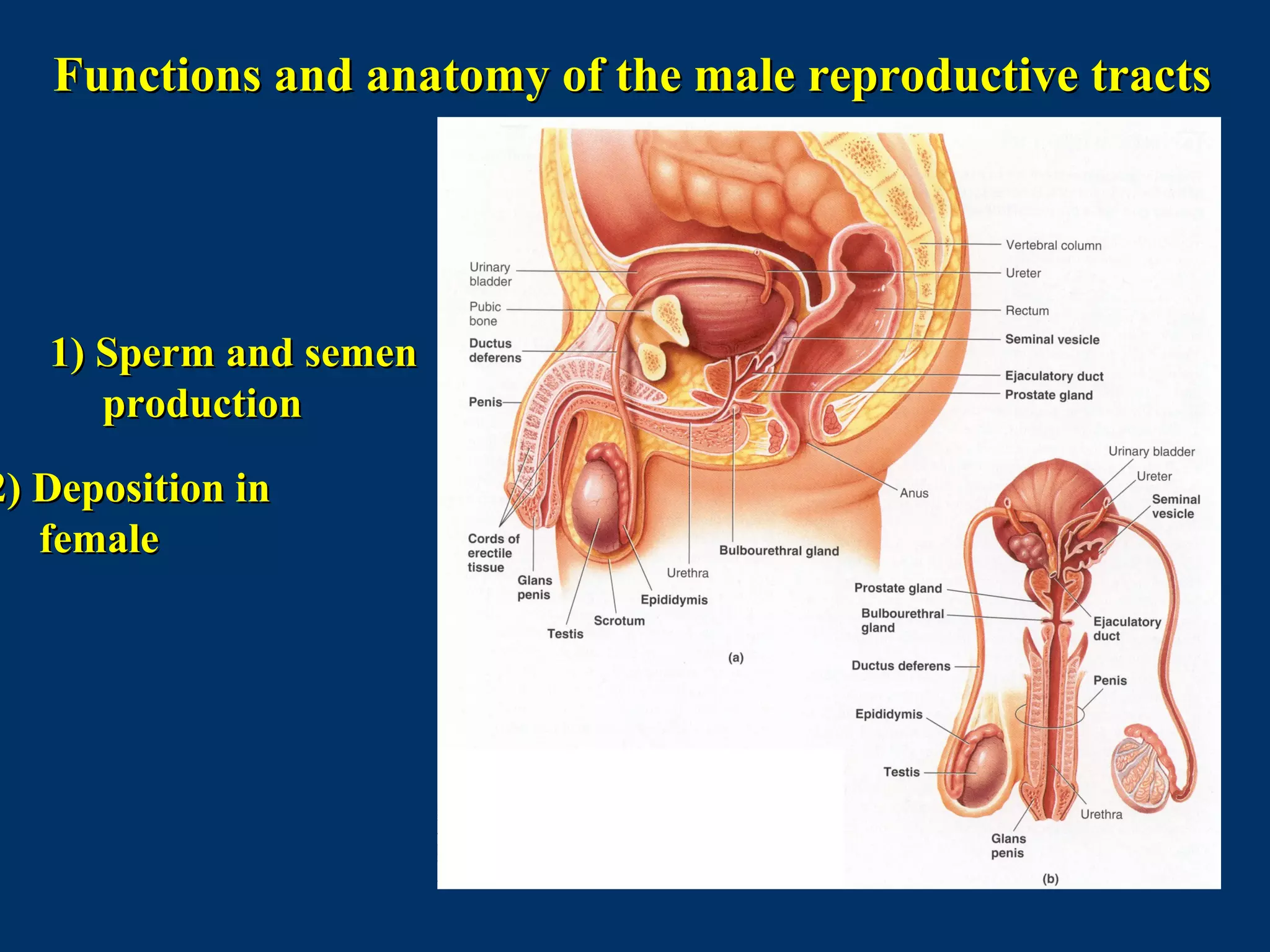
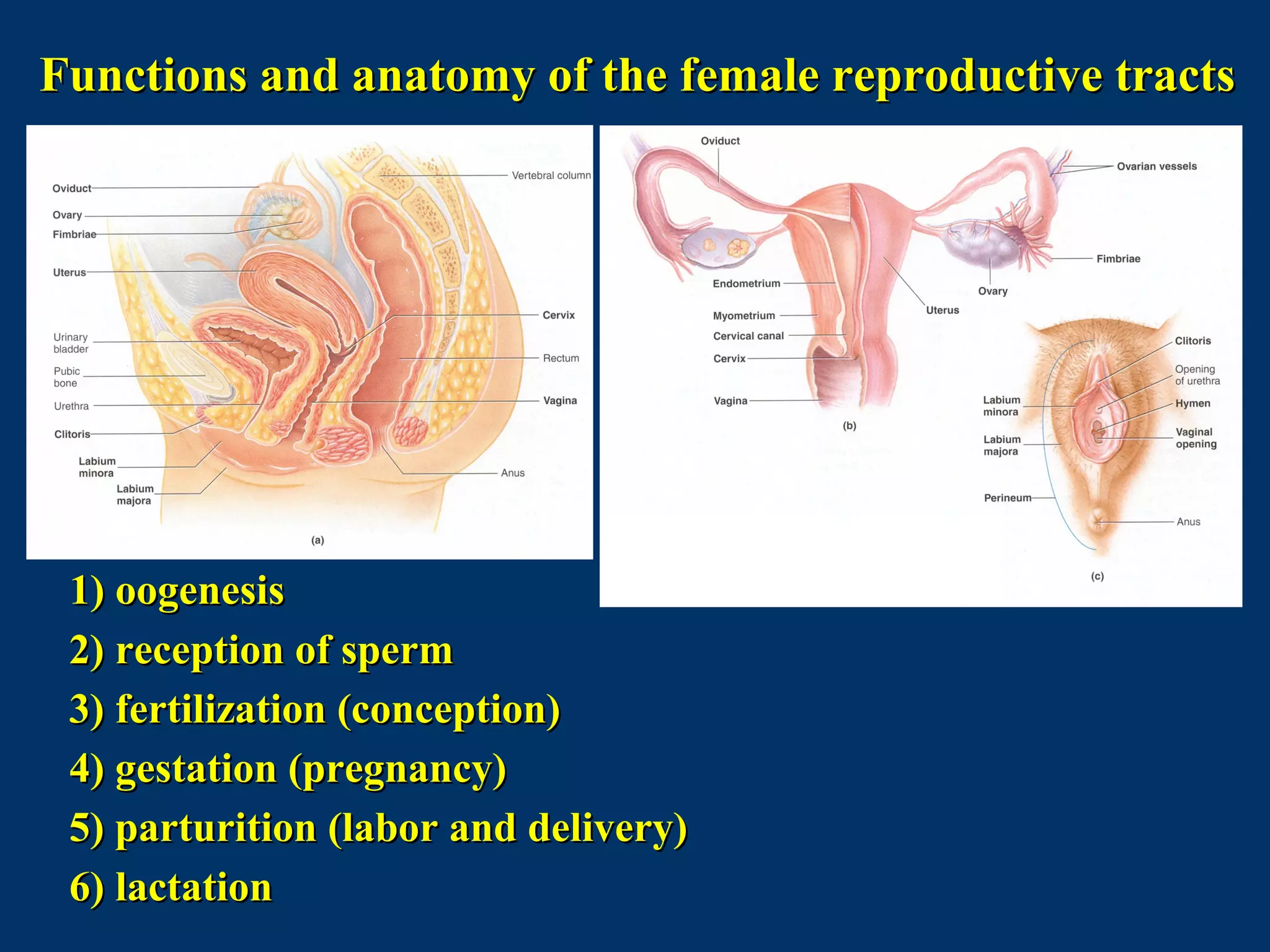
