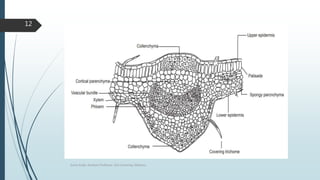
This document is a presentation by Sonia Singh on the plant Vinca (Catharanthus roseus). It discusses the biological source of Vinca, how it is cultivated and collected, its morphology and microscopic characteristics. Specifically, it notes that Vinca is native to Madagascar and is cultivated in many tropical/subtropical countries. It is propagated through direct seeding or in a nursery before being transplanted. Microscopically, its leaf has single-layered epidermis, palisade and spongy parenchyma tissue, and stomata on both surfaces. The presentation concludes with references and a quiz.