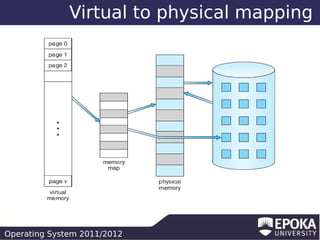
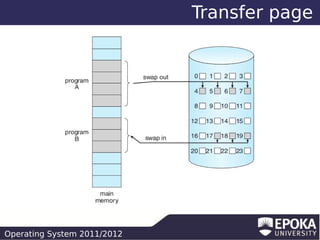
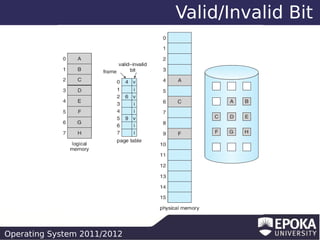
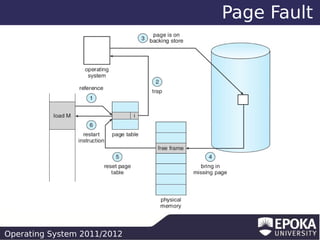
This document discusses virtual memory and demand paging in an operating system. It explains that virtual memory separates logical memory from physical memory, allowing processes to have a larger logical address space than physical memory. It also describes how demand paging works, bringing pages into memory only when needed, reducing I/O and memory usage. The document outlines different page replacement algorithms for when memory is full, such as FIFO, optimal, LRU, and counting-based approaches.