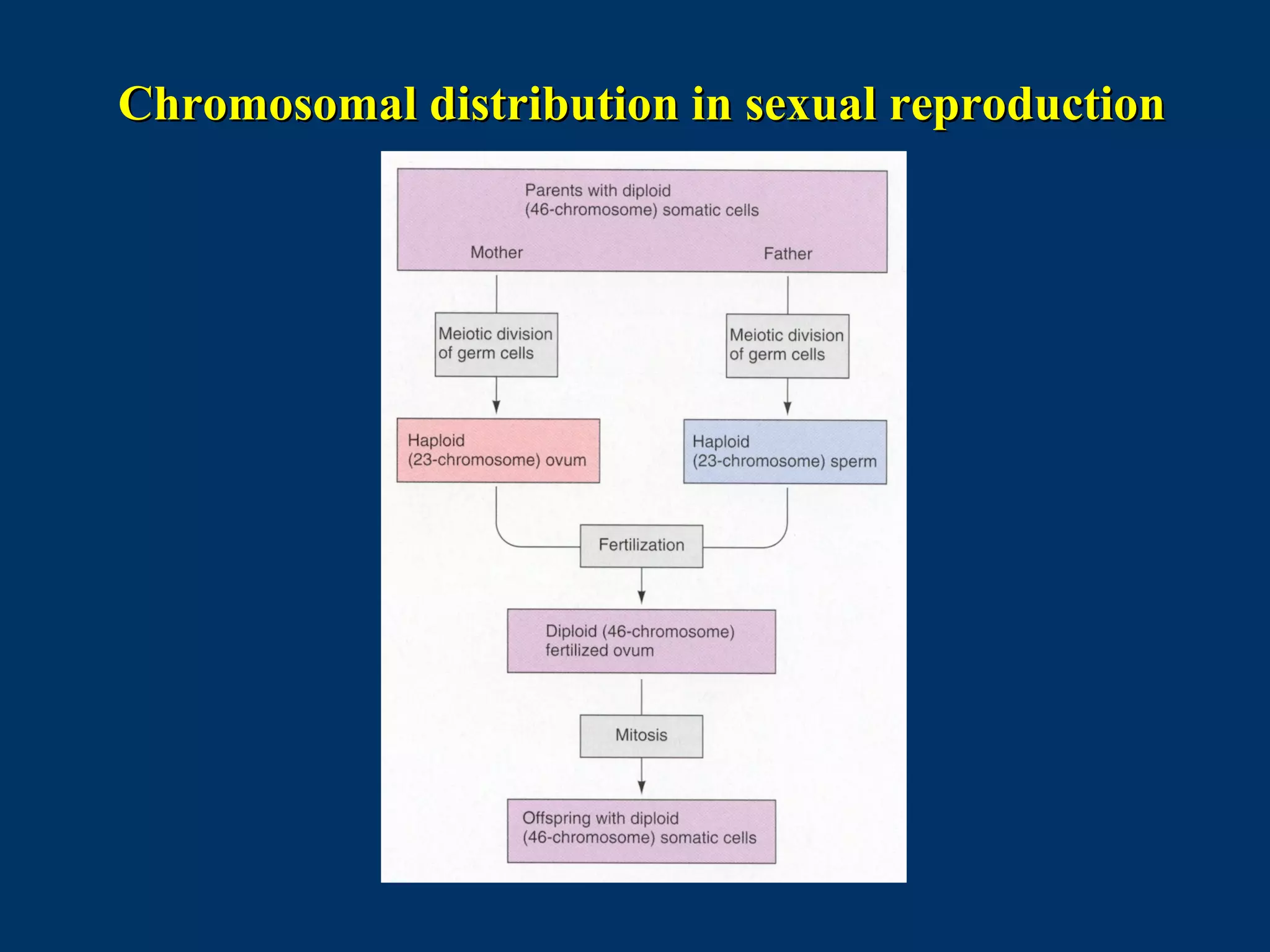
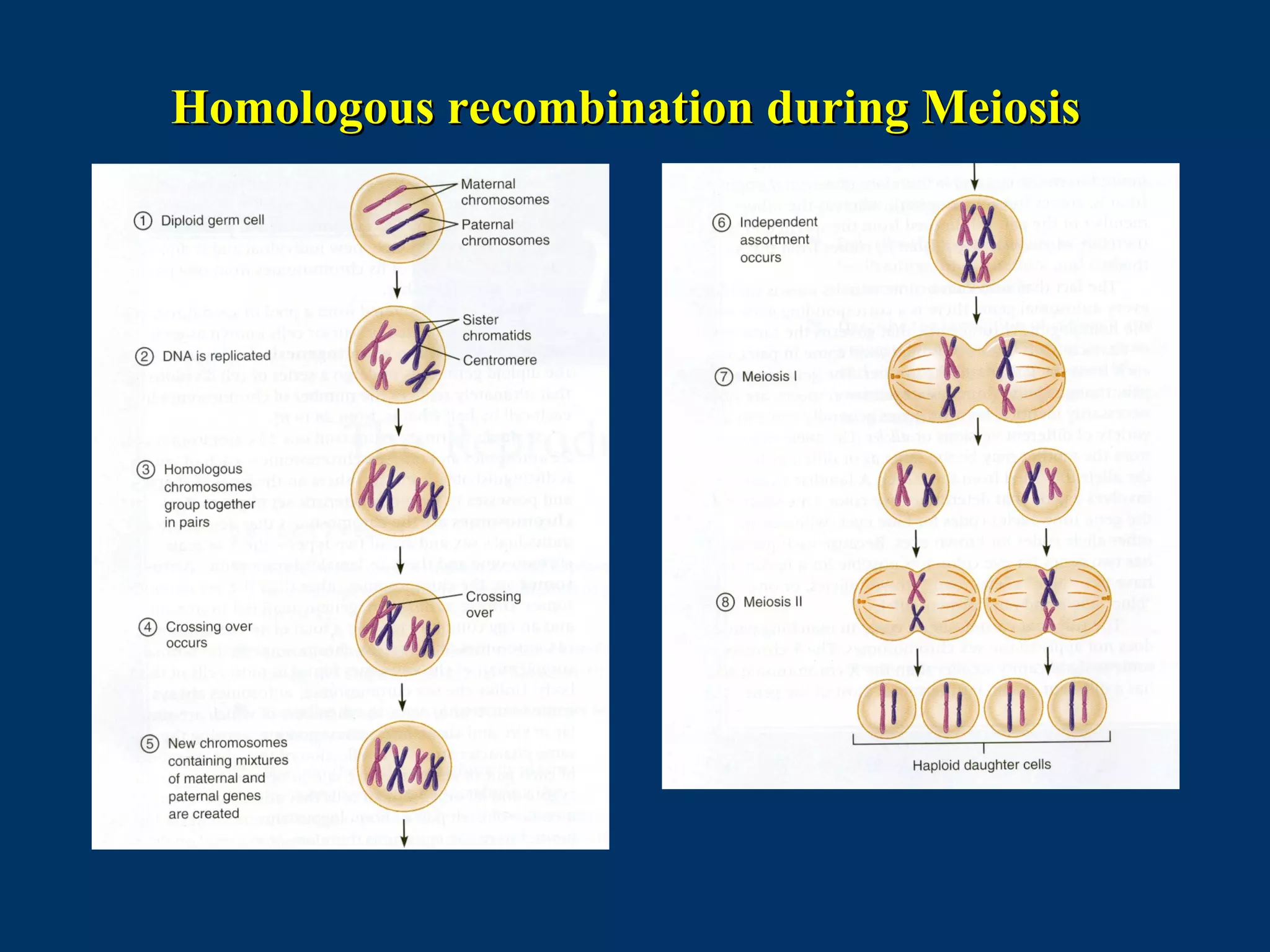
