Embed presentation
Download to read offline






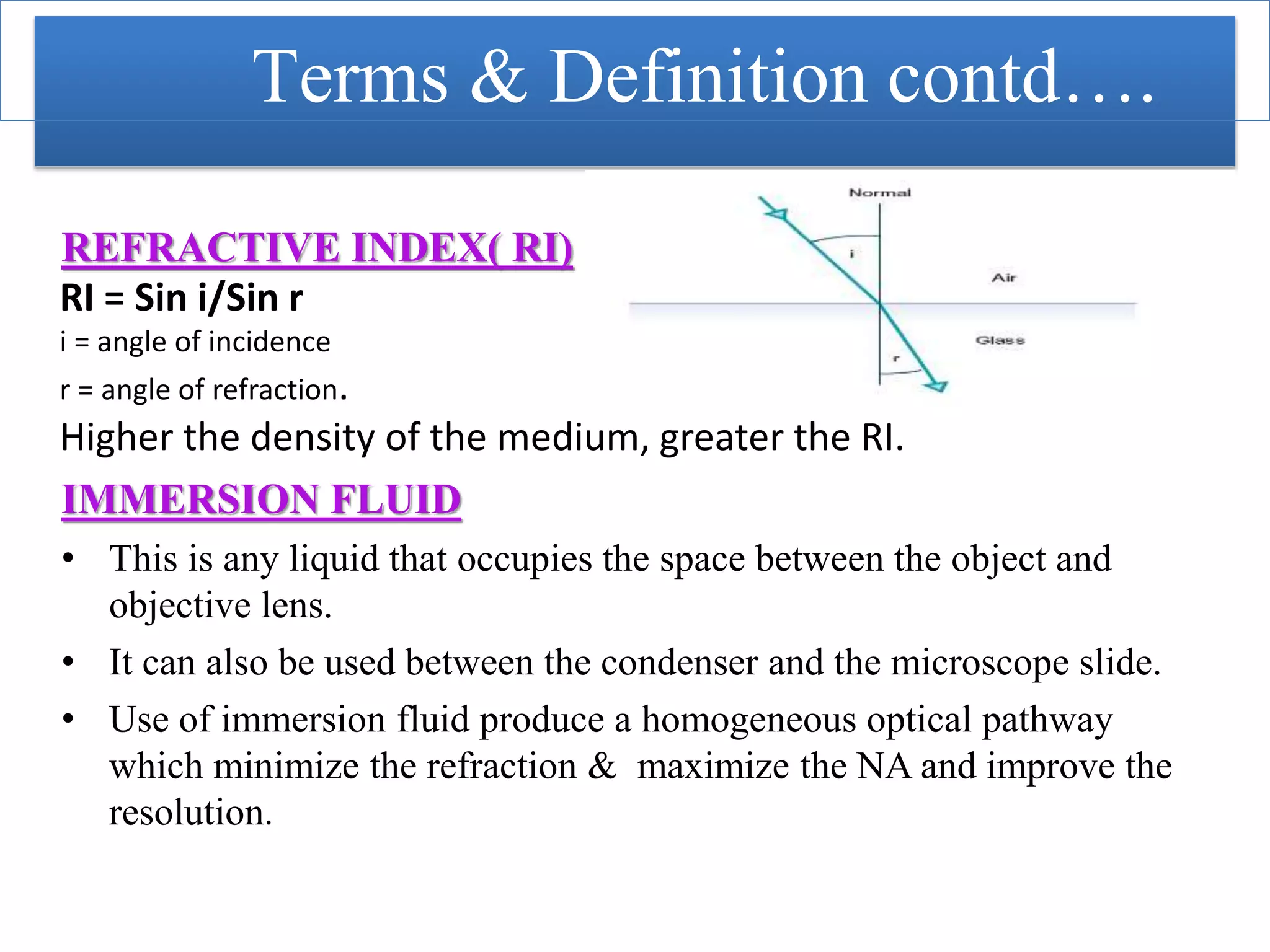




















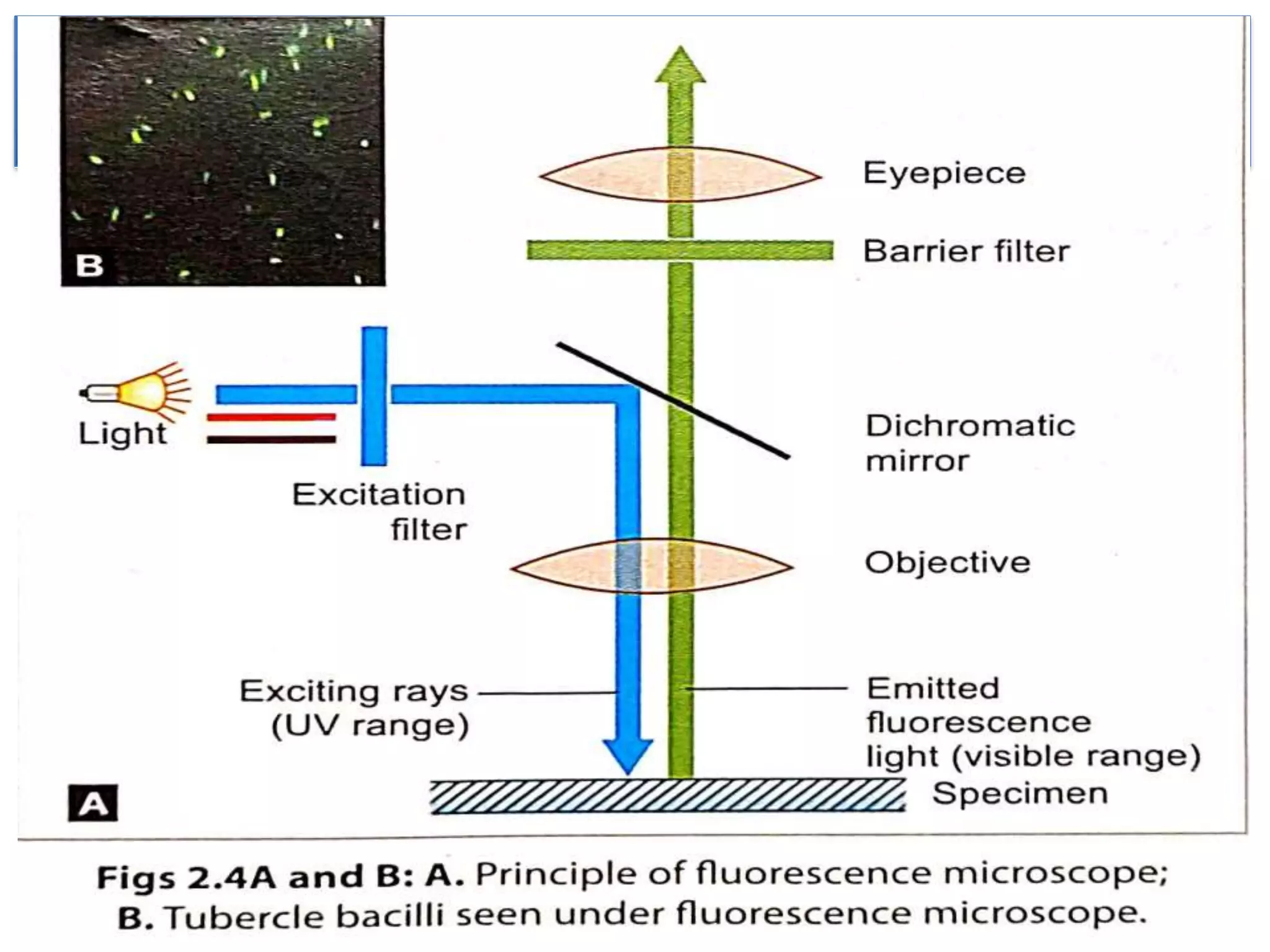



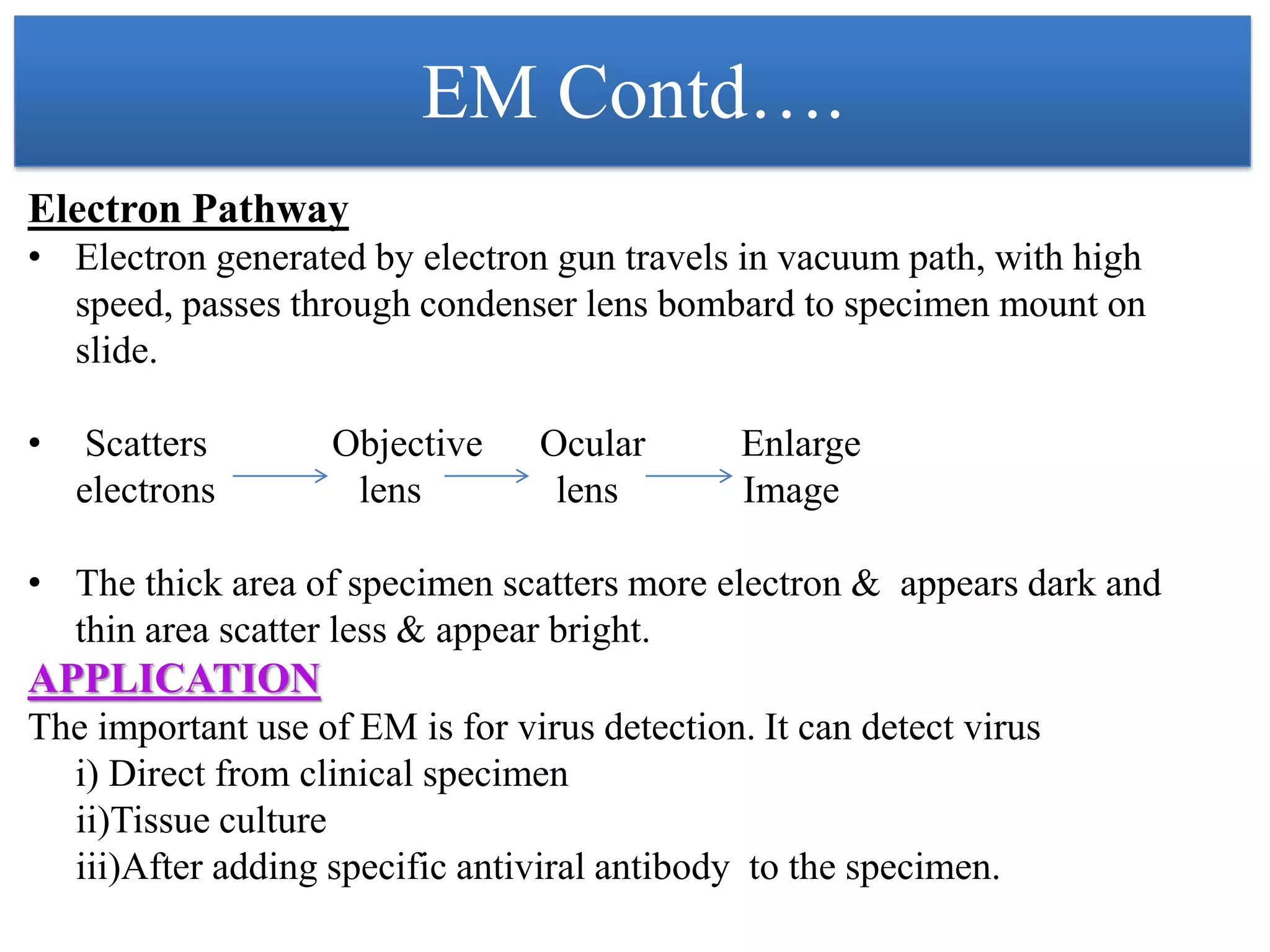

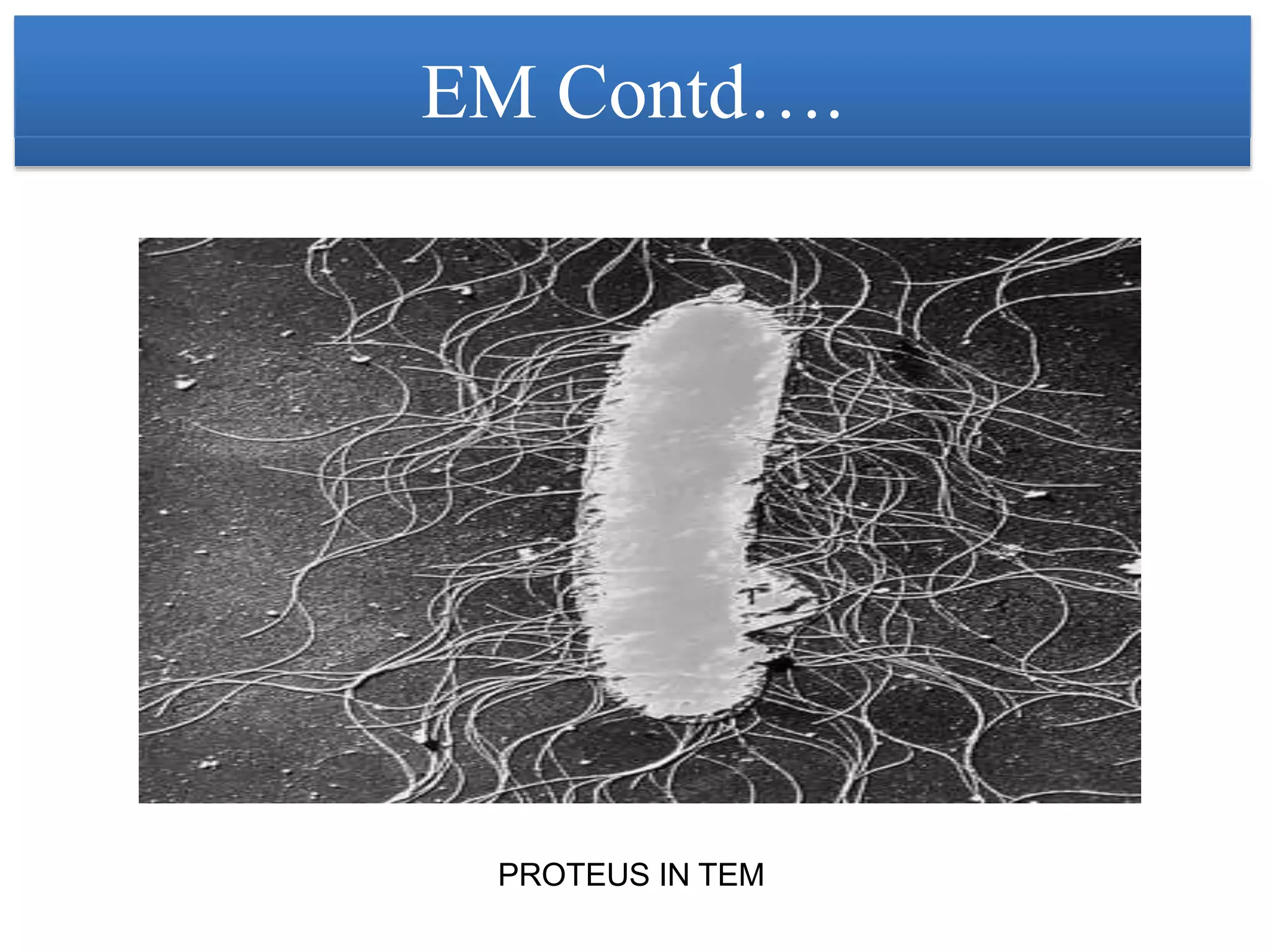







This document provides an overview of microscopy. It begins with an introduction to microscopes and their history. It then defines key microscope terms and describes different types of microscopes, including their components, working principles, applications and advantages/disadvantages. The document discusses brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast, fluorescence and electron microscopes. It also covers micrometry and best practices for microscope care and storage. In summary, the document provides a comprehensive guide to the basic concepts and components of light and electron microscopy.









































