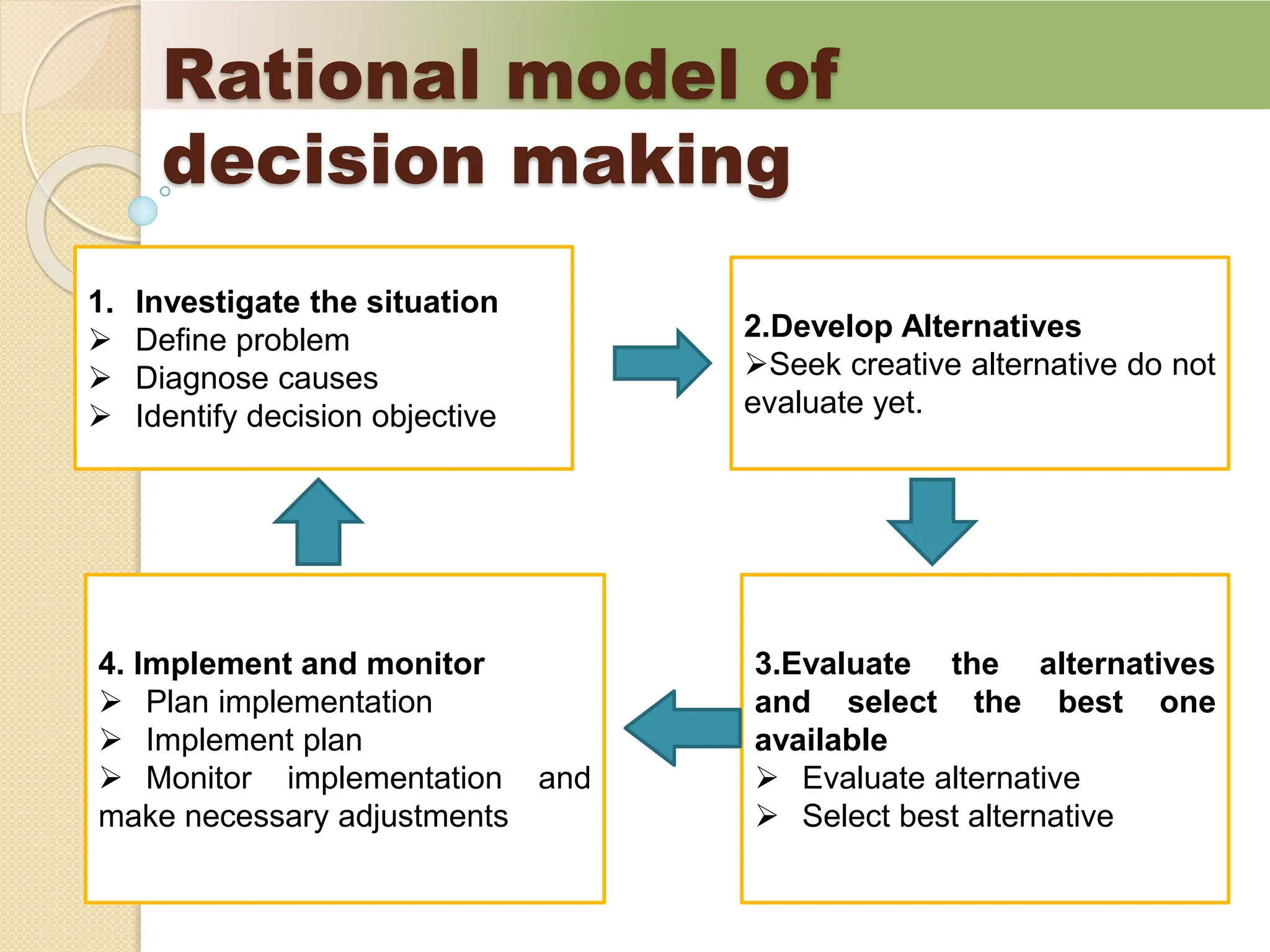
The document discusses decision-making processes, highlighting the importance of past experiences, present circumstances, and future objectives. It outlines various approaches to problem and opportunity identification, including the dialectical inquiry method and the rational model of decision-making, emphasizing both programmed and non-programmed decisions. Additionally, it introduces concepts like bounded rationality and heuristics in managerial decision-making, which address the challenges of limited information and the complexity of choices.