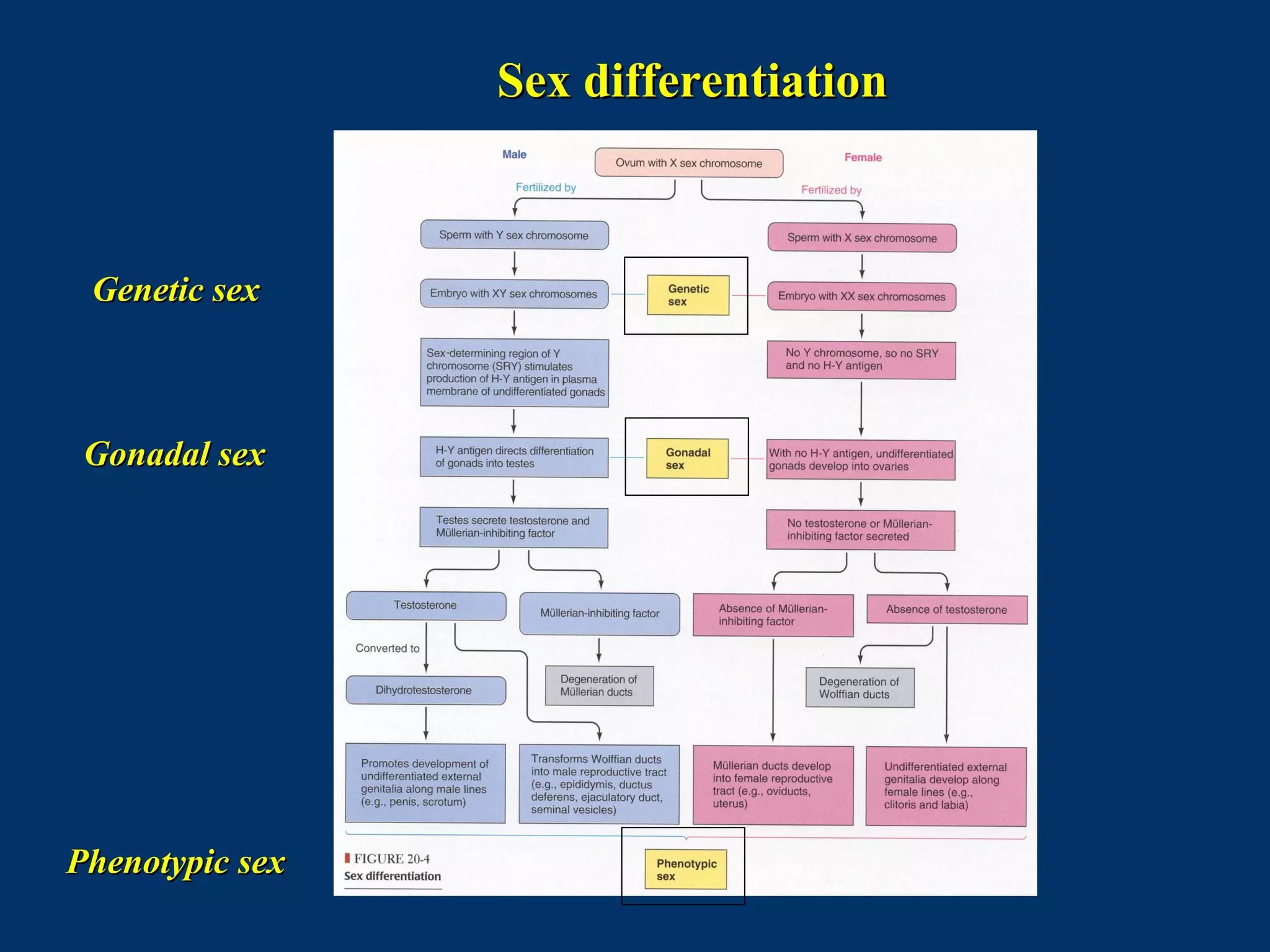
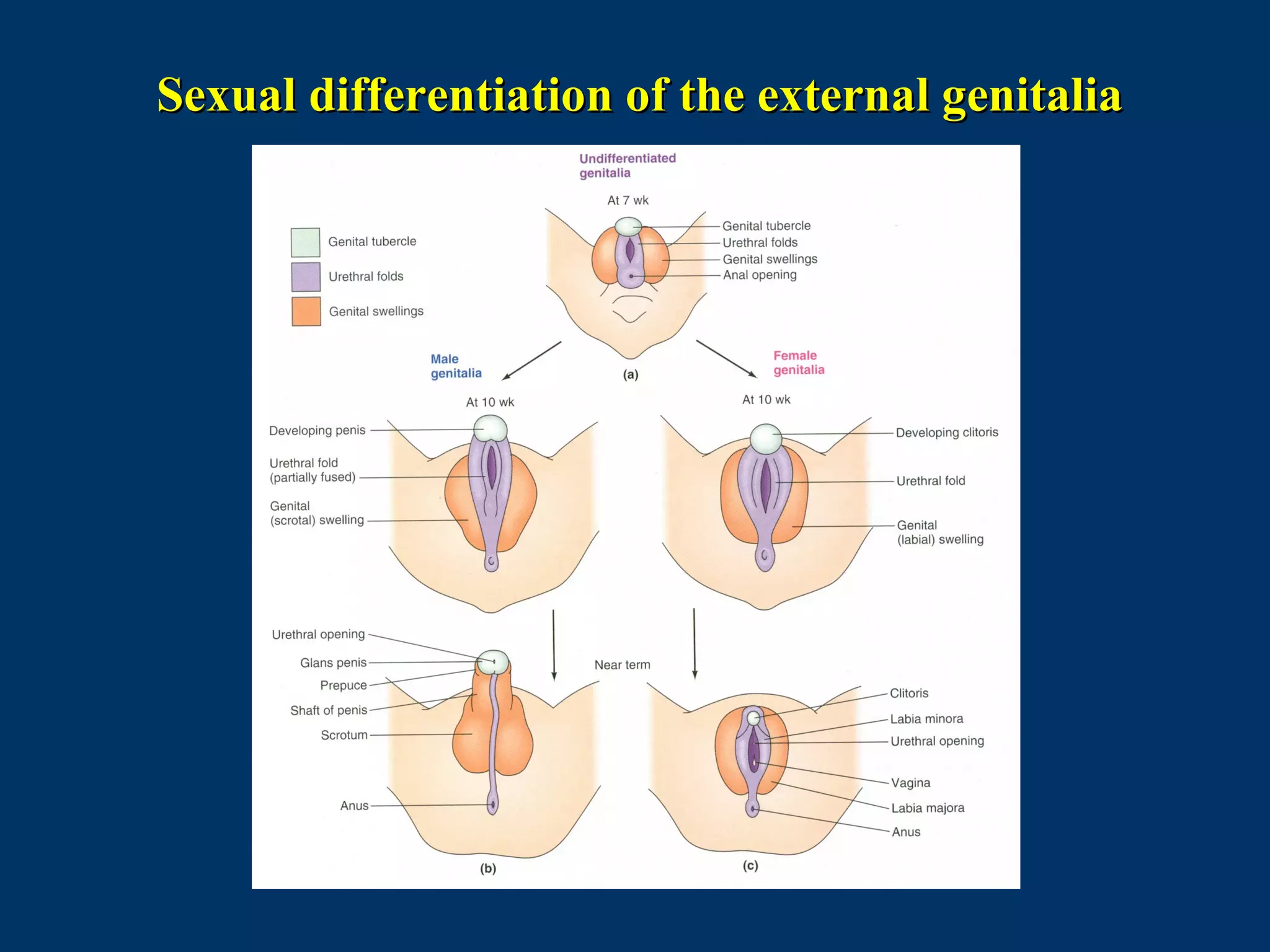
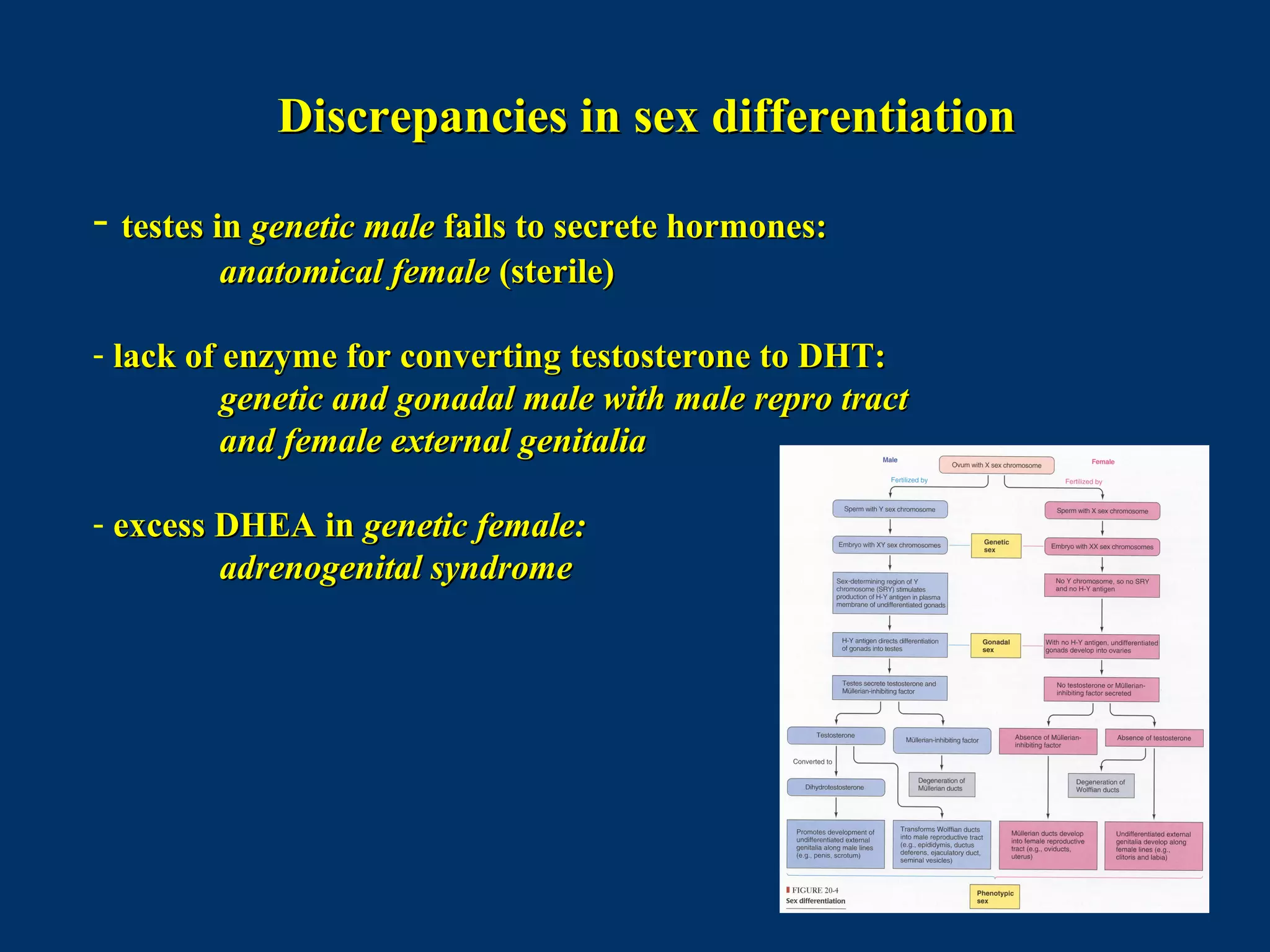
