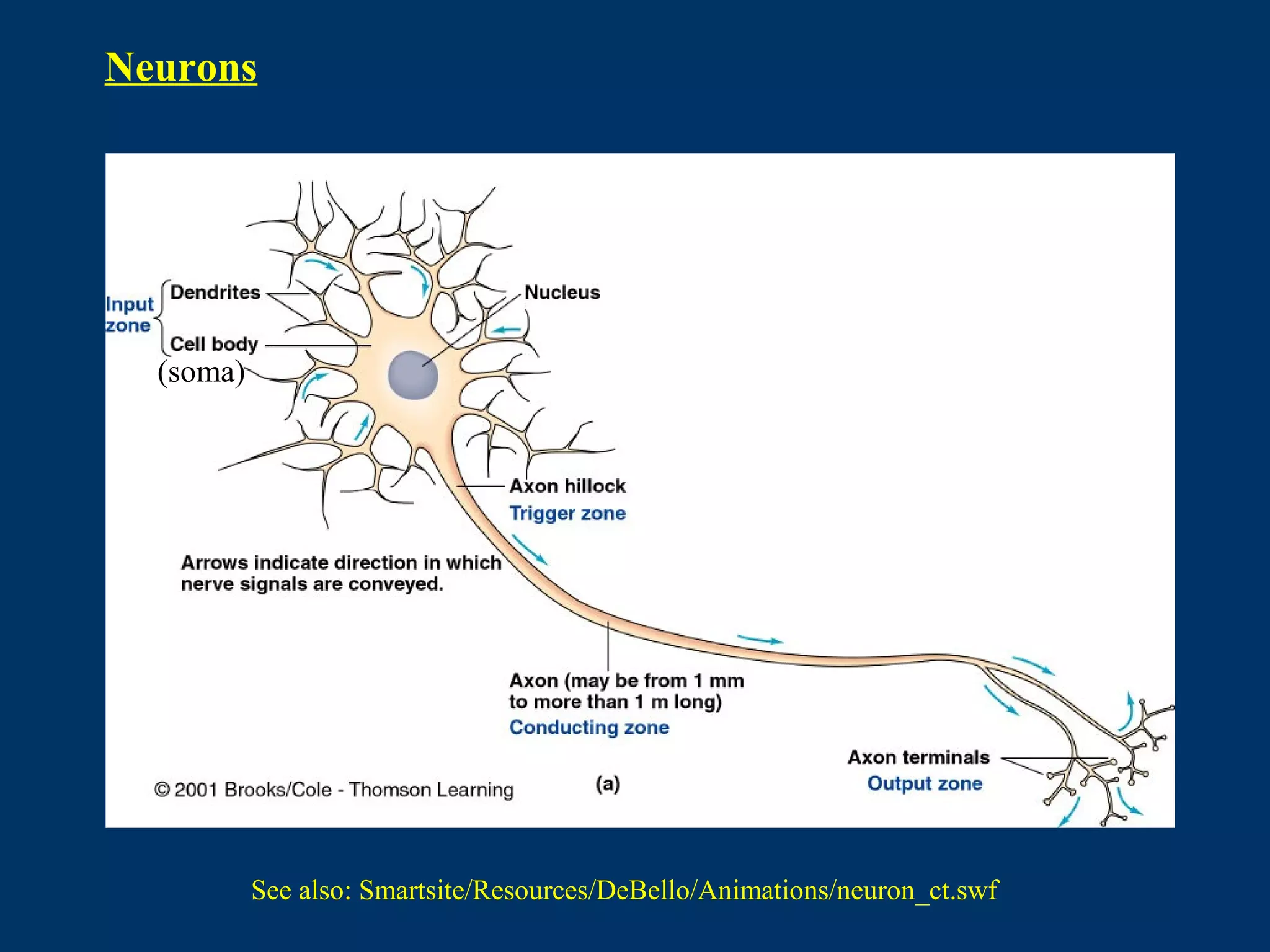
1. The document discusses facilitated diffusion, which is the transport of substances across a membrane with the aid of carrier proteins. It involves substances moving uphill against a concentration