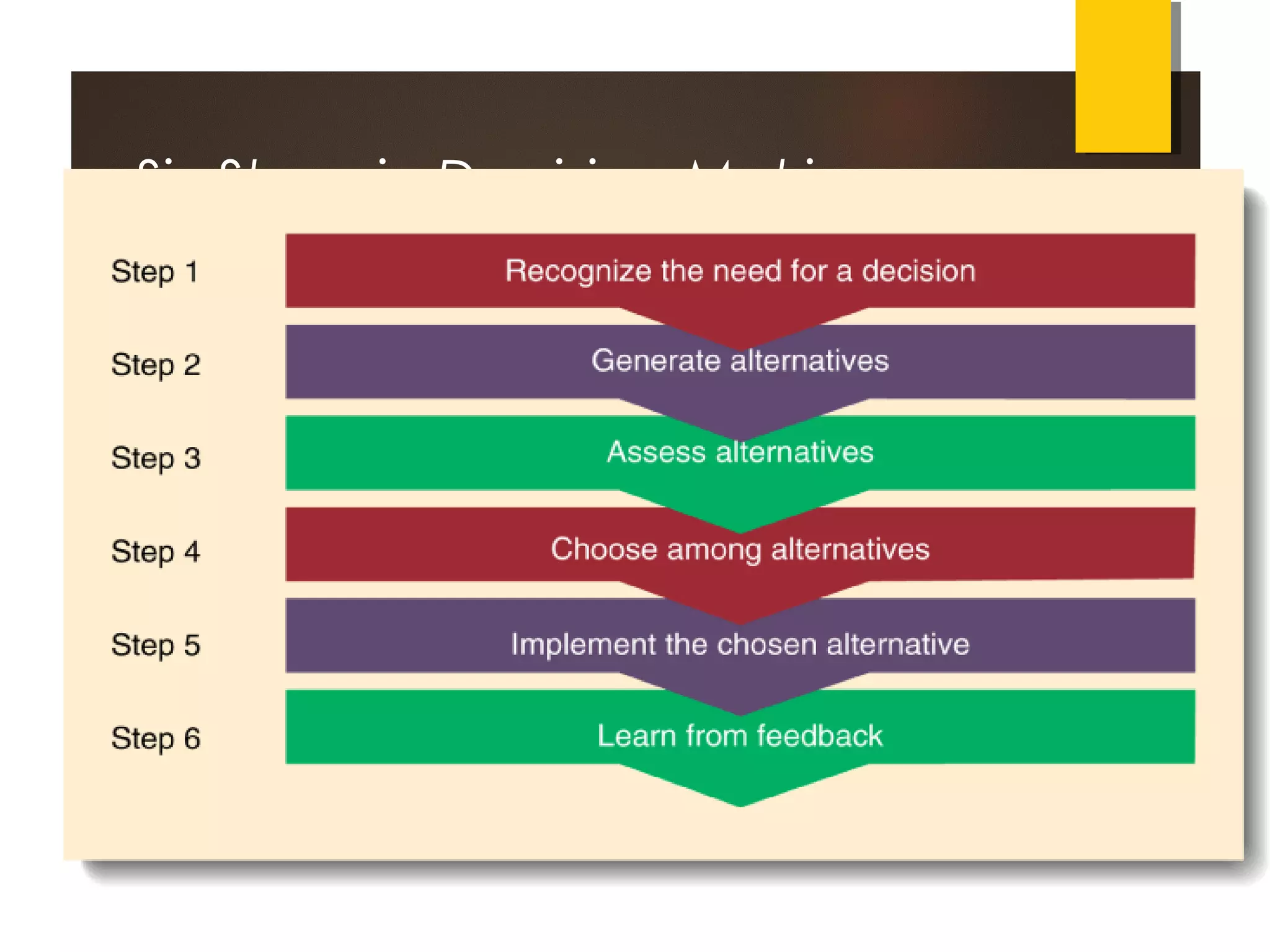
Managerial planning and decision-making face several limitations, including a lack of reliable data, lack of initiative from managers, and high costs. Planning can also be rigid and resist change. External factors beyond a manager's control also limit planning. Some managers prefer focusing on the present rather than the future. Decision-making involves responding to opportunities and threats, and can be programmed or non-programmed. The classical and administrative models provide different approaches to decision-making. The administrative model recognizes limitations like bounded rationality and incomplete information due to risk, uncertainty, and time constraints. Effective decision-making follows six steps: recognizing the need, generating alternatives, evaluating options, choosing, implementing, and learning from feedback.