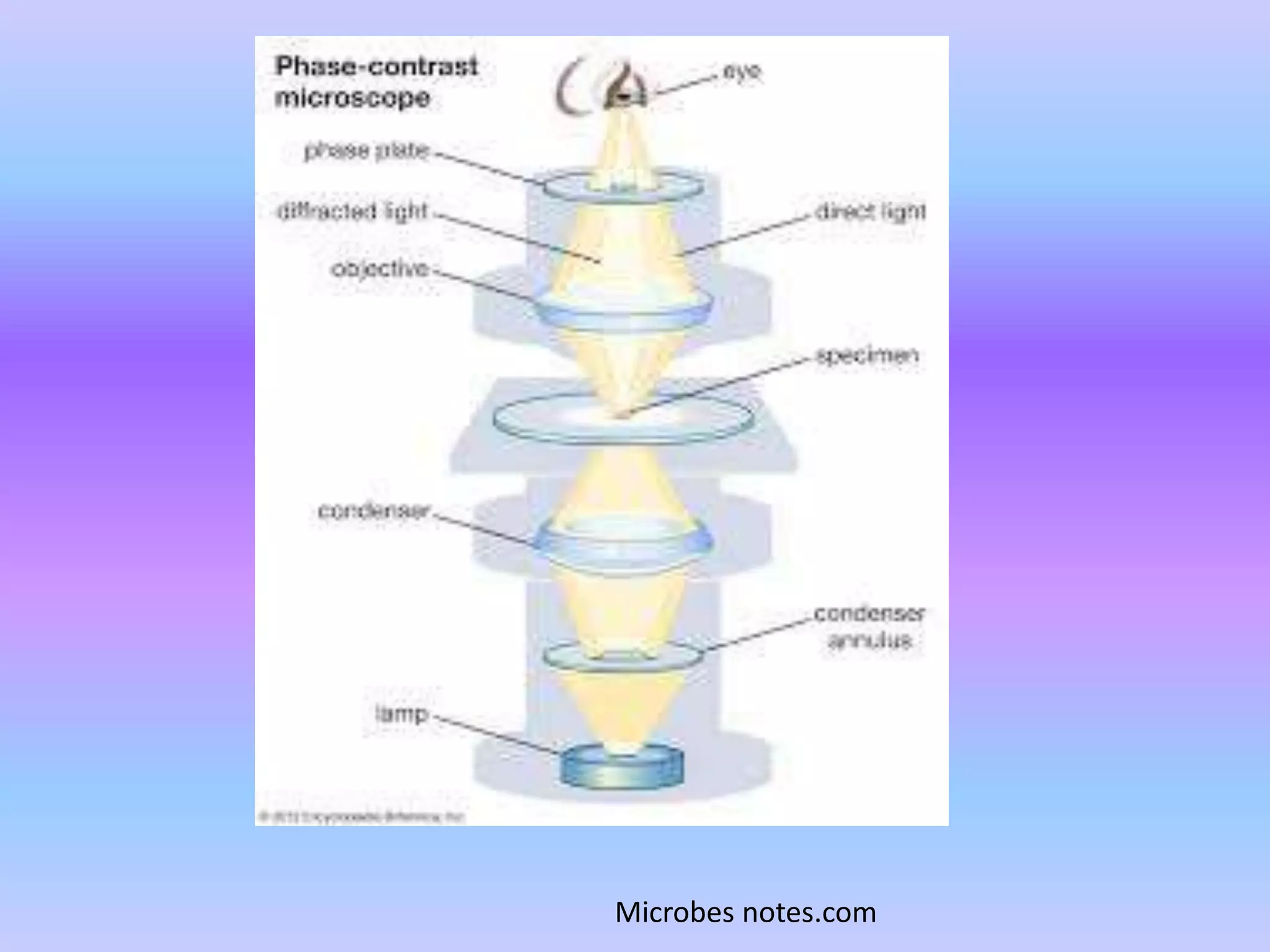
Light microscopy uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify small samples. It has been used since the 17th century and remains a popular technique due to its simplicity. The basic components are a light source, lenses of varying magnification, and mechanical stages to position samples. There are three main types - brightfield microscopy uses transmitted light, phase contrast separates illuminated and scattered light, and darkfield blocks light entering directly to view transparent samples. Each technique has advantages for examining different types of unstained or living specimens.