gradient, with the carrier protein having a fixed affinity for the substance and ATP being used to flip the orientation or change the affinity of the binding site.
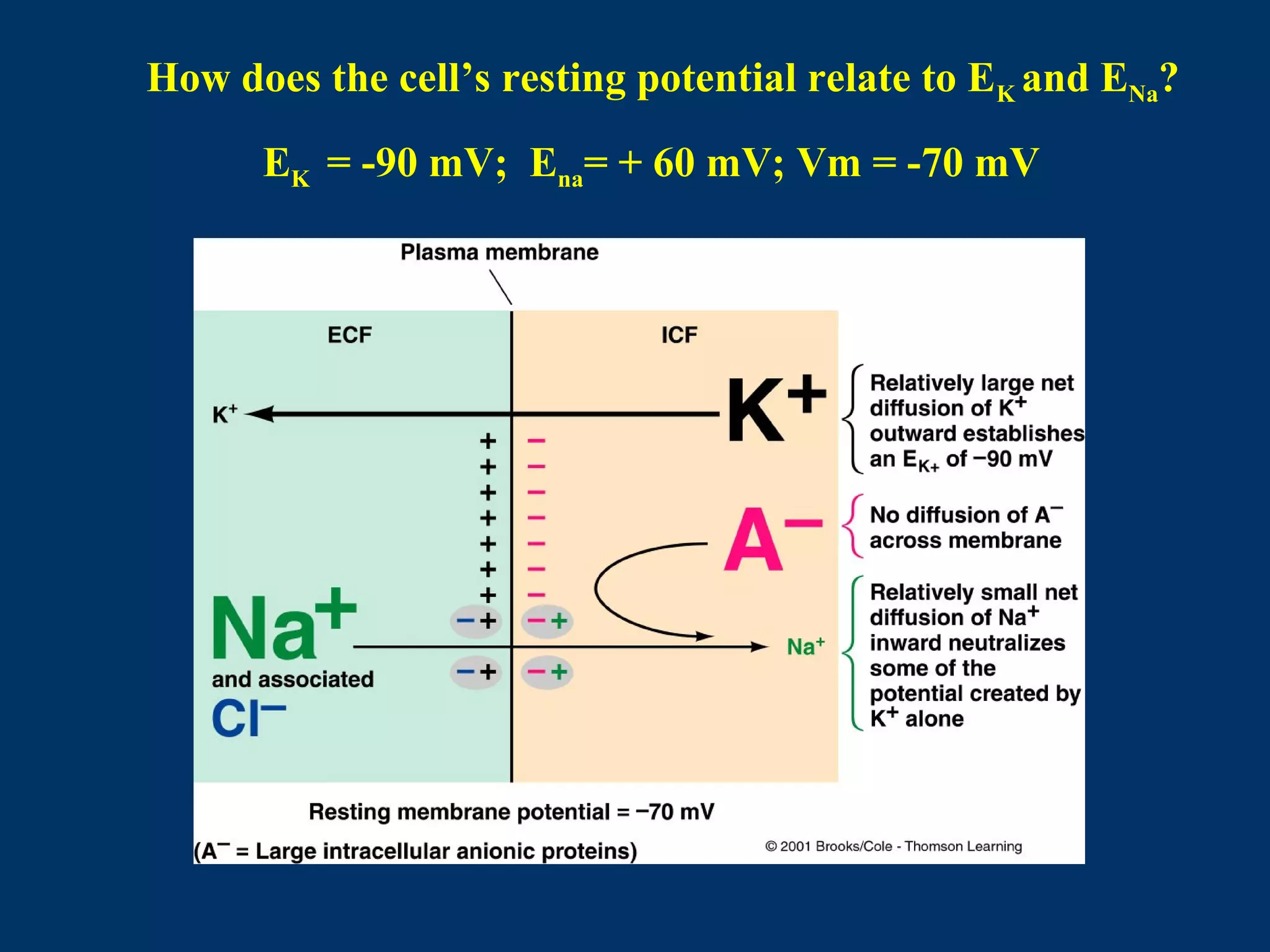
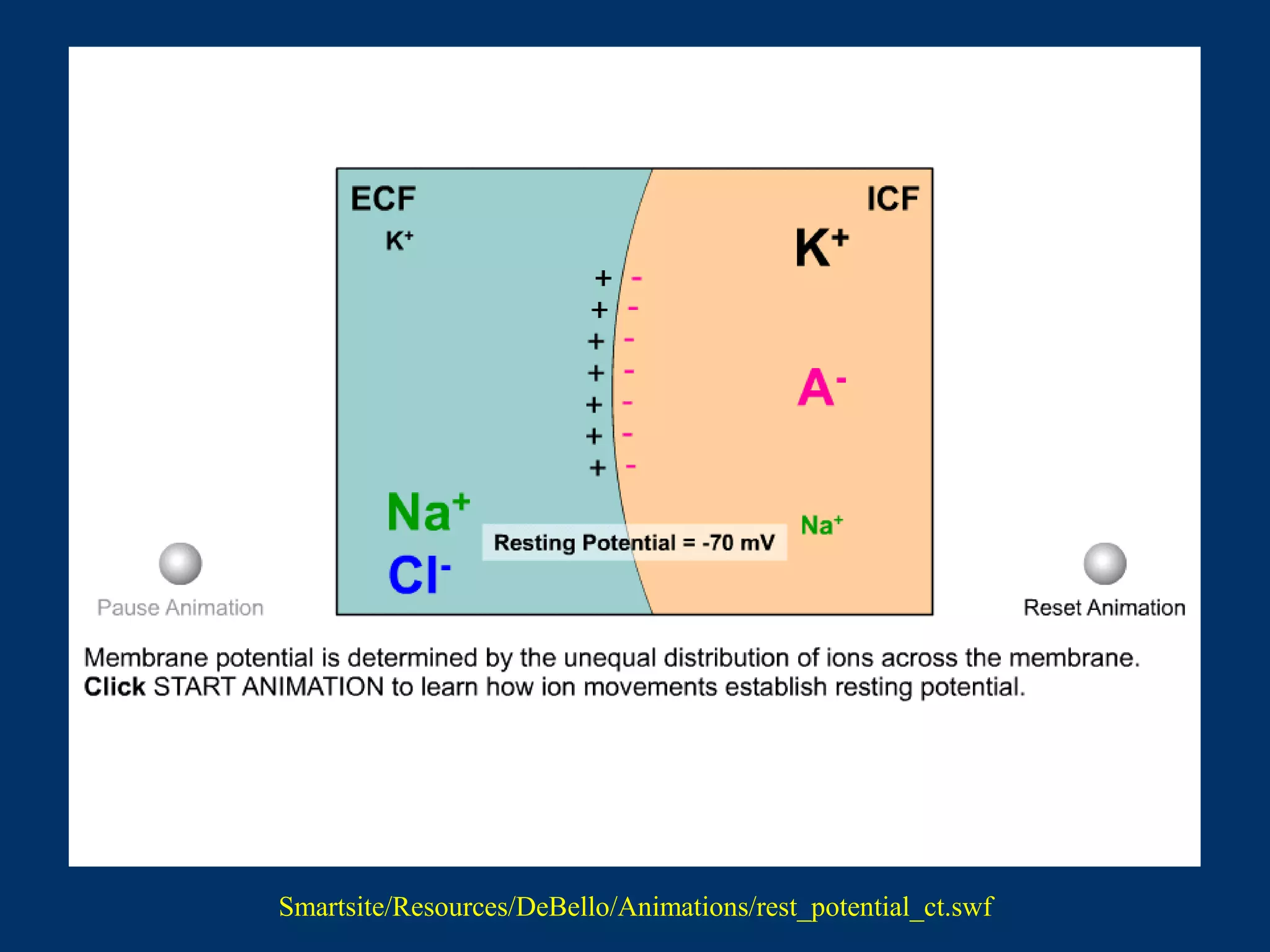
