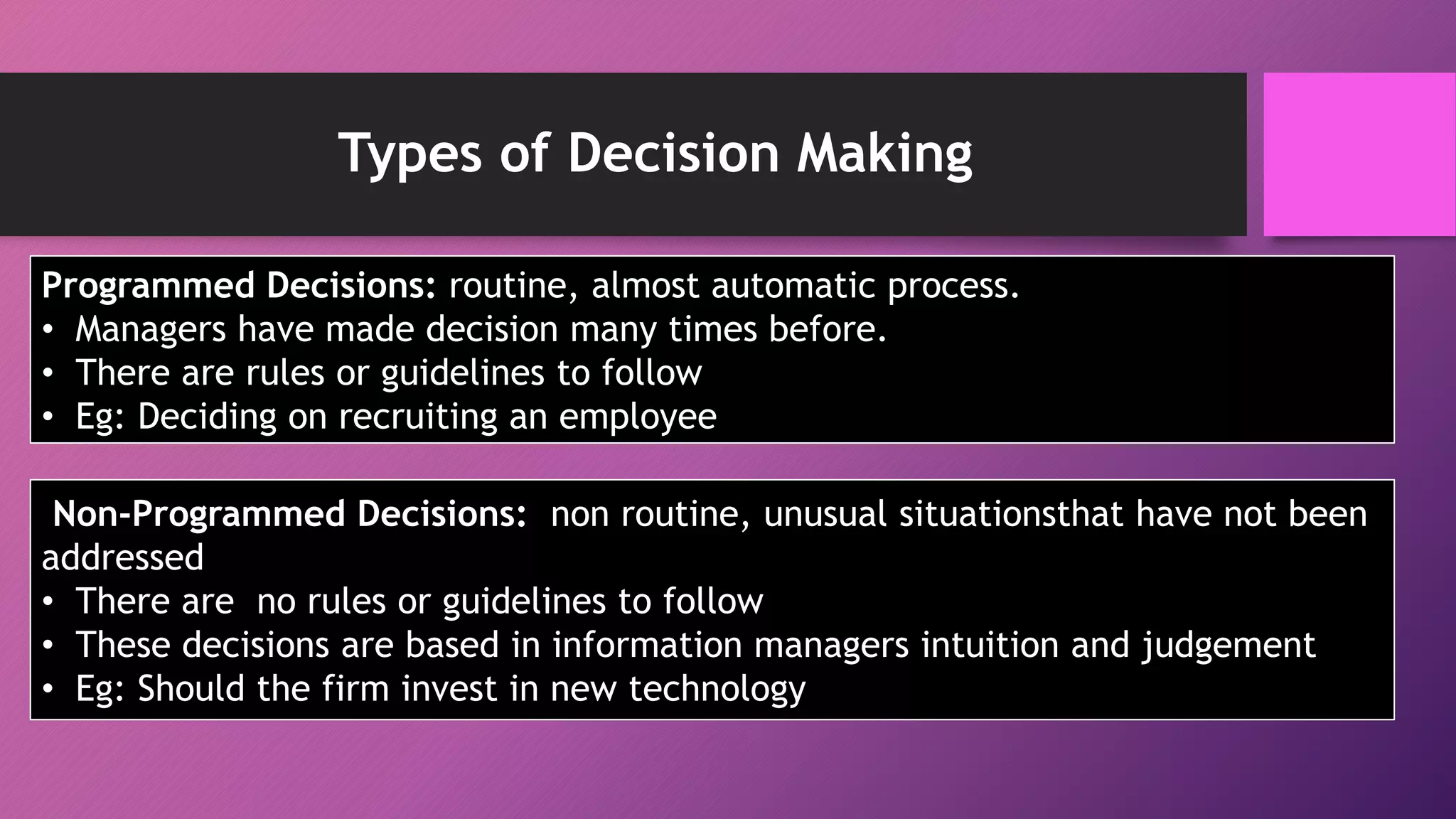
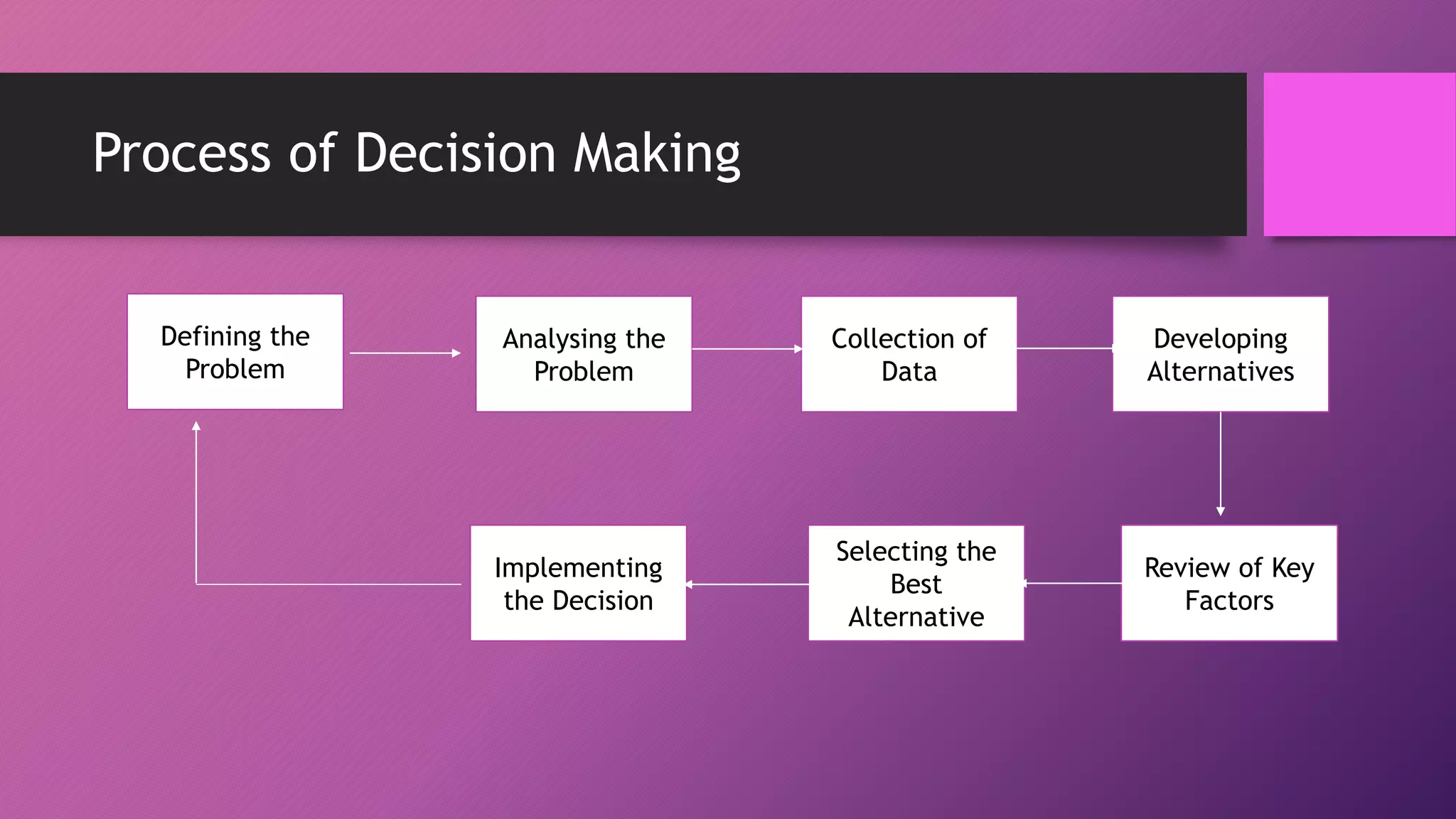
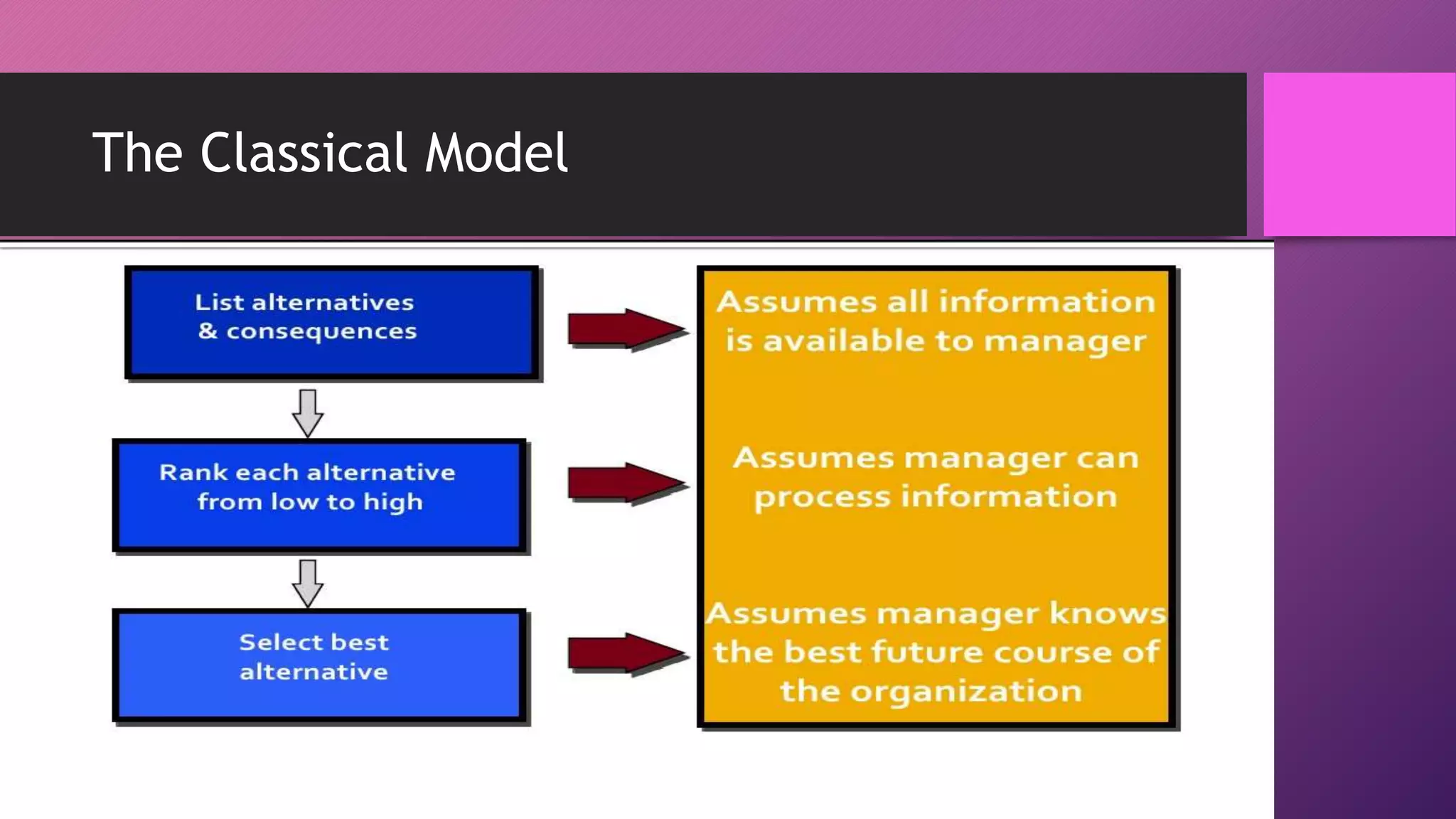
Decision making is a process of selecting the best course of action to achieve desired outcomes, intertwining with planning activities. It involves programmed decisions, which are routine and guided by prior experience, and non-programmed decisions, which require intuition and judgment for unique situations. The concept of bounded rationality explains that decisions may not be optimal due to personal biases, limited knowledge of alternatives, and a focus on satisfactory rather than ideal solutions.