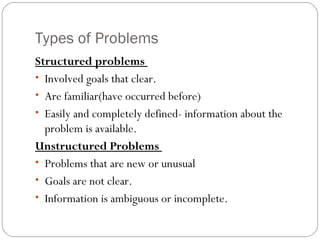
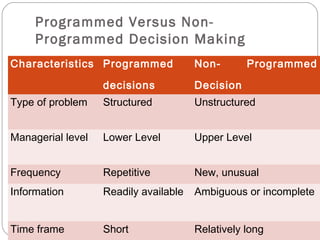
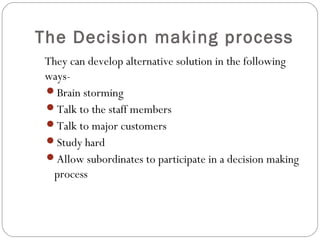
Managers make two types of decisions: programmed and non-programmed. Programmed decisions are repetitive and involve structured problems with clear goals and available information. Non-programmed decisions are unique, less frequent decisions that involve unstructured problems with ambiguous goals and information. The decision-making process involves identifying problems, developing alternative solutions, evaluating those alternatives, and making a choice. Effective decision-making is logical, consistent, straightforward, reliable, flexible, and uses only necessary information and analysis. Decision-making risk depends on certainty of information and predictability of outcomes, ranging from minimal risk under certainty to highest risk under uncertainty.