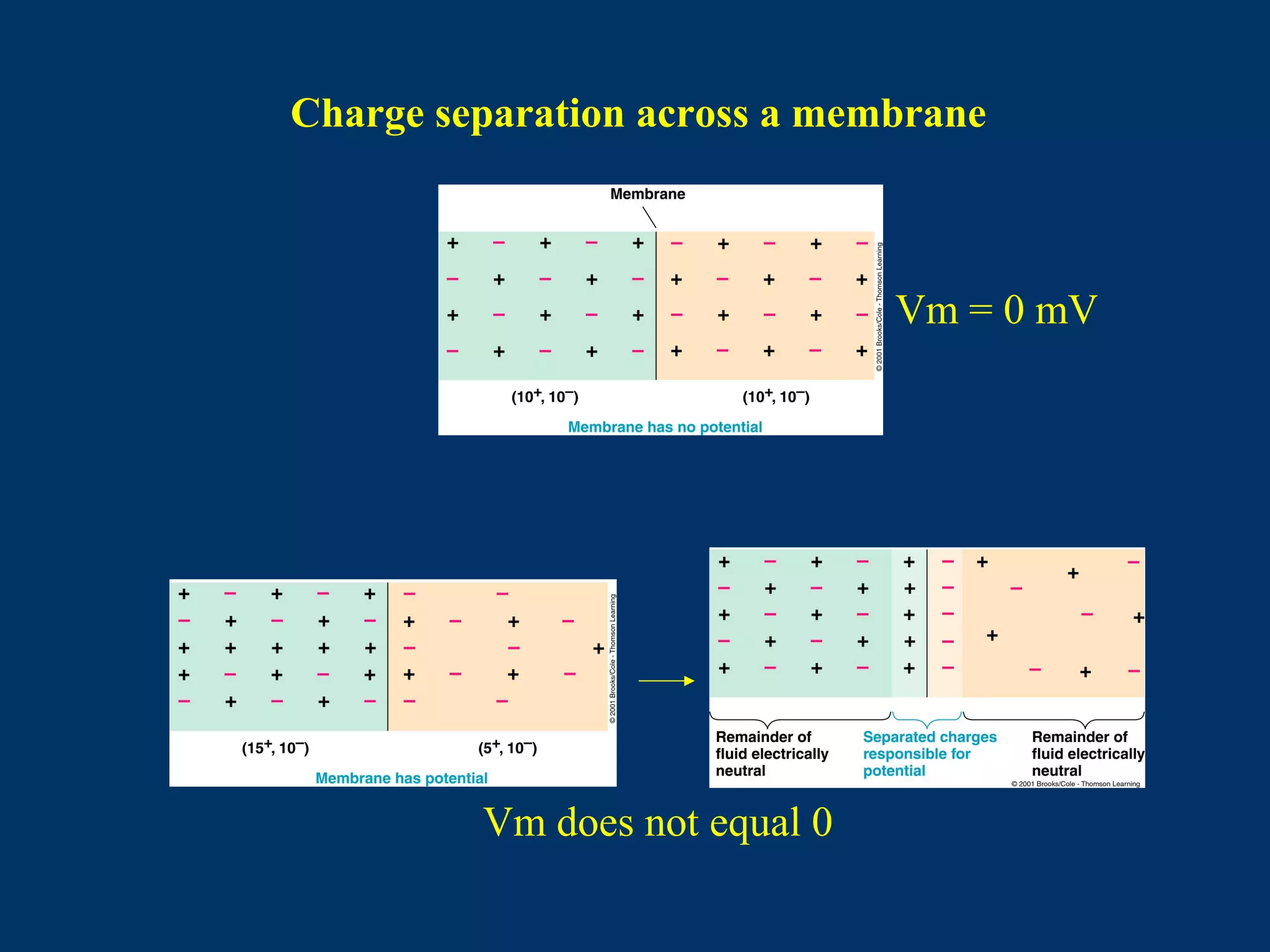
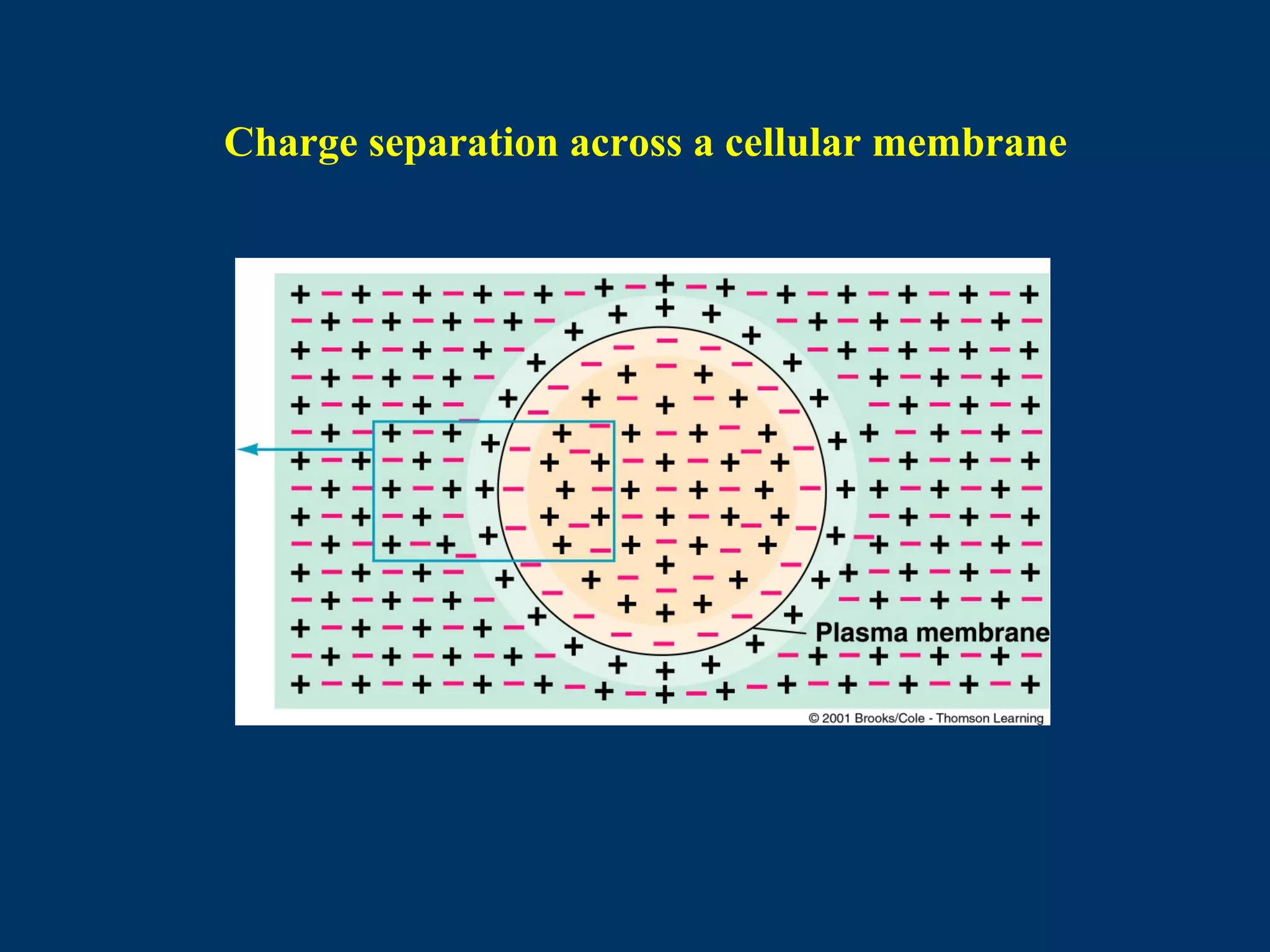
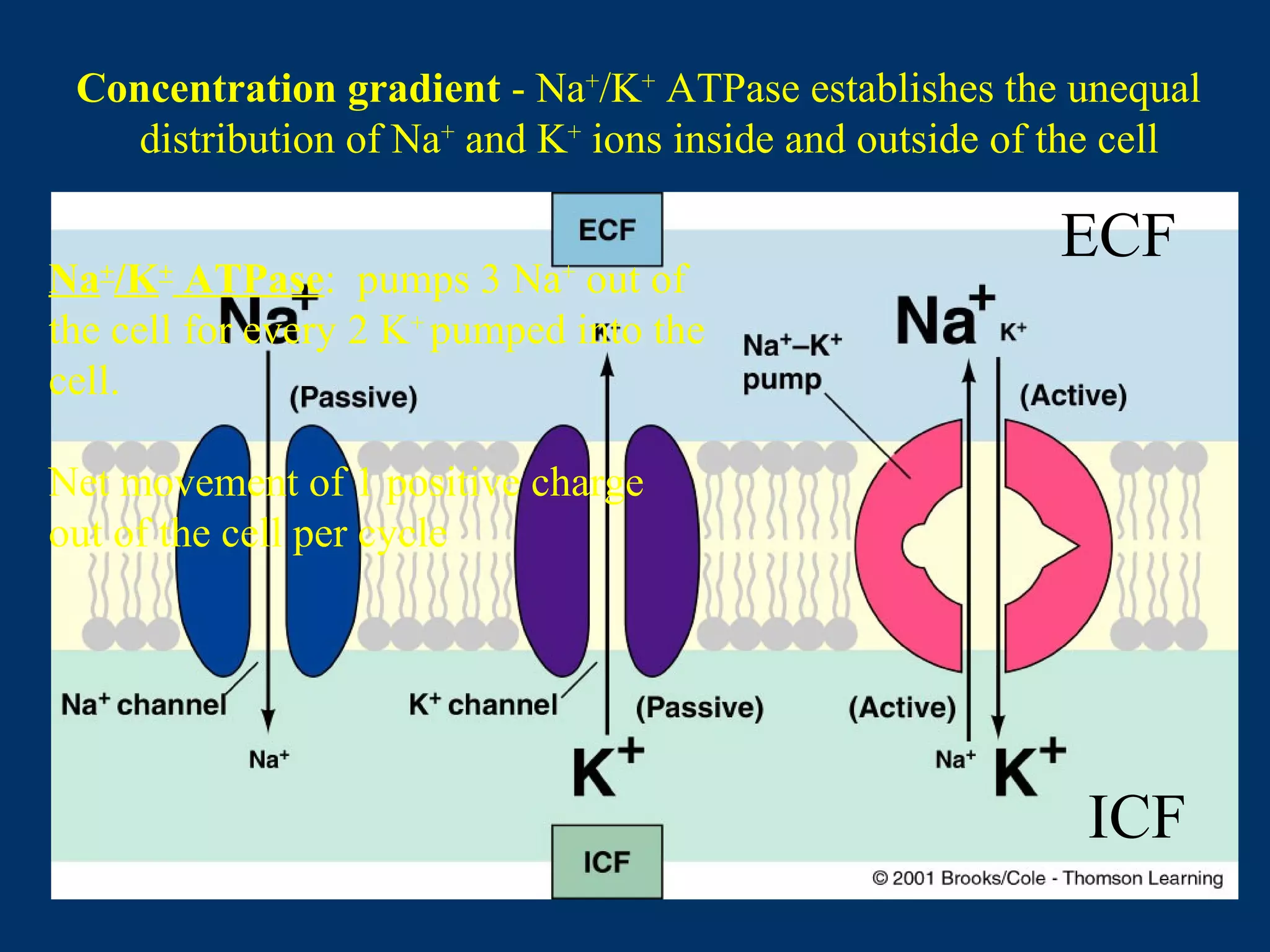
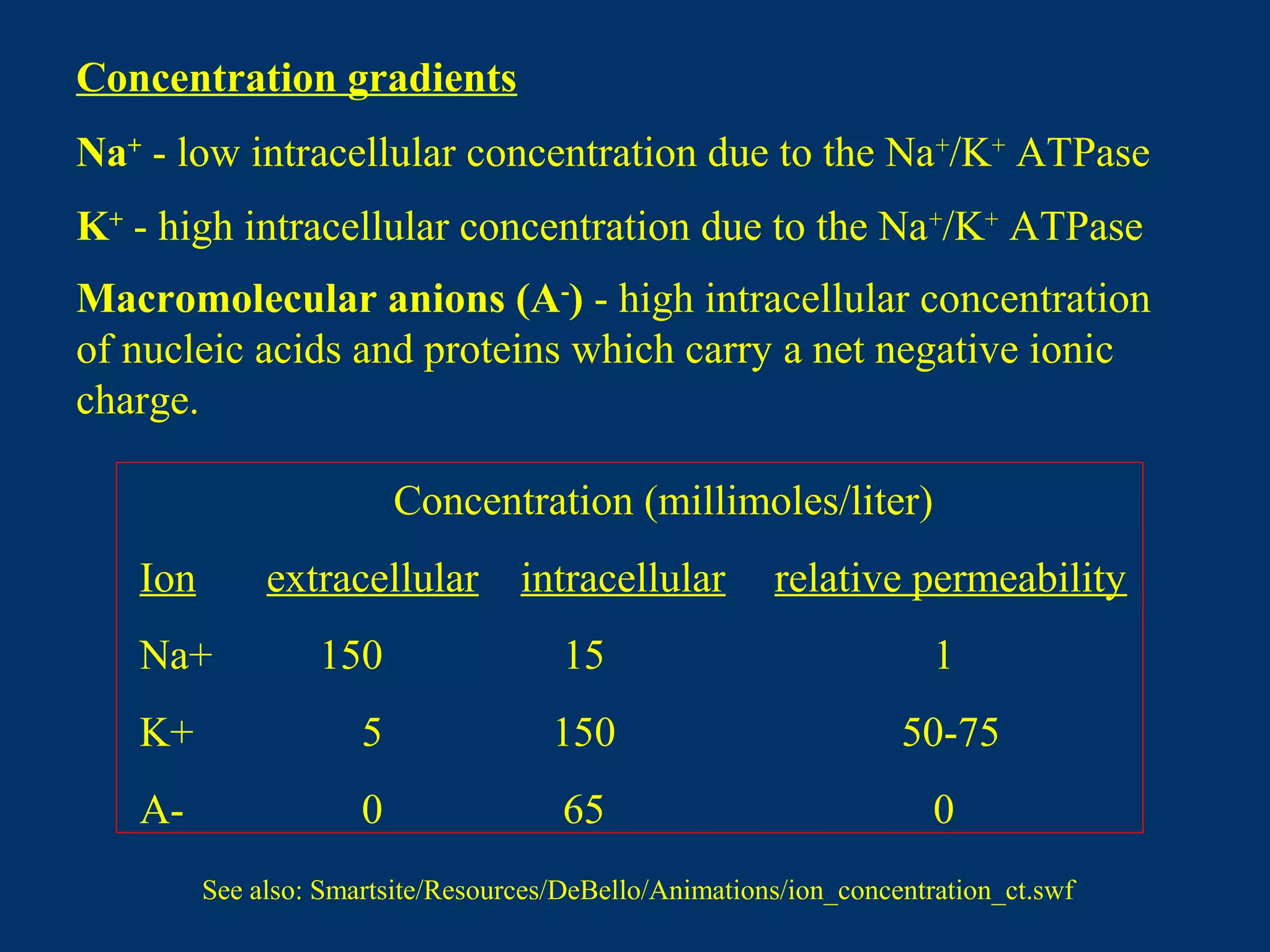
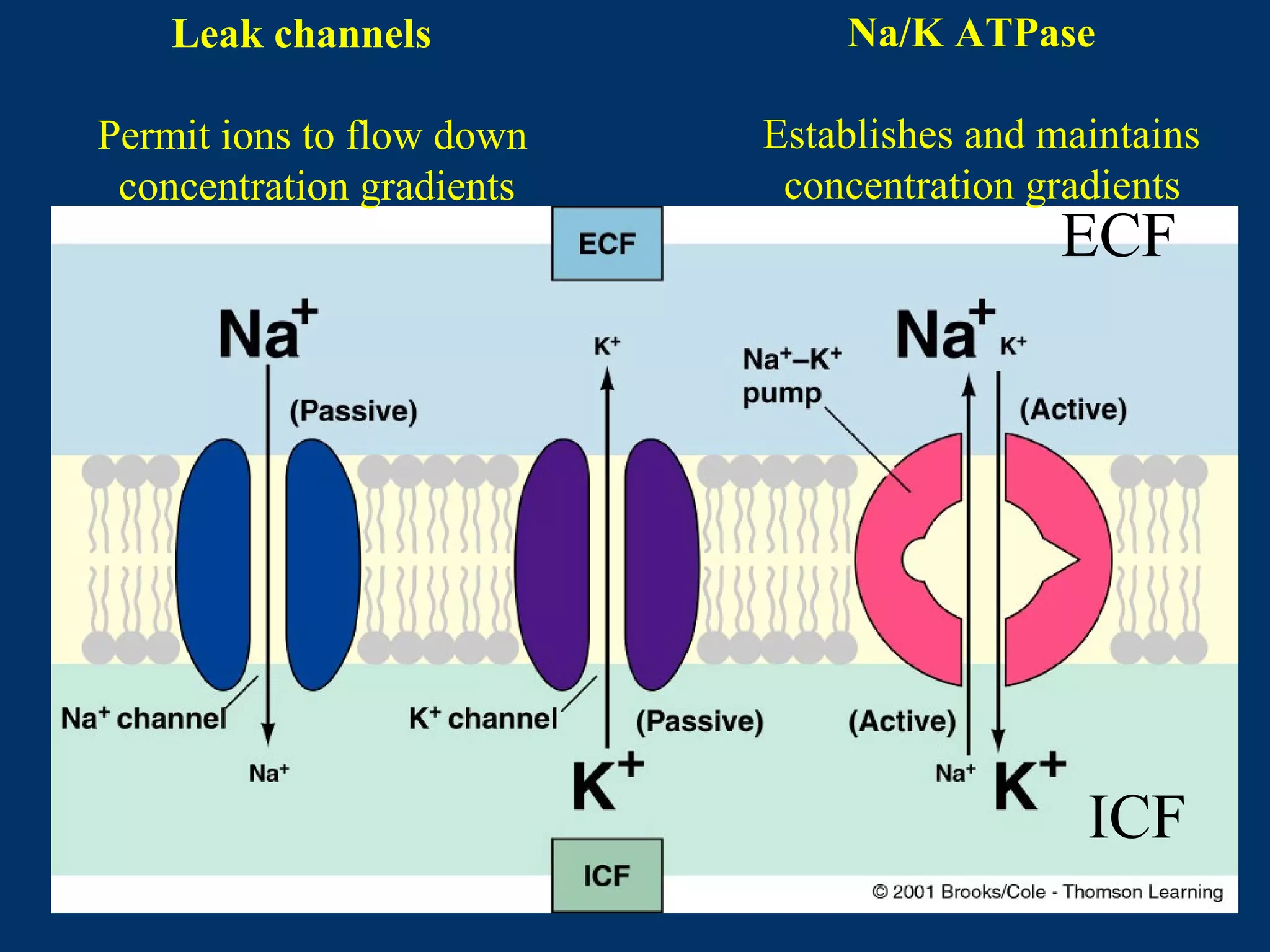
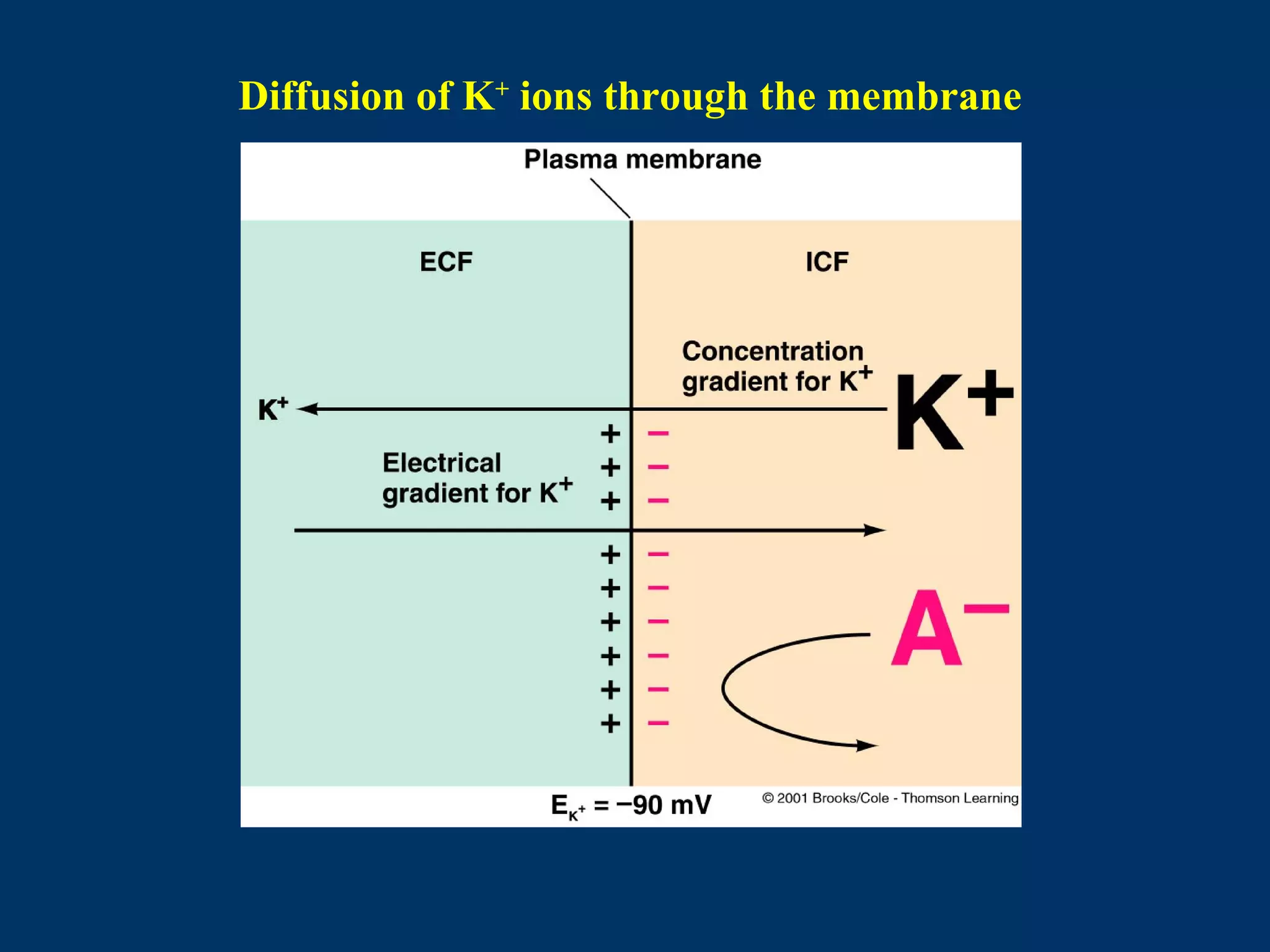
