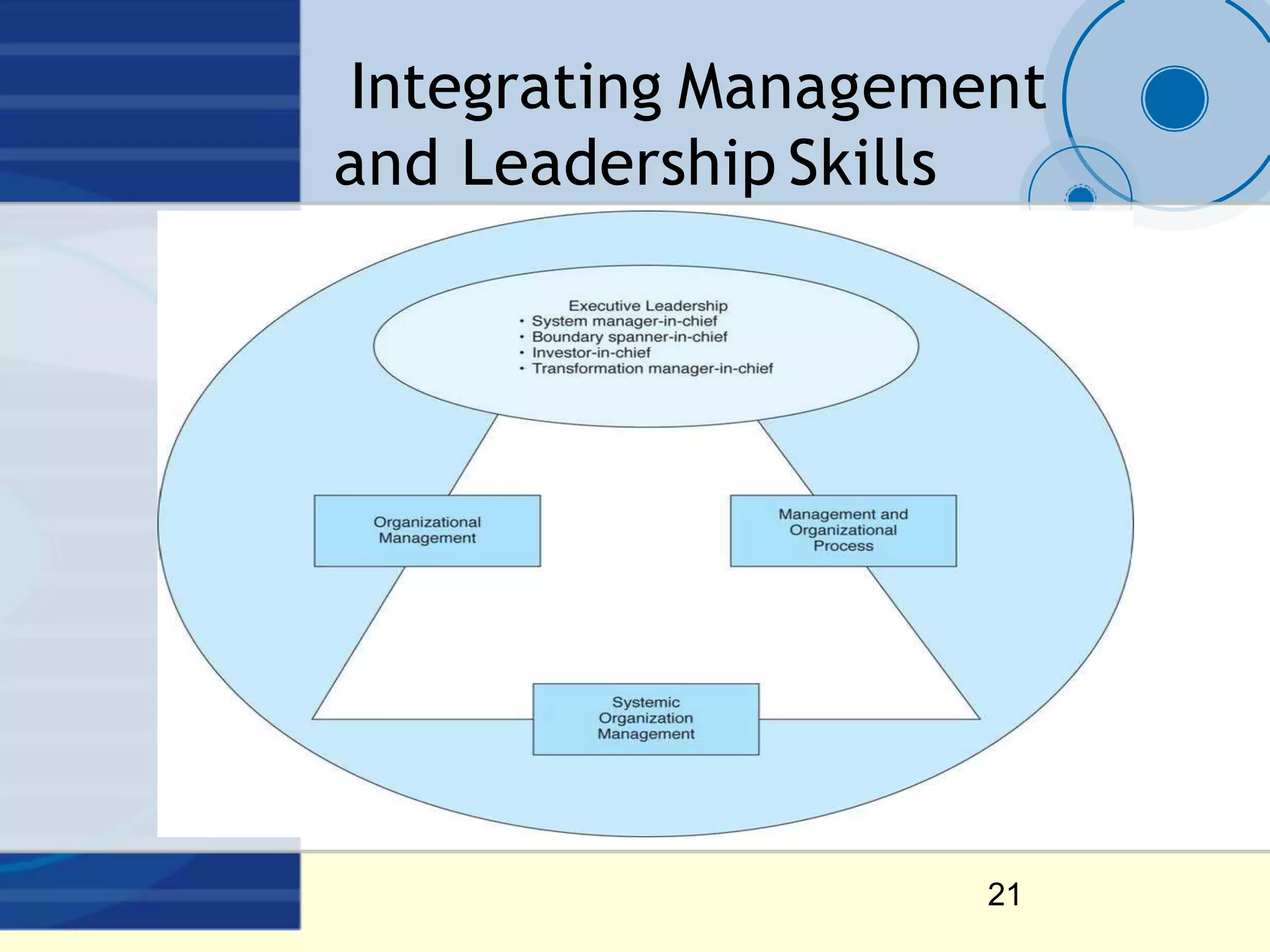
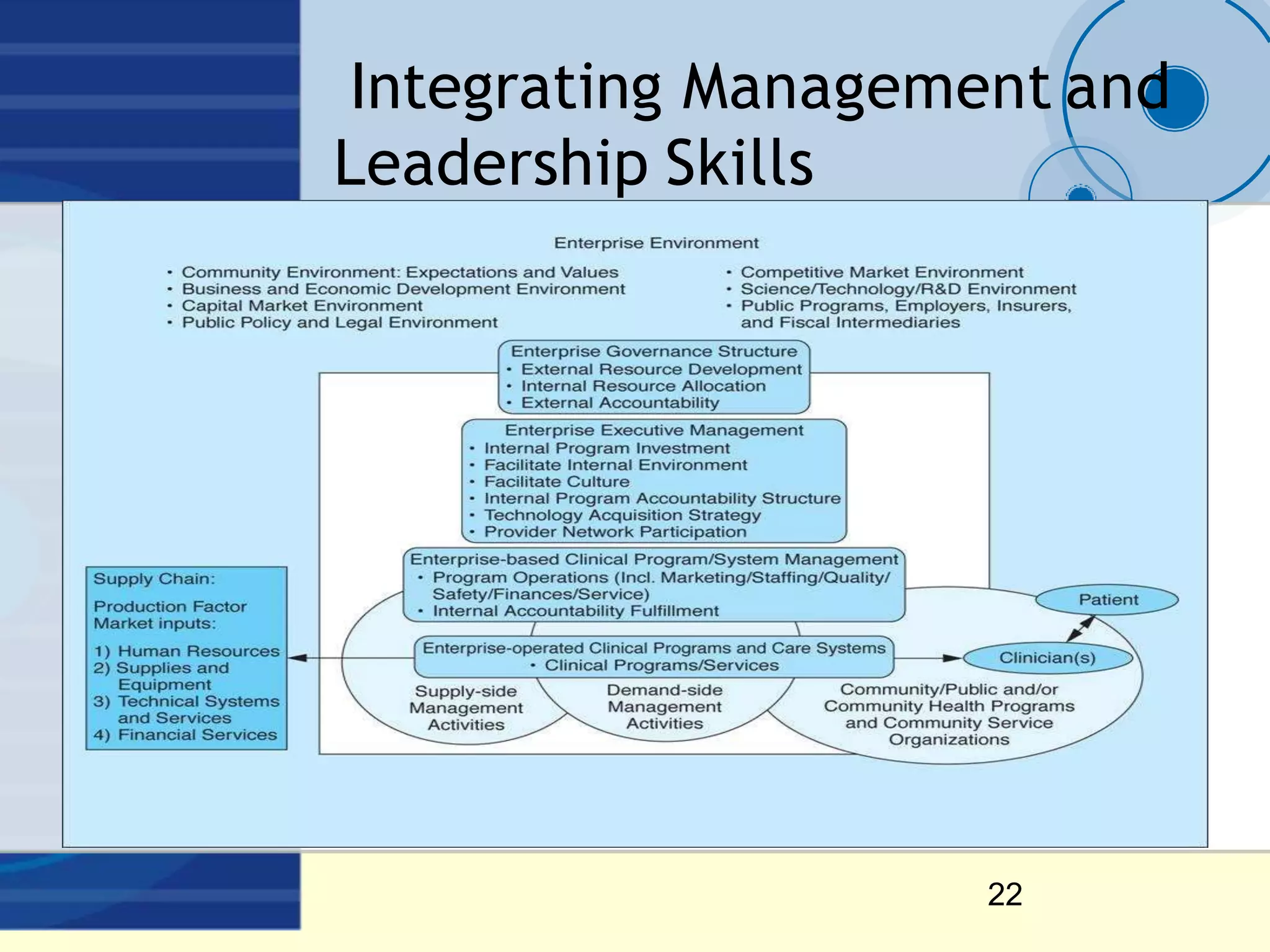
Leadership styles include autocratic, democratic, and free-rein. Autocratic leadership makes quick decisions but can reduce follower motivation and satisfaction. Democratic leadership involves follower consultation, giving them recognition and awareness but could allow them to dominate. Free-rein leadership maximizes follower talent and satisfaction but provides little leadership support and motivation. Effective leadership requires influencing followers, directing organizations towards success, and balancing decision-making and planning.