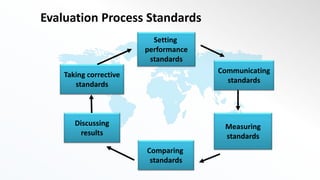
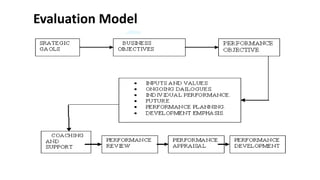
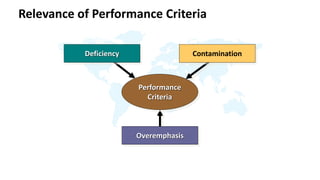
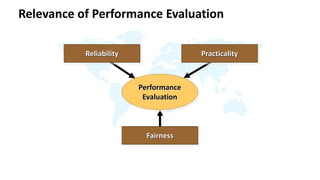
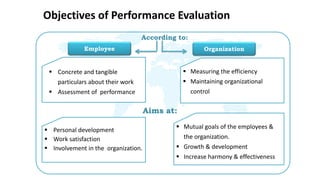
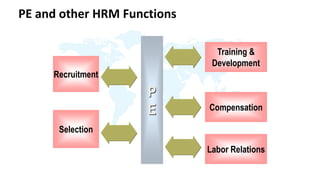
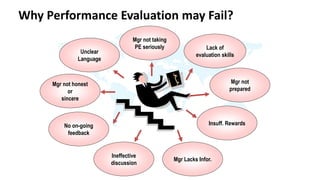
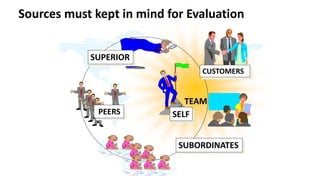
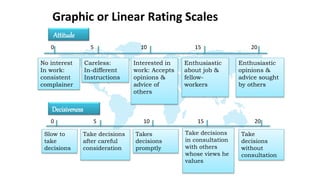
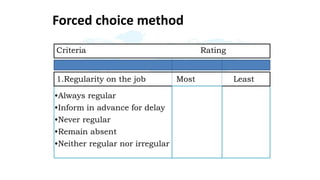
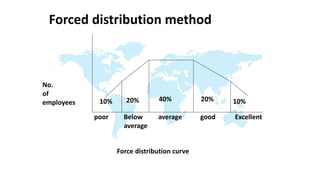
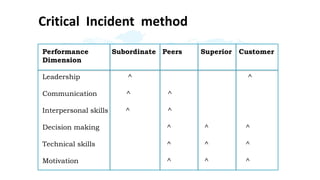
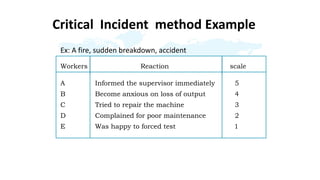
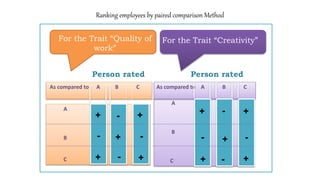
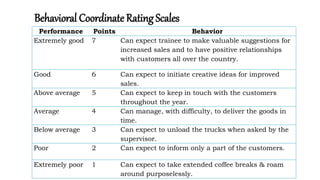
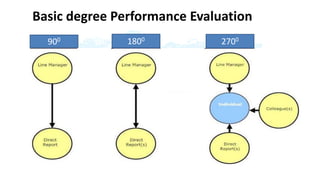
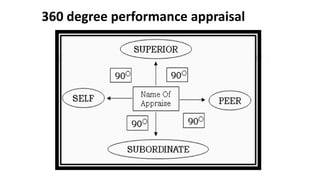
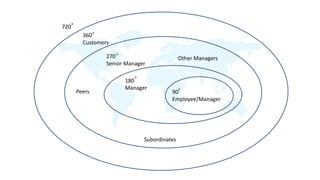
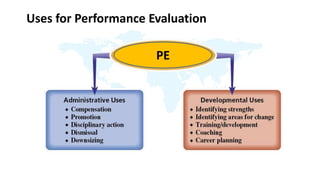
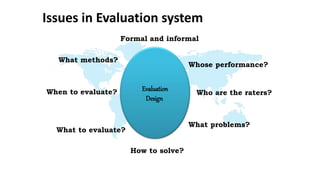
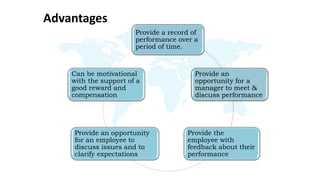
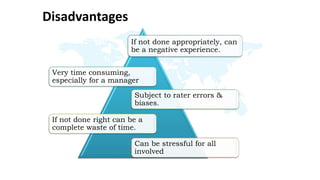
The document discusses performance evaluation as a systematic process for assessing employee contributions over time, including setting standards and measuring performance. Various evaluation methods, both traditional and modern, are outlined, such as paired comparison and 360° feedback, each with their advantages and disadvantages. Key objectives include measuring efficiency, supporting employee development, and maintaining organizational control, while also addressing potential pitfalls in the evaluation process.