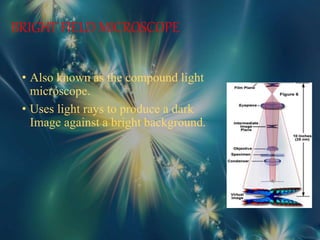
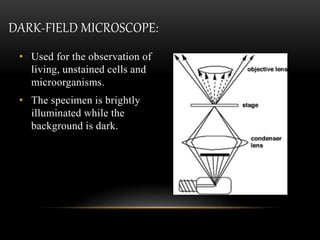
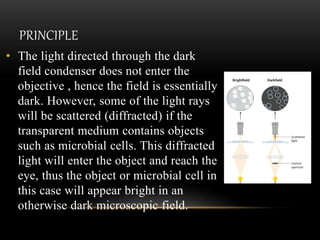
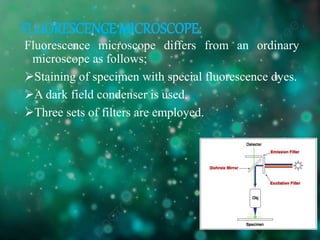
The document discusses different types of light microscopes, including their basic principles and applications. It describes bright field, dark field, phase contrast, and fluorescent microscopes. Bright field microscopes use light rays to produce a dark image on a bright background and are used to visualize cells. Dark field microscopes illuminate specimens to appear bright on a dark background, allowing observation of unstained living cells. Phase contrast microscopes convert phase shifts in light passing through specimens into brightness changes, while fluorescent microscopes use fluorescent dyes and specific filter sets to detect light emission from excited specimen molecules.