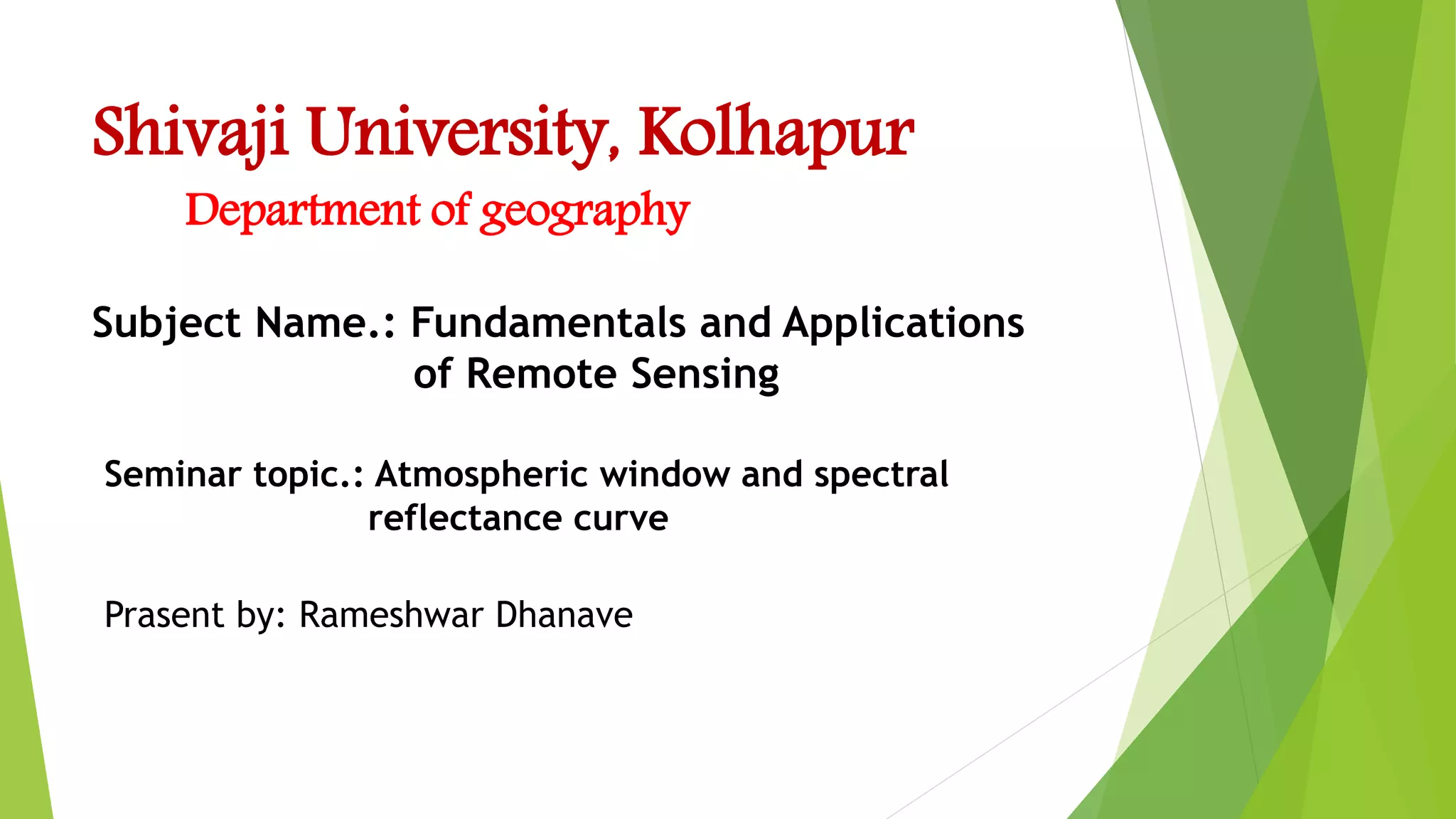
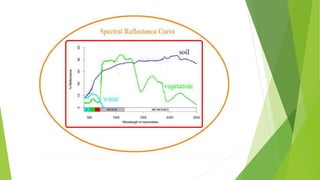
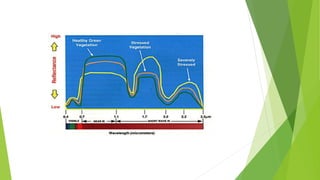
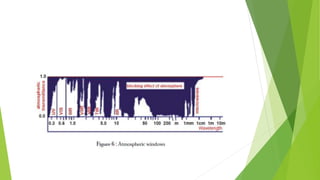
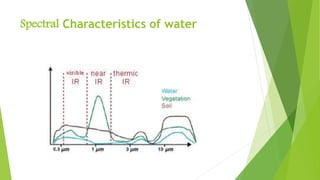
The document discusses atmospheric windows and spectral reflectance curves. It states that the atmosphere selectively transmits certain wavelengths, known as atmospheric windows, which are present in the visible and infrared regions. It also explains that different materials reflect and absorb light differently at varying wavelengths, shown via spectral reflectance curves. These curves plot wavelength against reflectance and vary for different materials like vegetation, soil, and water.