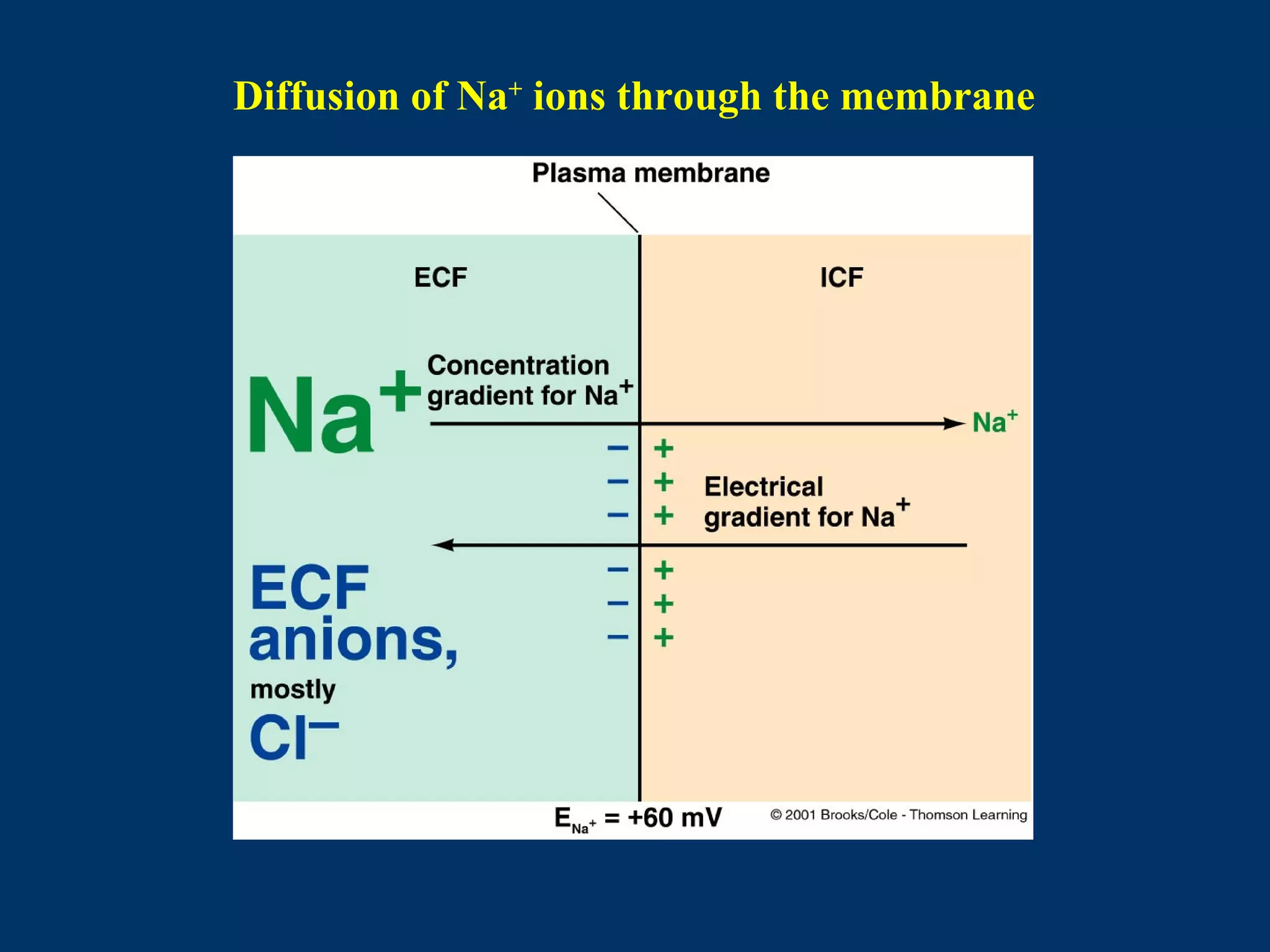
2. It then covers the resting membrane potential, how cells create charge separation across the membrane by establishing ion concentration gradients and allowing diffusion through leak channels, and