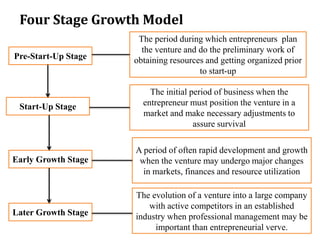
Feasibility planning evaluates the viability of a business idea and is crucial for starting, expanding, or acquiring businesses. A thorough feasibility study assesses operational, technical, and economic aspects, providing valuable insights for decision-making and attracting investment. It contrasts with a business plan by analyzing multiple alternatives before determining which is the most viable for implementation.