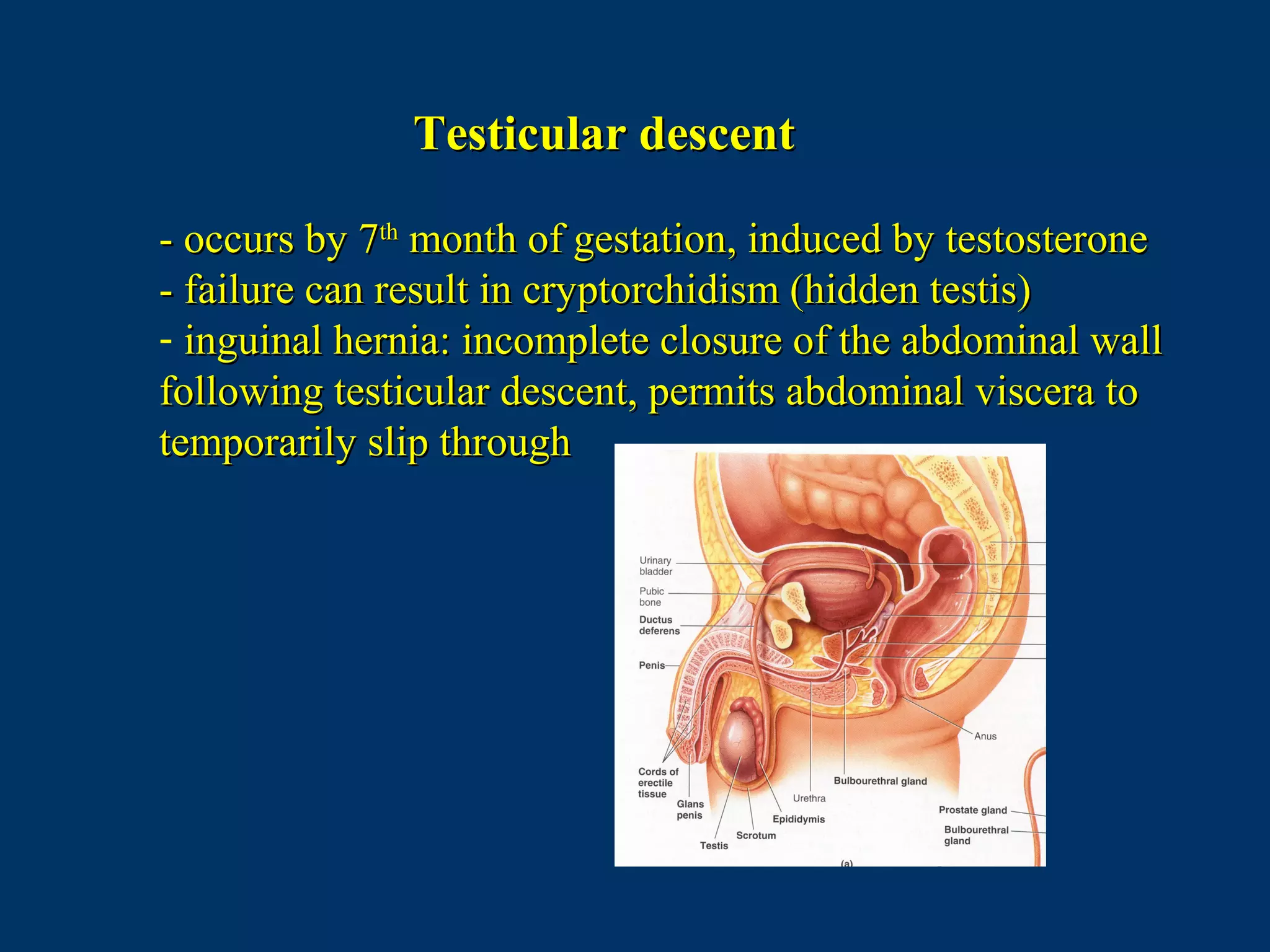
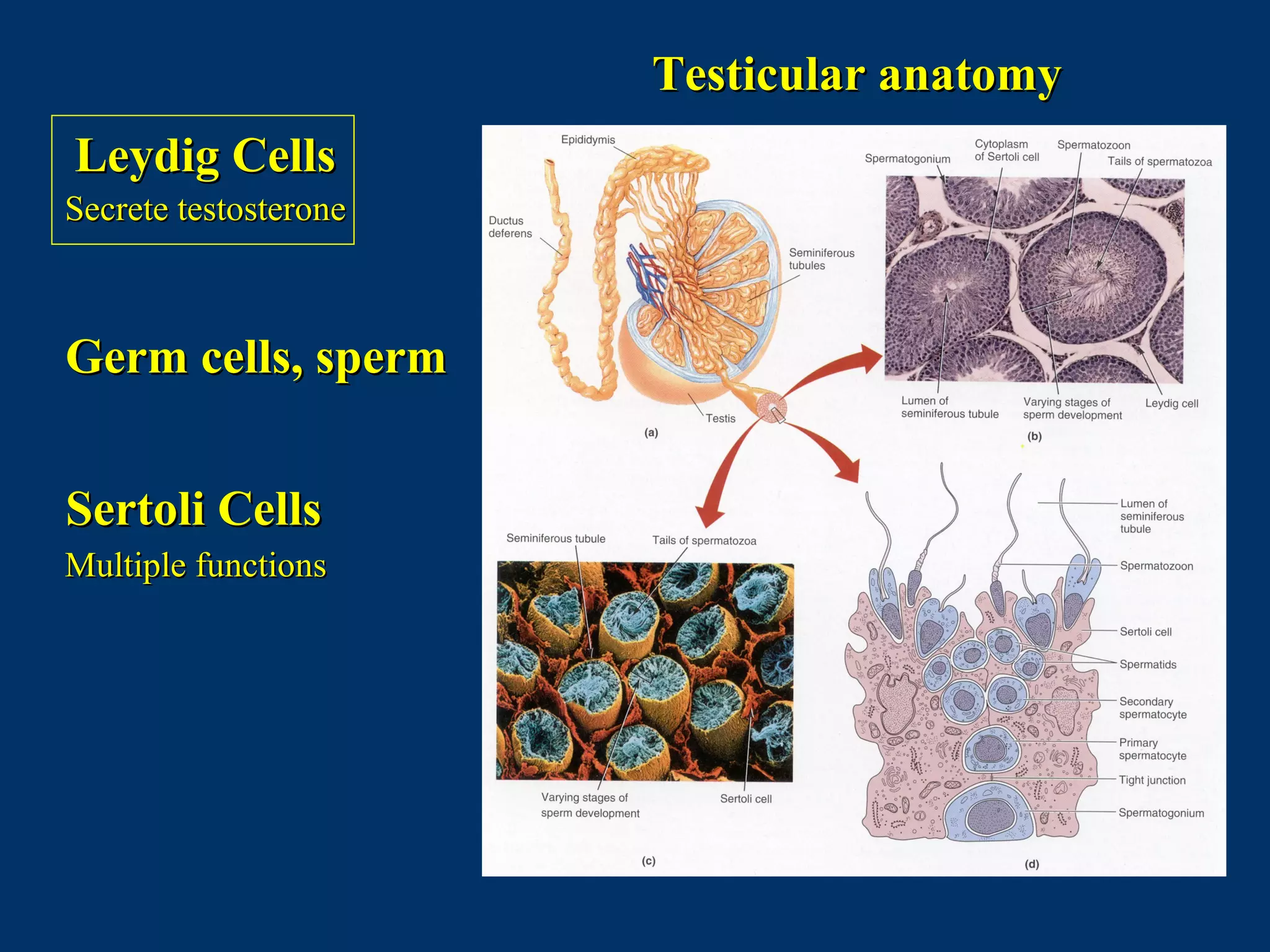
