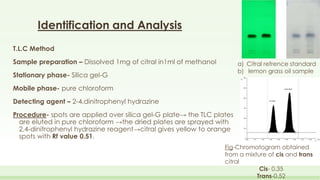
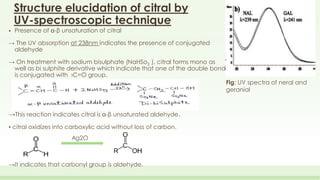
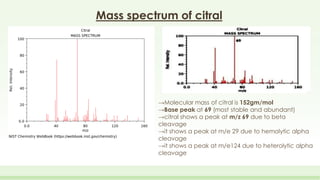
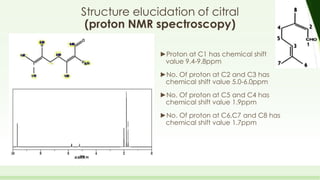
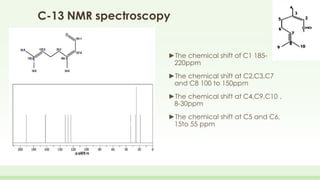
The document discusses the structure elucidation of citral, primarily derived from lemon grass oil, and details its chemical properties, occurrence, isolation, and identification methods. Citral, consisting of two isomers (geranial and neral), displays significant therapeutic properties and is used in various industries. Analytical techniques such as UV, IR, MS, and NMR spectroscopy are highlighted for its analysis and identification.