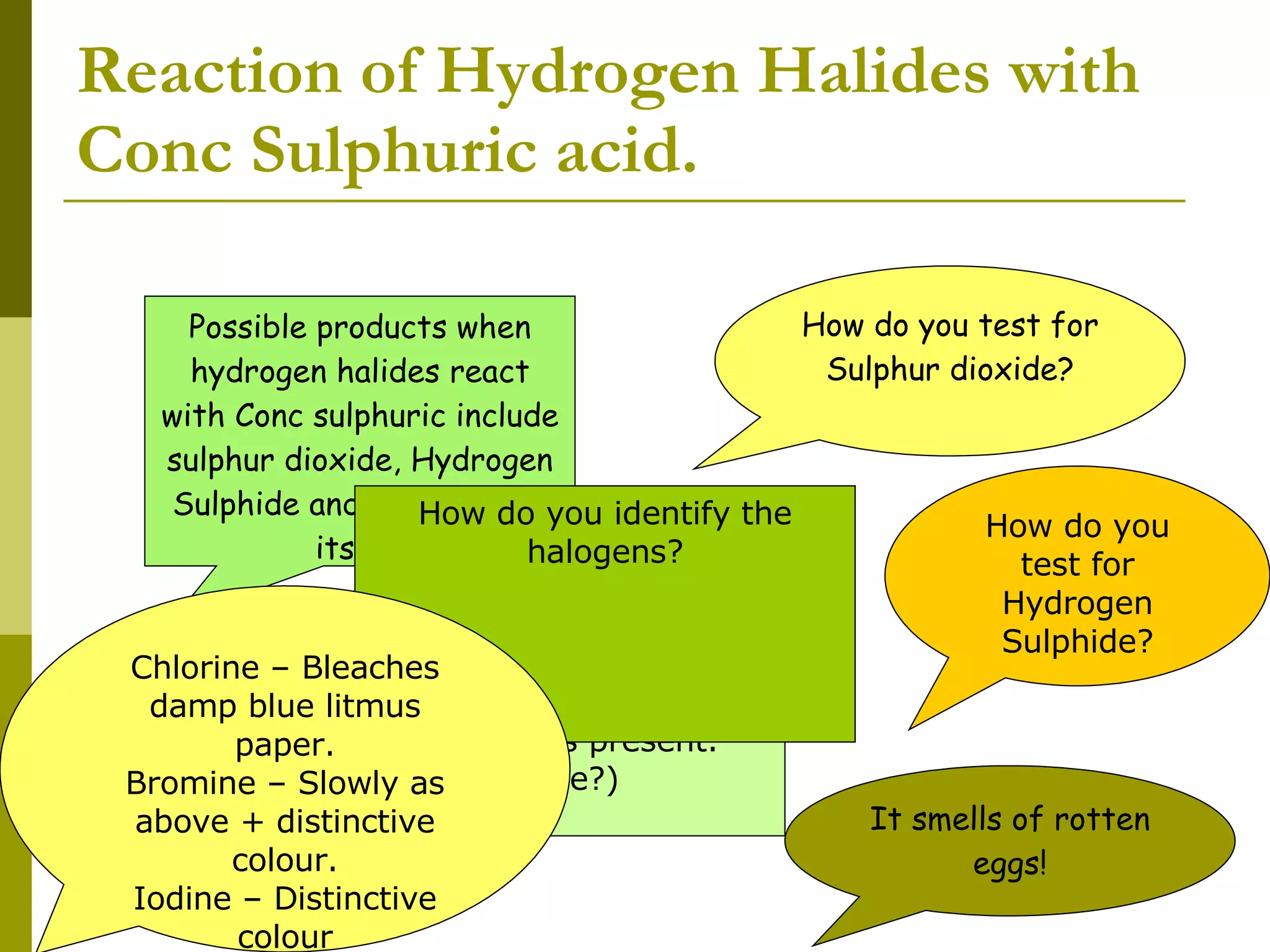
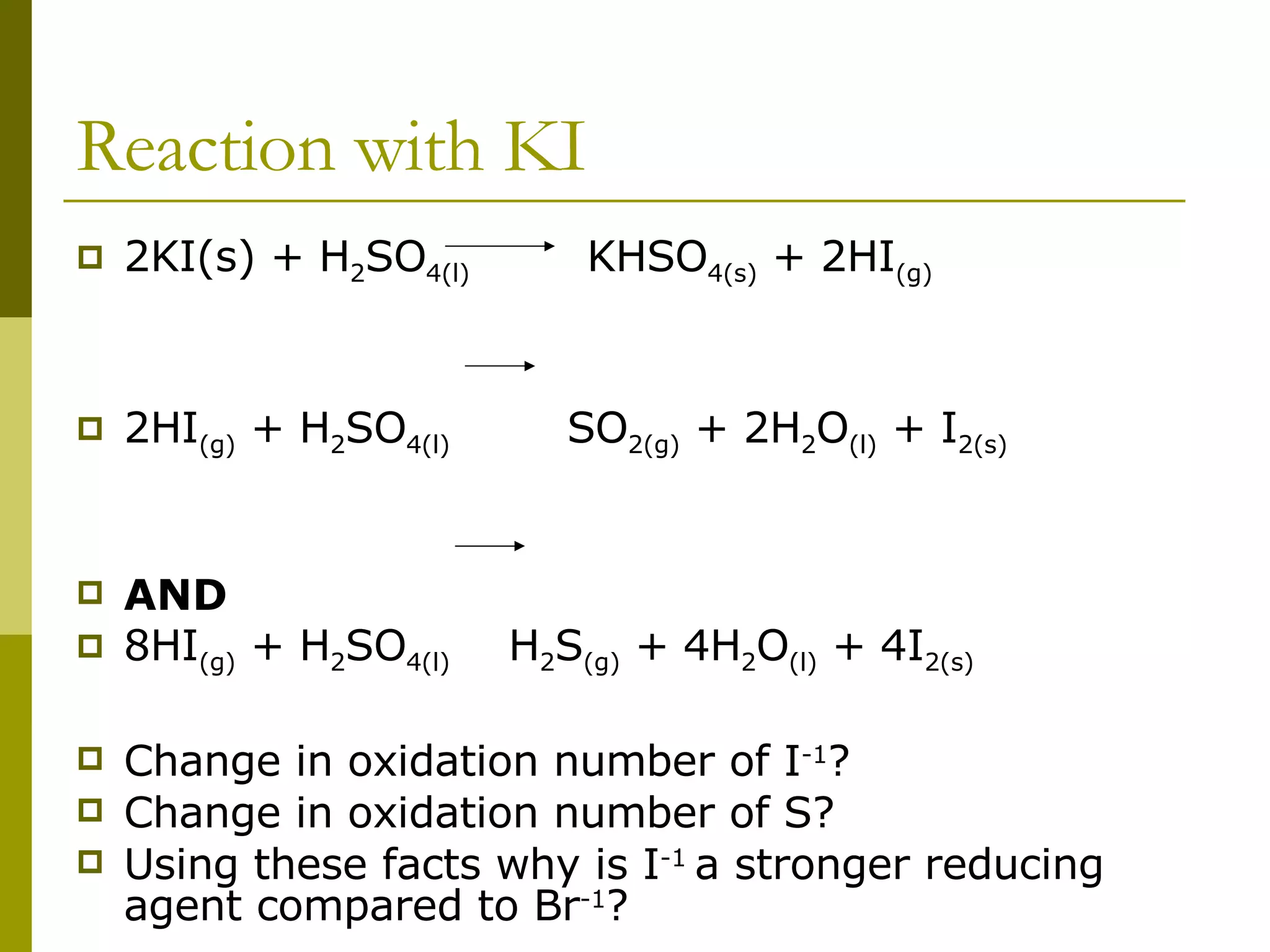
The document summarizes the properties and reactions of halide salts. Halide ions such as I- act as reducing agents in reactions. When halide salts react with concentrated sulfuric acid, hydrogen halides are produced which can further reduce the acid. Iodide is the strongest reducing agent of the halide ions due to its ability to reduce sulfuric acid to sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide. Bromide and chloride are weaker reducing agents.