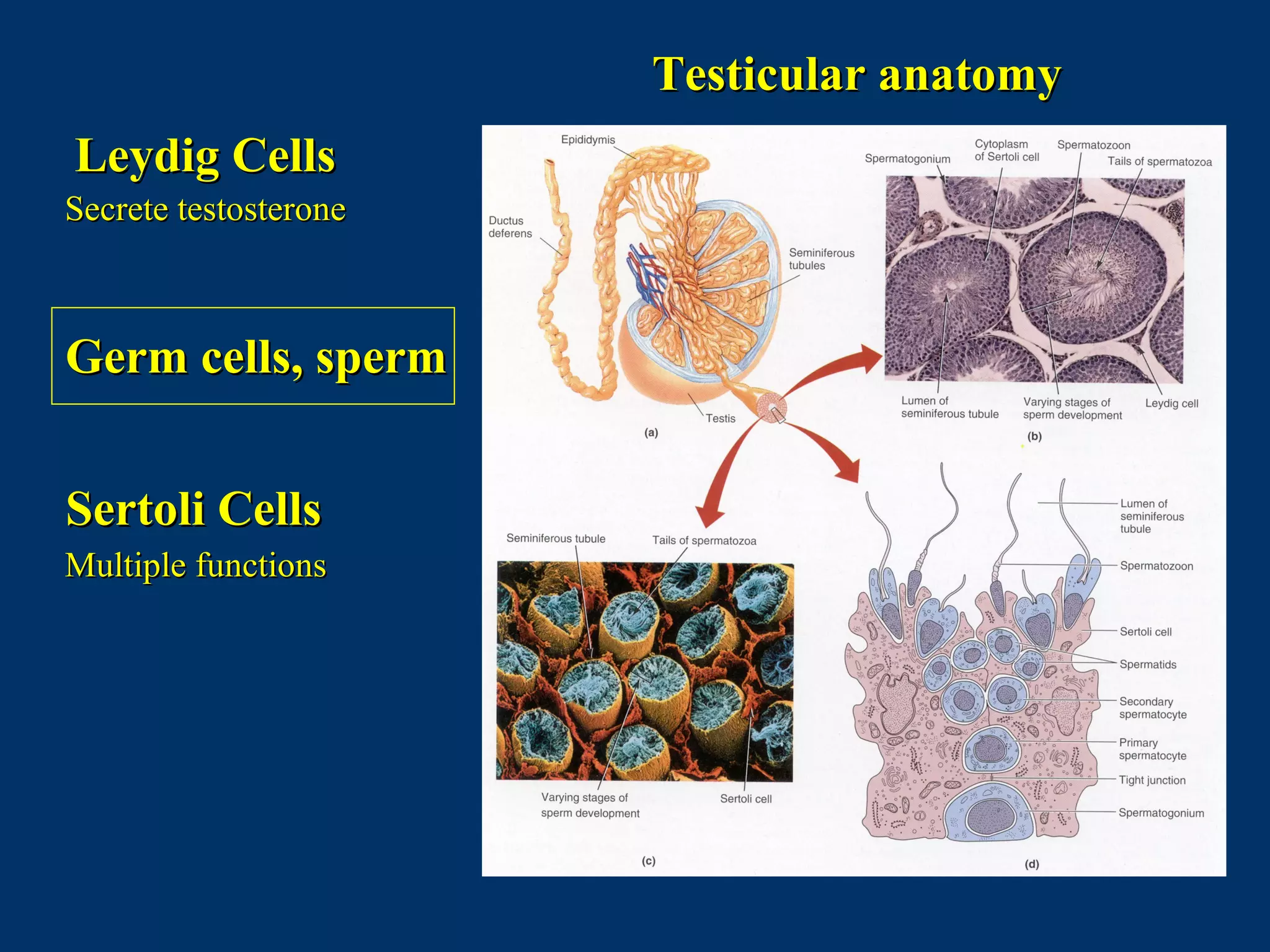
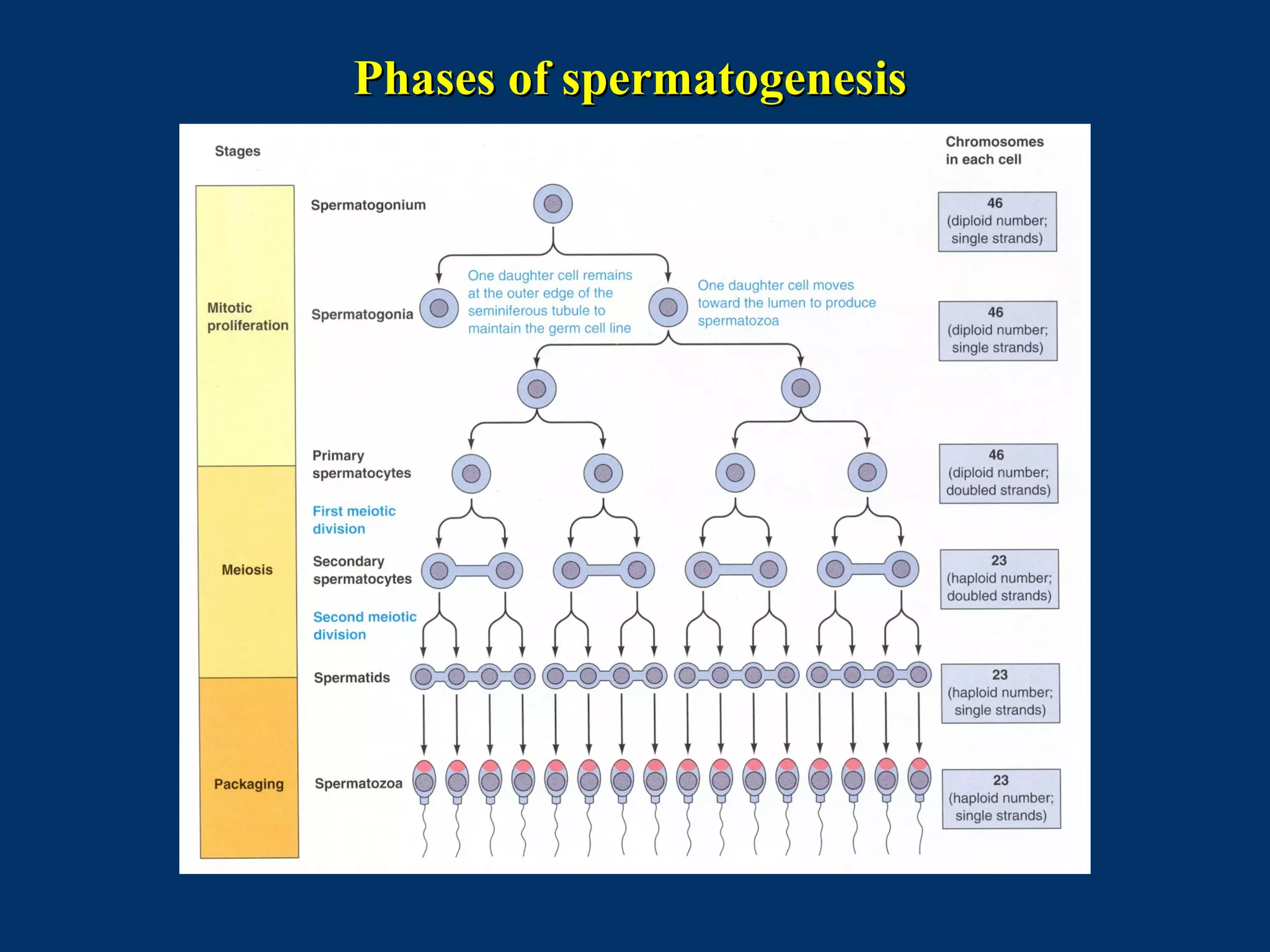
