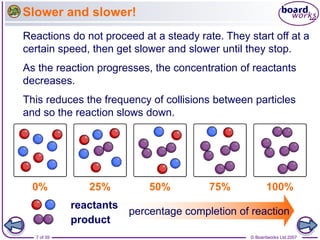
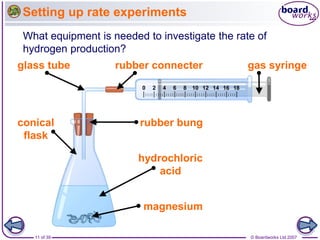
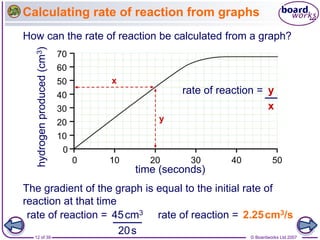
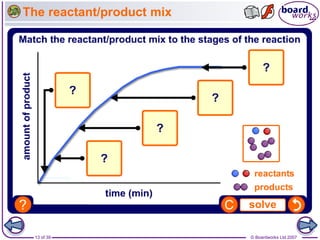
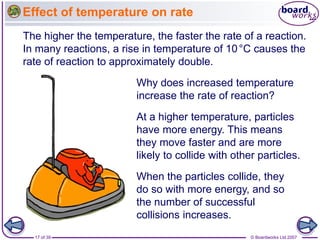
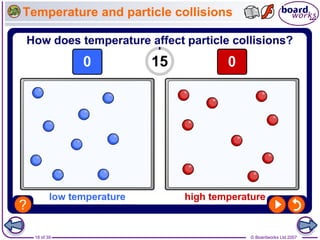
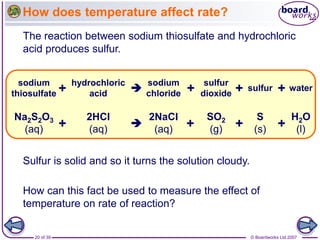
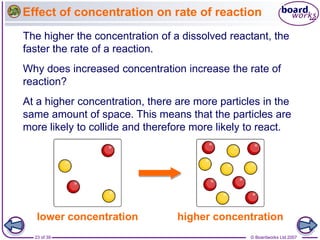
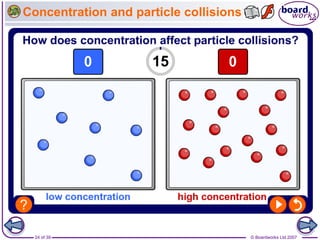
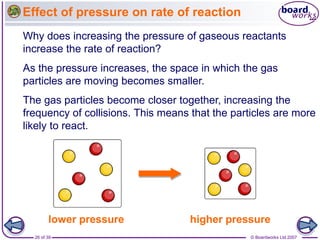
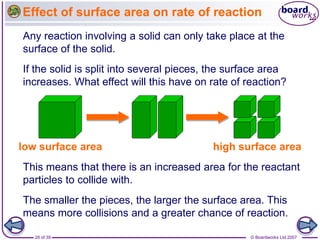
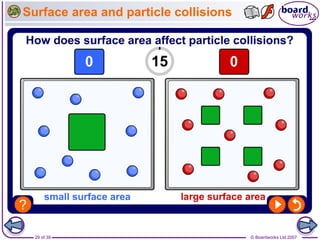
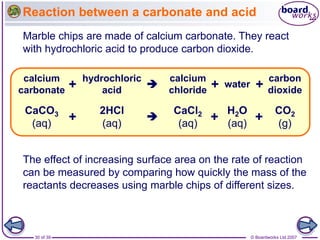
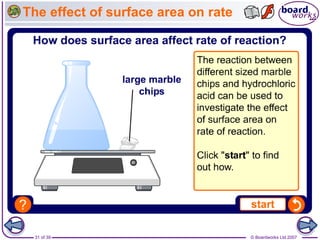
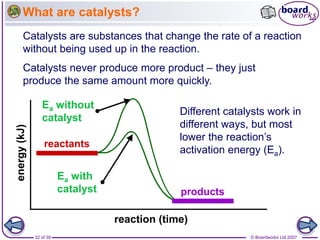
The document discusses factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions, including temperature, concentration, pressure, and surface area of reactants. Increased temperature leads to more frequent and more energetic collisions between particles, speeding up reactions. Higher concentration and pressure also increase the frequency of collisions. Greater surface area of solid reactants provides more sites for collisions and reactions to occur. Catalysts increase reaction rates by reducing the activation energy required without being used up in the reaction.