The document discusses several chemistry concepts and experiments including:
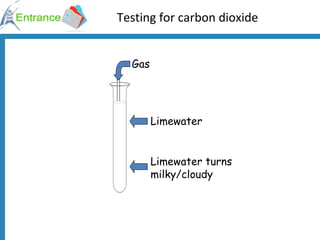
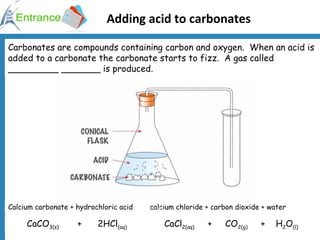
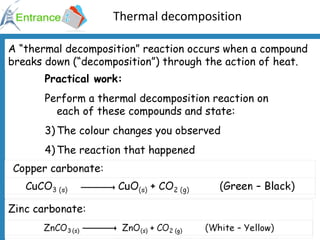
1) Testing for carbon dioxide by adding acid to carbonates which produces carbon dioxide gas.
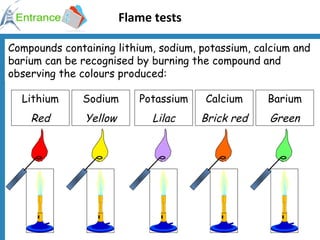
2) Using flame tests to identify metal ions based on the color of flames they produce.
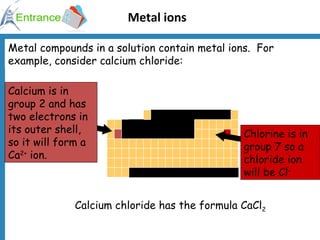
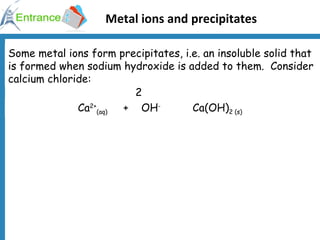
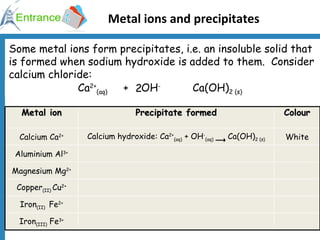
3) Metal ions forming precipitates when sodium hydroxide is added, such as calcium ions forming calcium hydroxide.
4) Experiments to test for chloride, sulfate, ammonium, nitrate, bromide and iodide ions using chemical reactions and indicators.