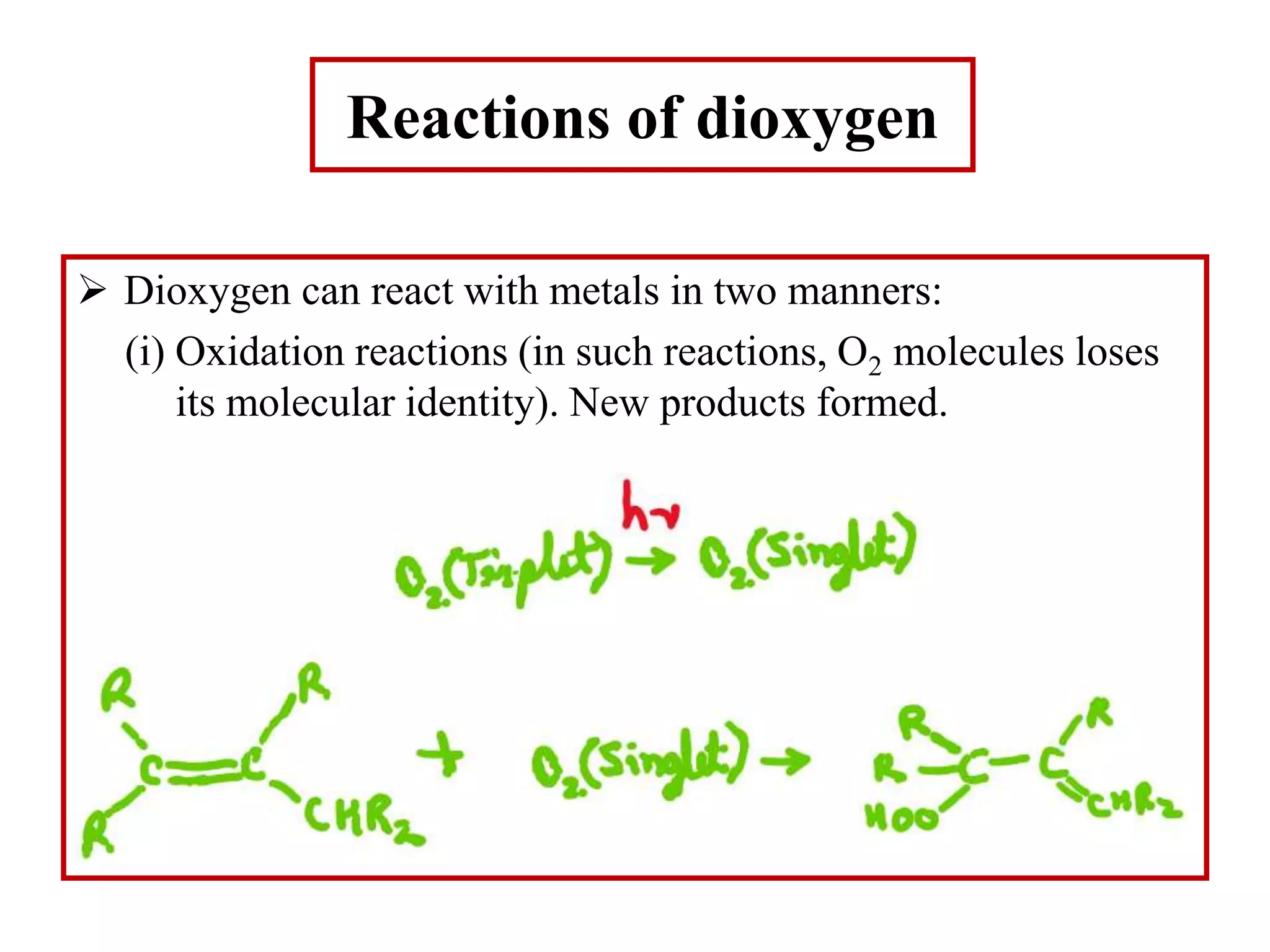
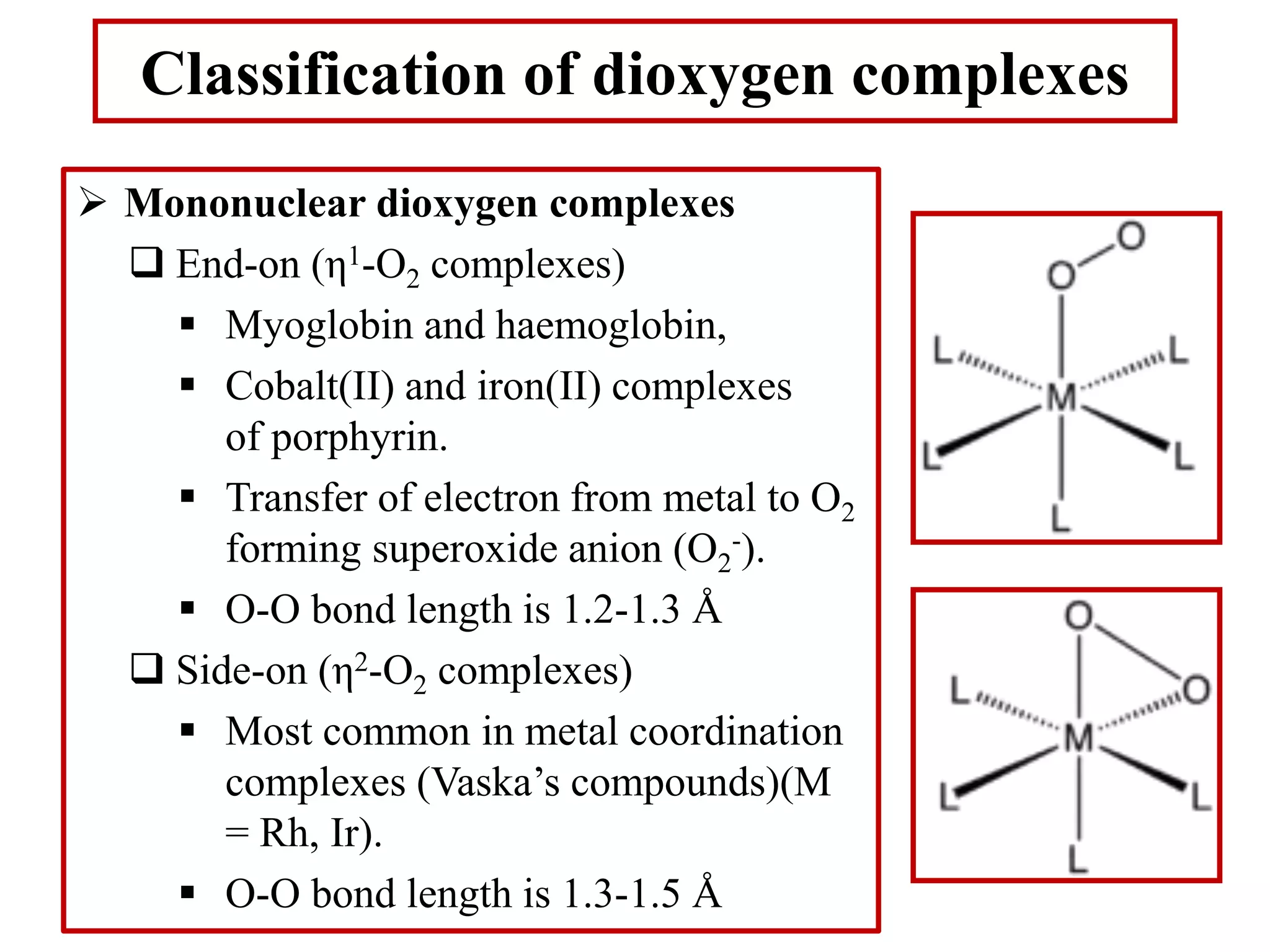
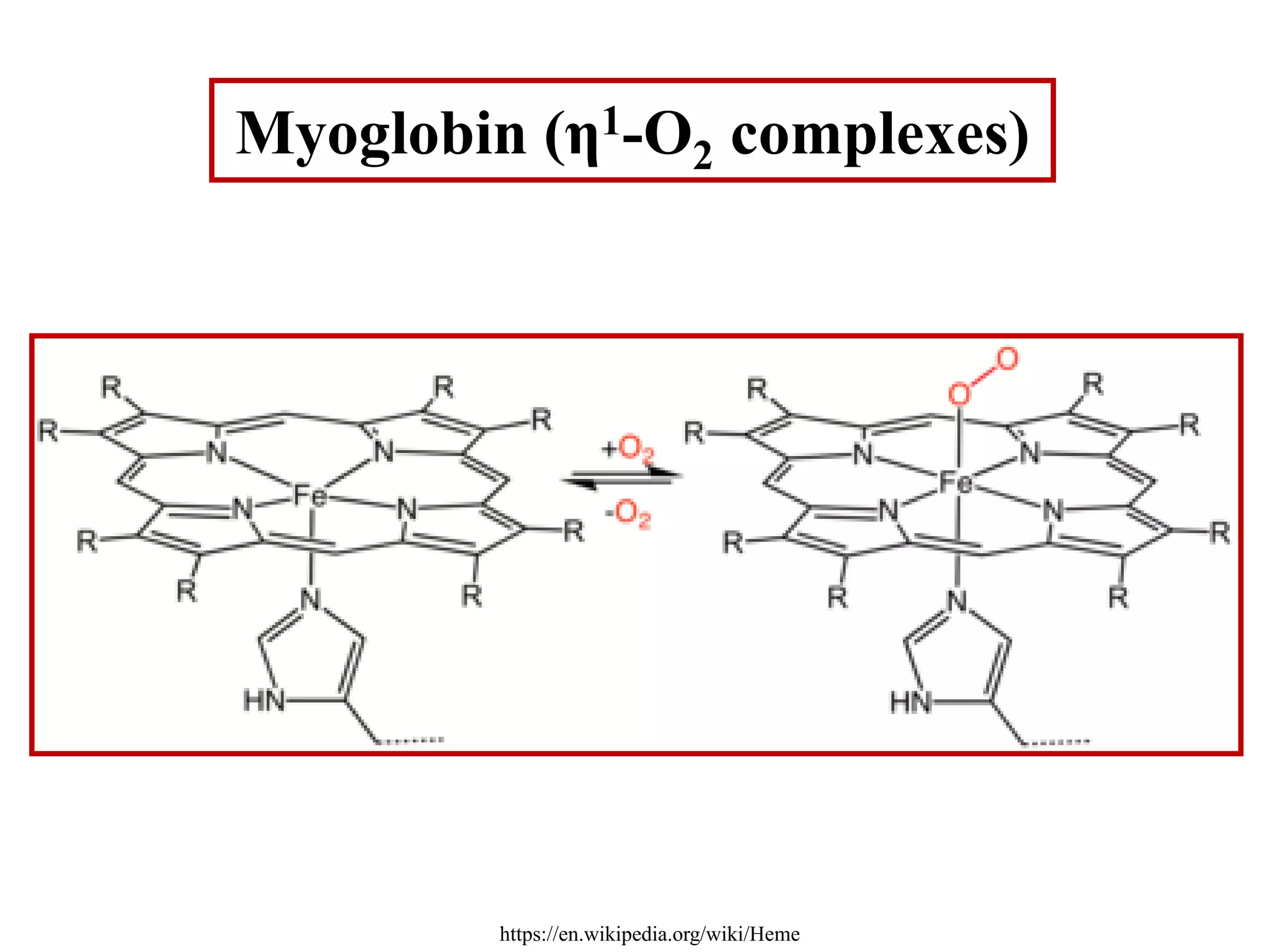
The document discusses metal dioxygen complexes, focusing on their properties, reactions, and classification. It covers the reactions of dioxygen with metals, including oxidation and oxygenation processes, and describes various dioxygen complexes such as mononuclear and dinuclear. Additionally, it explores practical applications of dioxygen complexes in catalysis and oxygen purification.