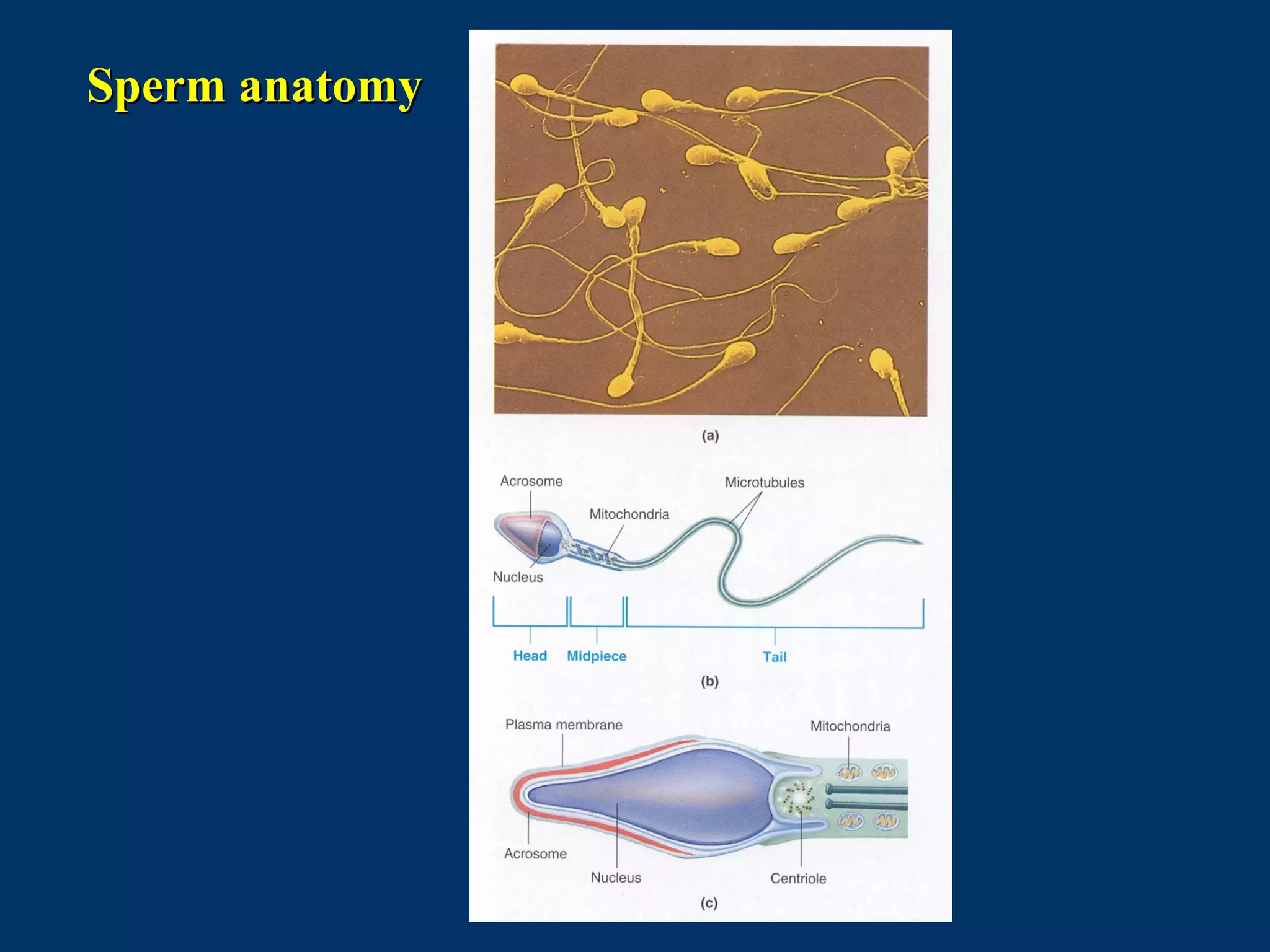
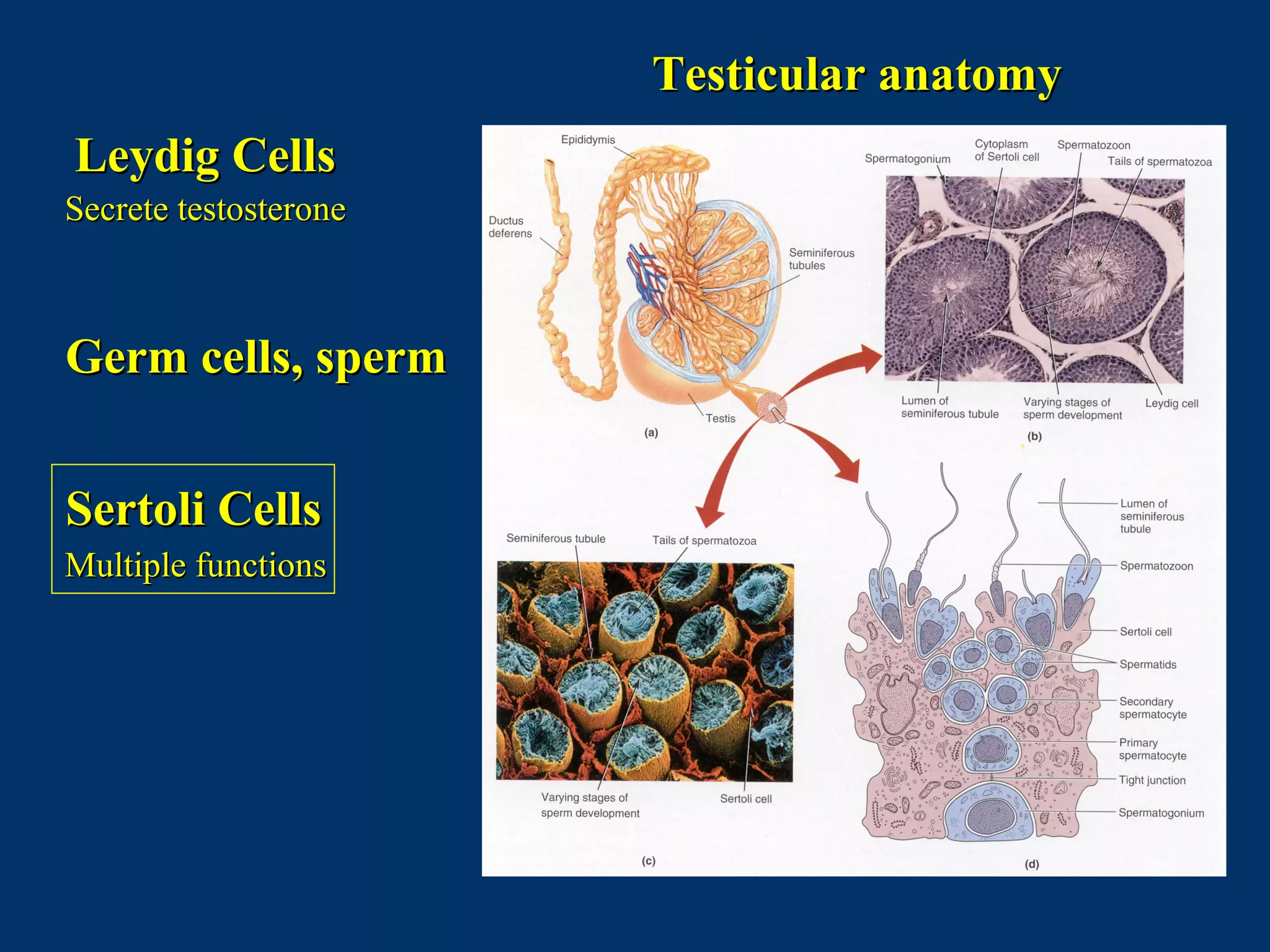
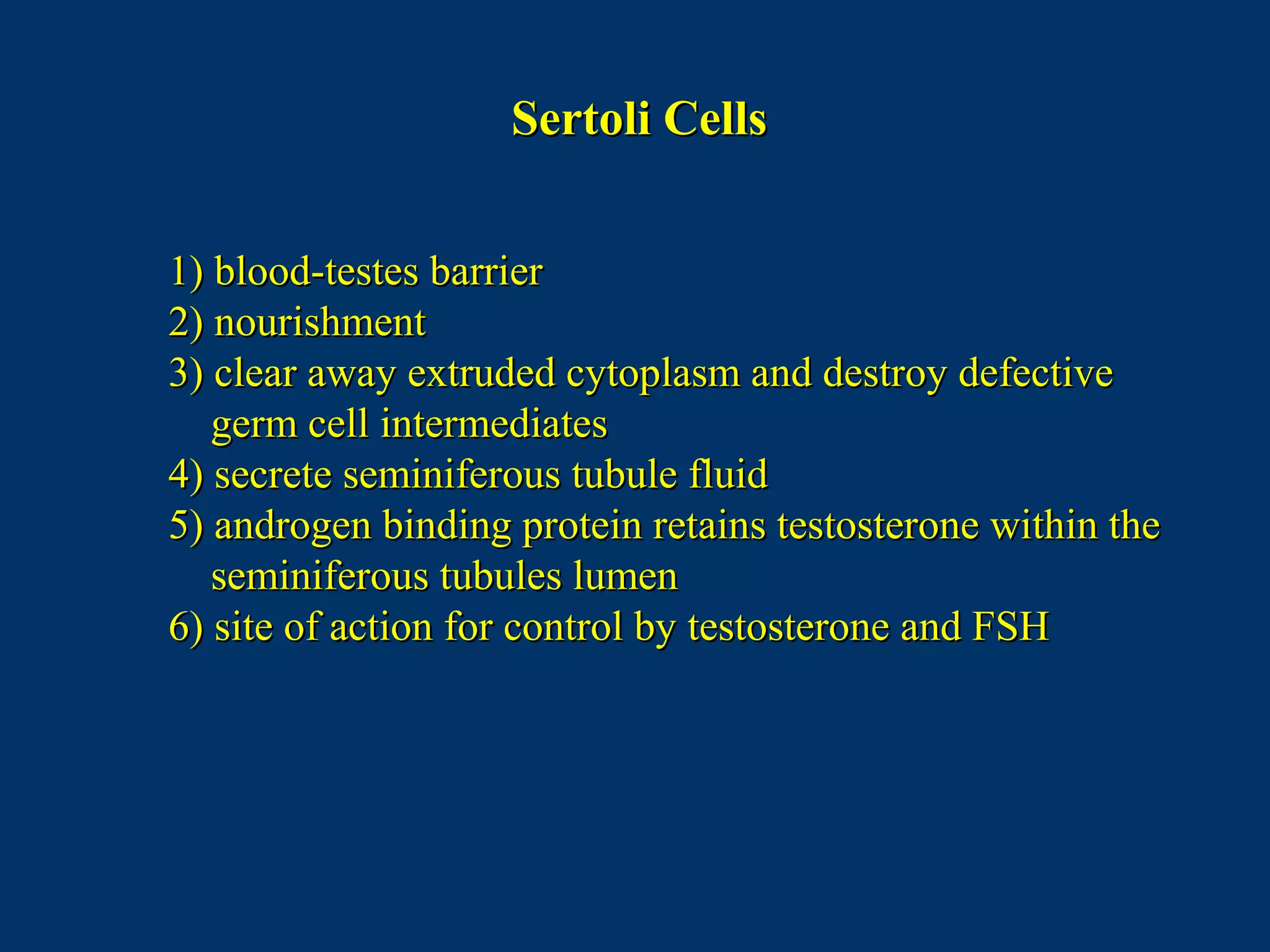