how this results in a membrane potential. Key ions involved are sodium, potassium, and macromolecular anions.
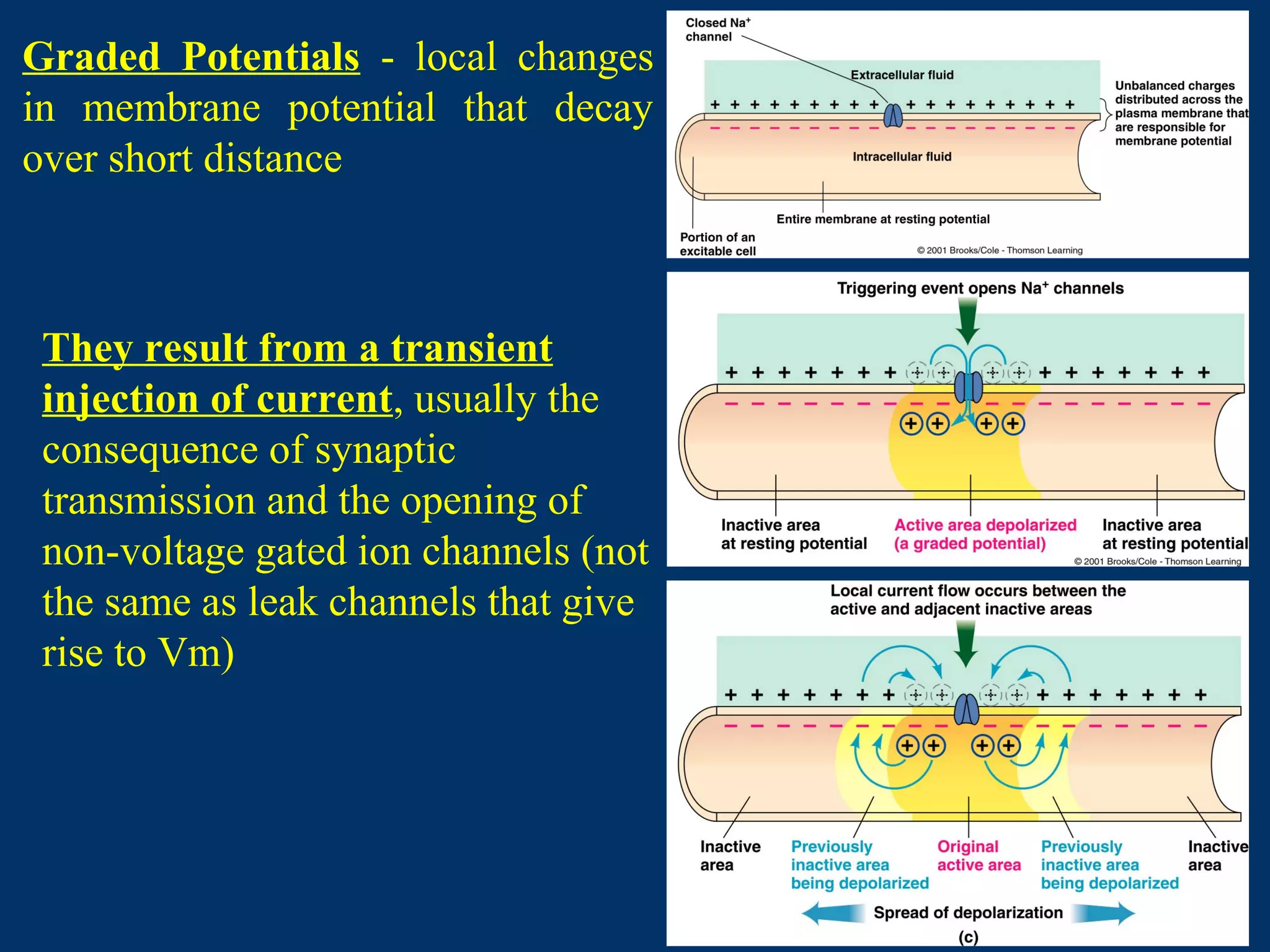
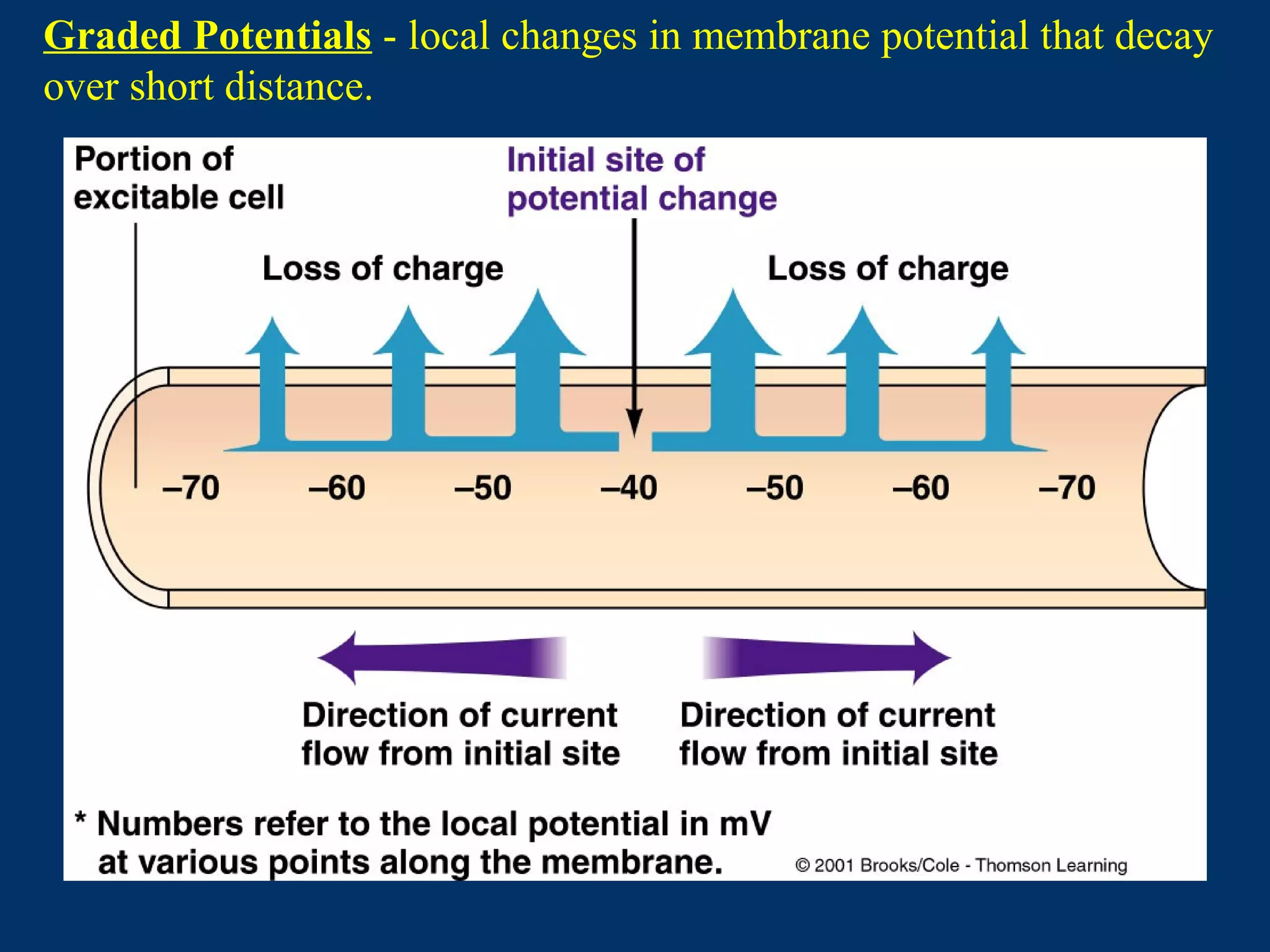
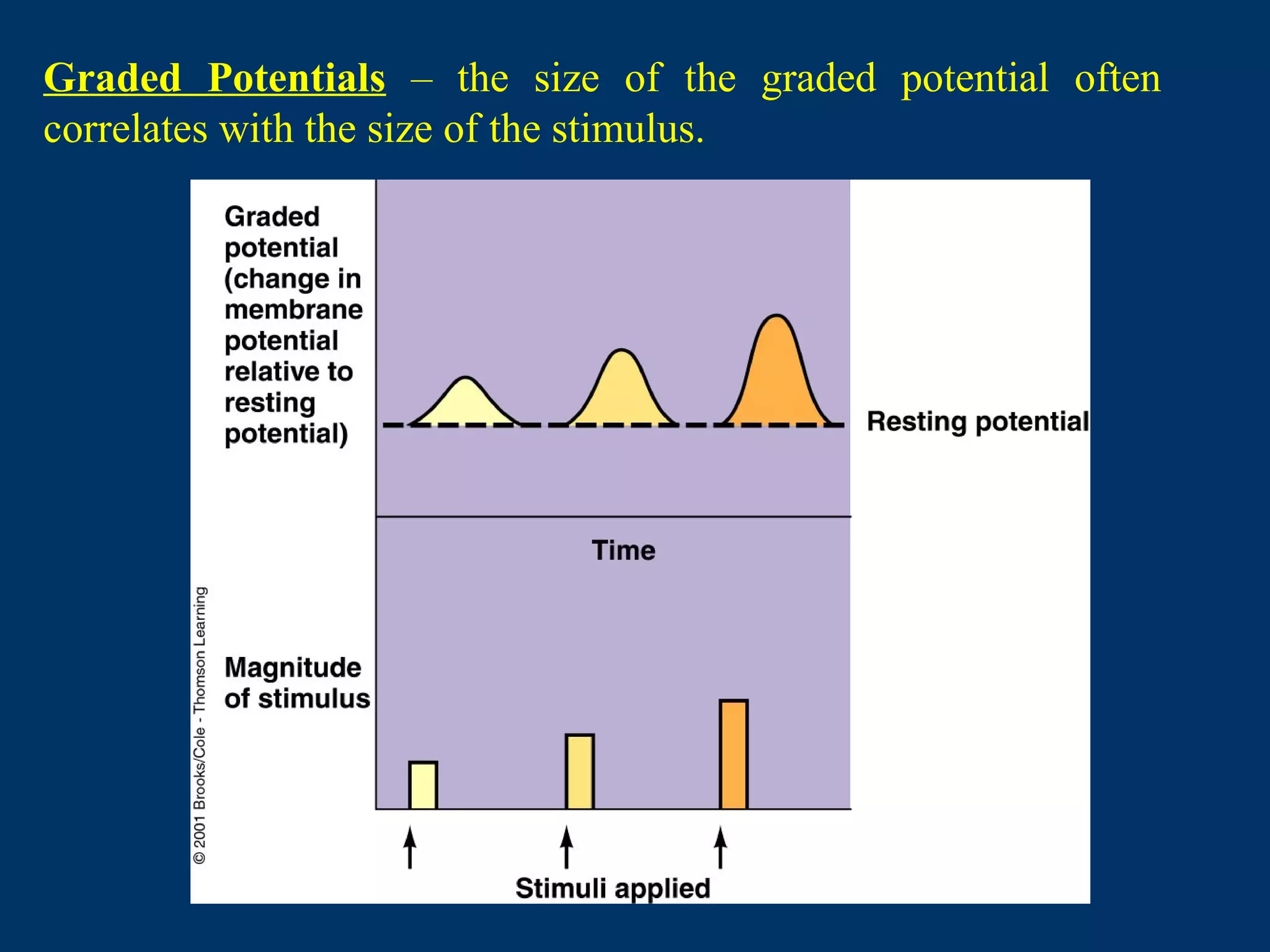
