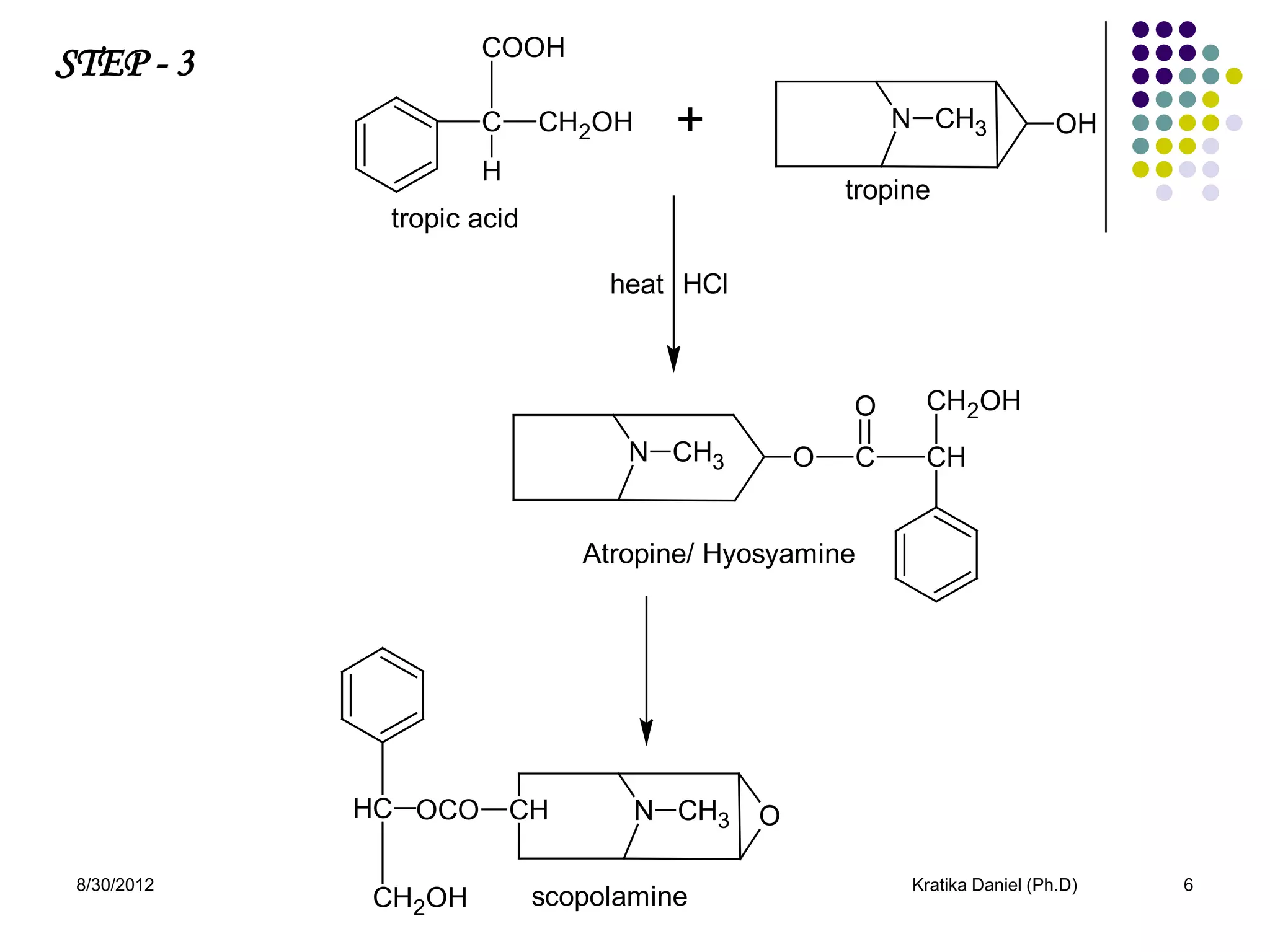
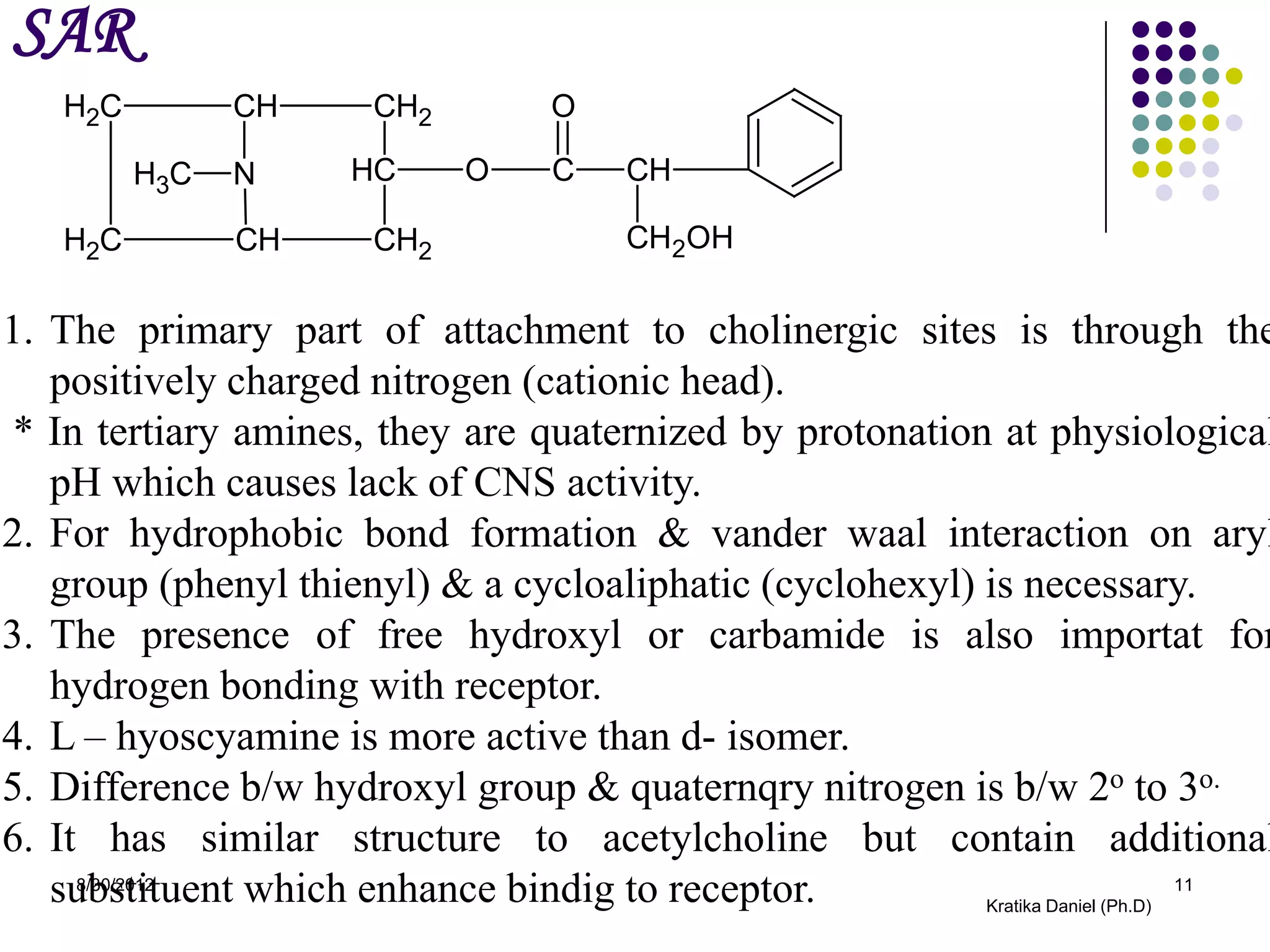
This document discusses tropane alkaloids, specifically atropine alkaloid. It summarizes that atropine alkaloid is mainly found in plants from the solanaceae family, like Atropa belladona and Datura stromonium. It then describes the isolation, biosynthesis, identification tests, chemistry and properties, structure-activity relationships, uses, and mechanism of action of atropine alkaloid.