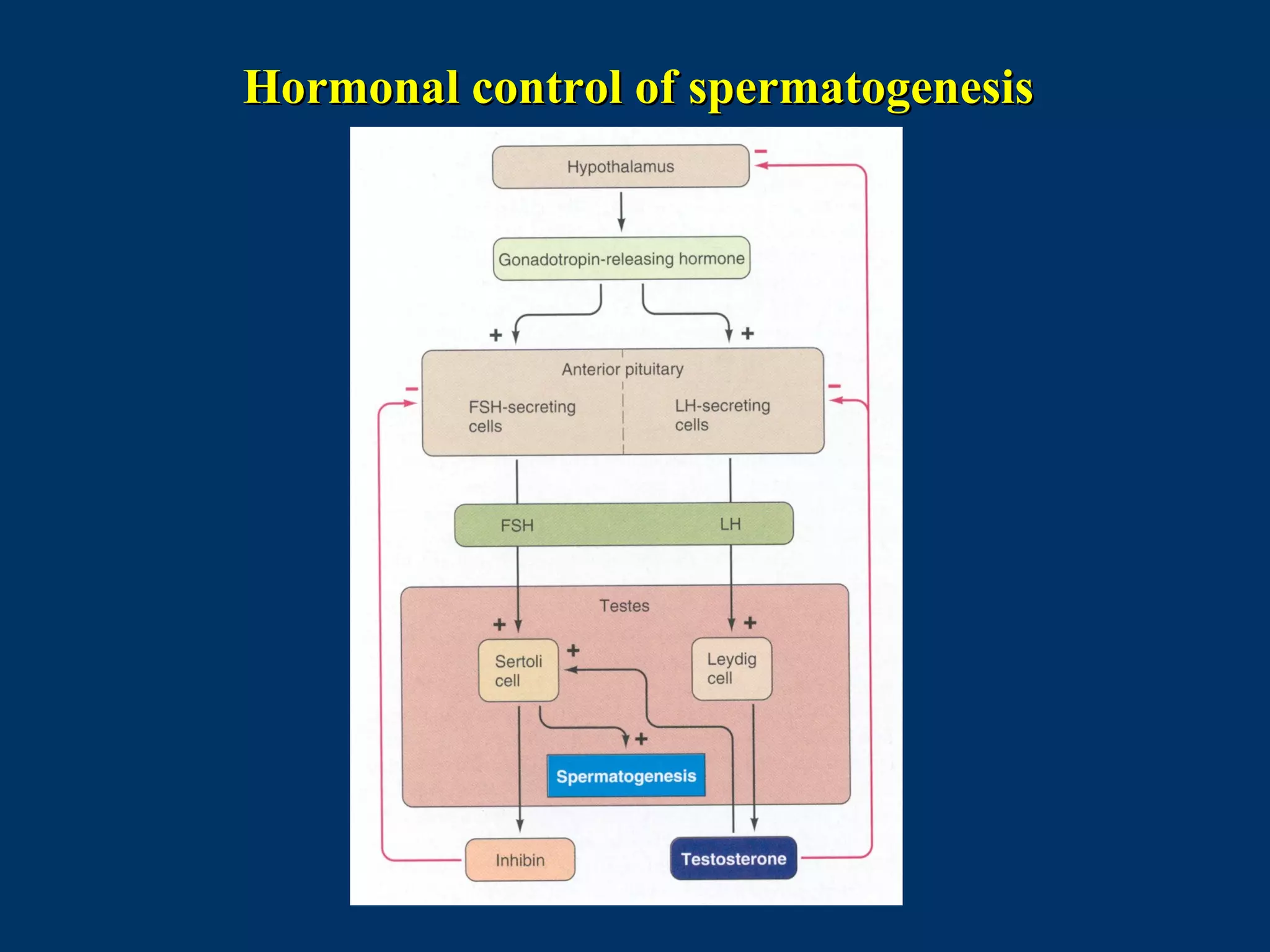
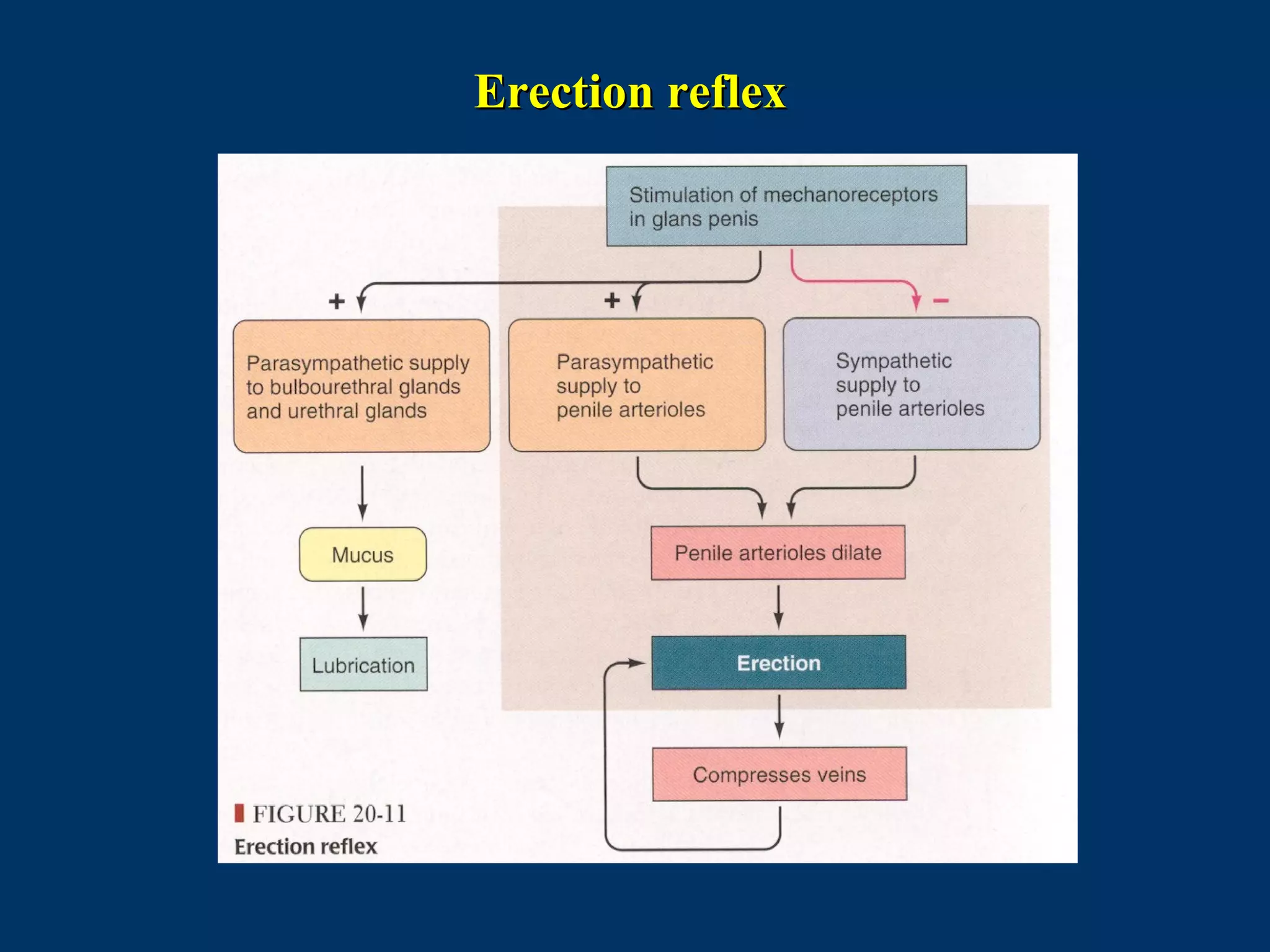