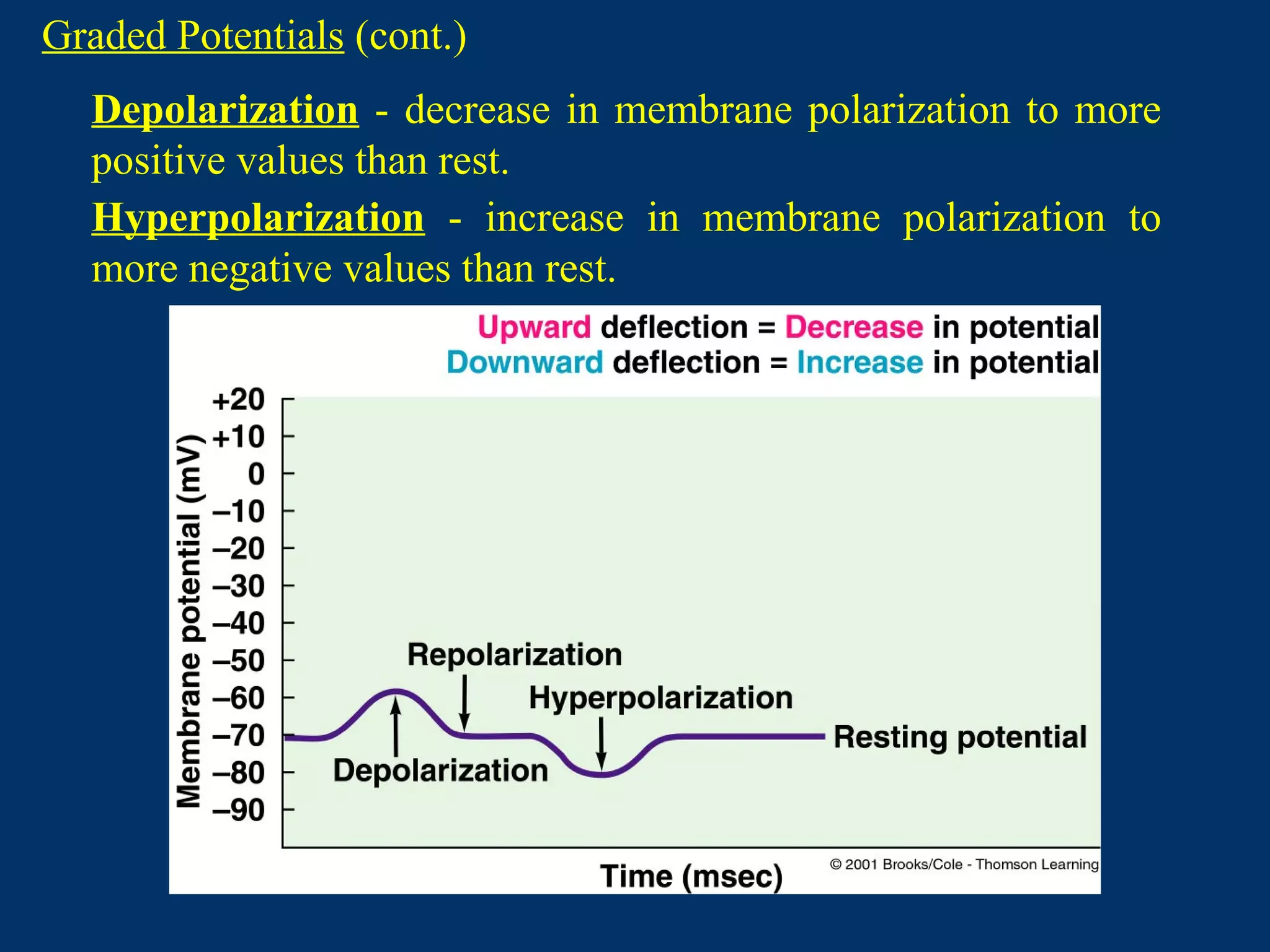
3. It defines graded potentials as local changes in membrane potential caused by transient opening of non-voltage gated ion channels that






![Nernst equation - equation describing the equilibrium potential for
a particular ion (i)
Ei = RT/zF ln [i]o/[i]i = 61/z log [i]o/[i]i
where R is the gas constant, T is the temperature in degrees Kelvin,
z is the valence of the ionic species, and F is the Faraday constant.
Thus, the equilibrium potential for K+
is:
EK = 61 log (5/150) = - 90 mV
the equilibrium potential for Na+ is:
ENa = 61 log (150/15) = + 60 mV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-150111170514-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture4-14-2048.jpg)