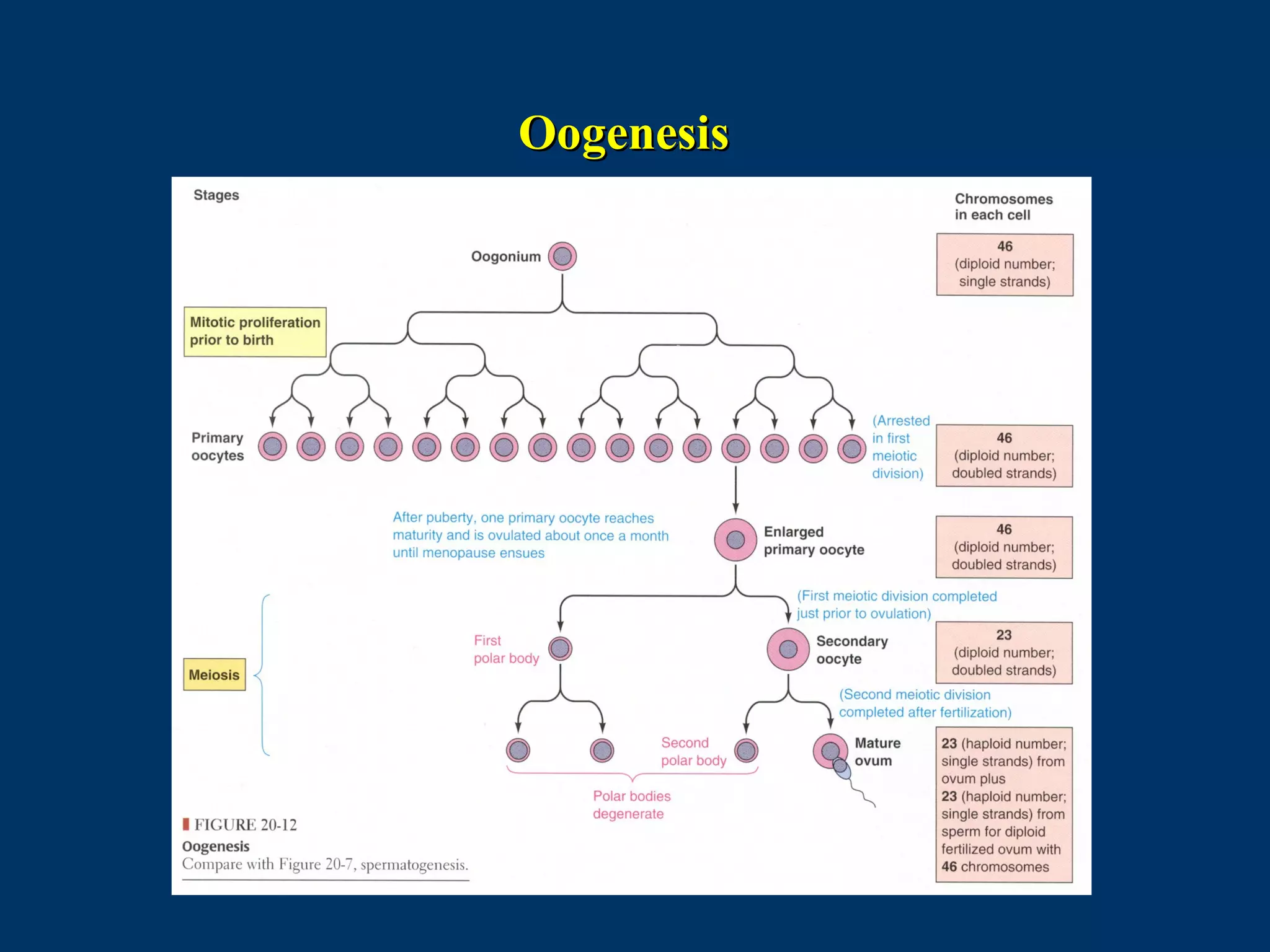
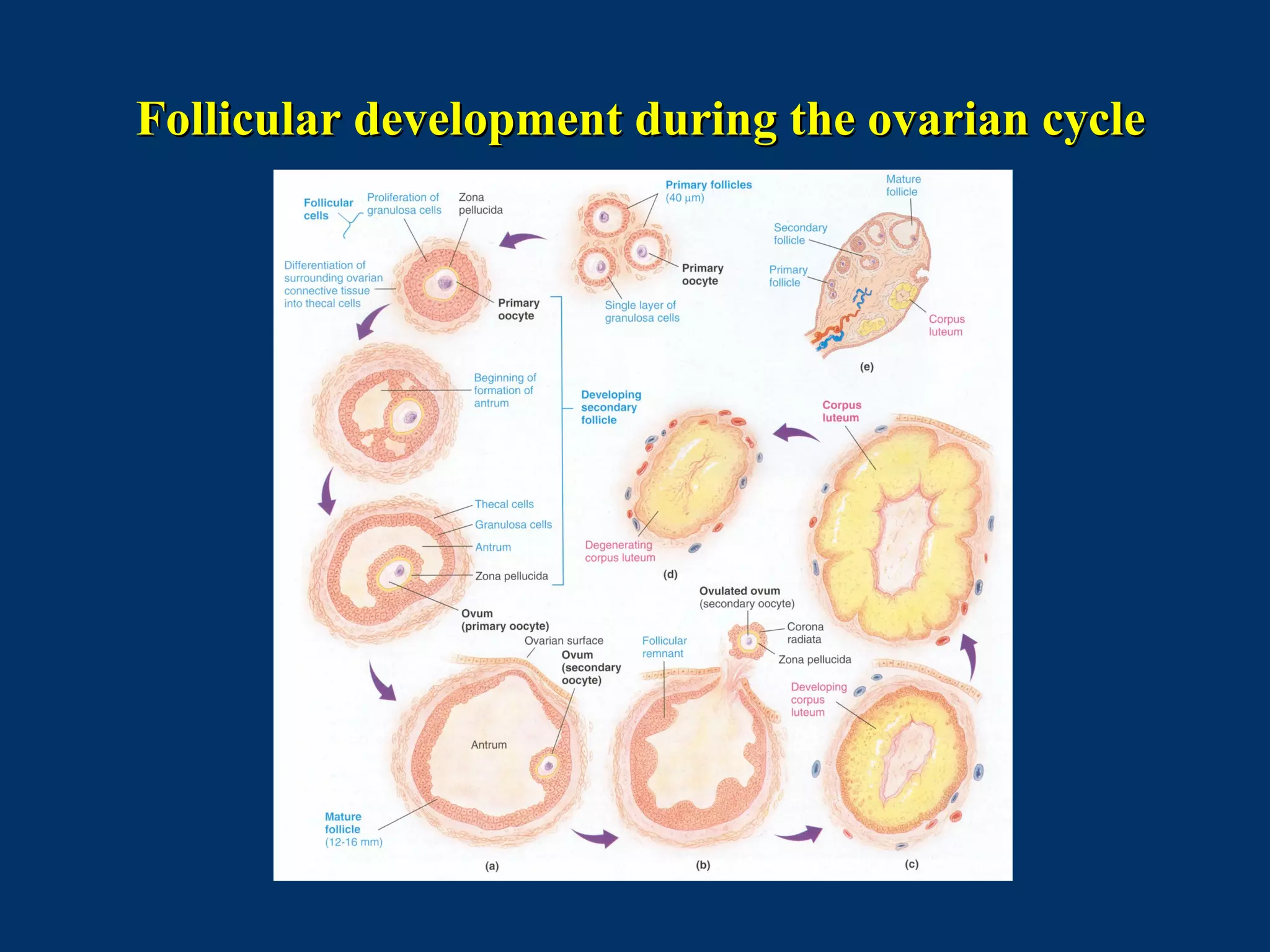
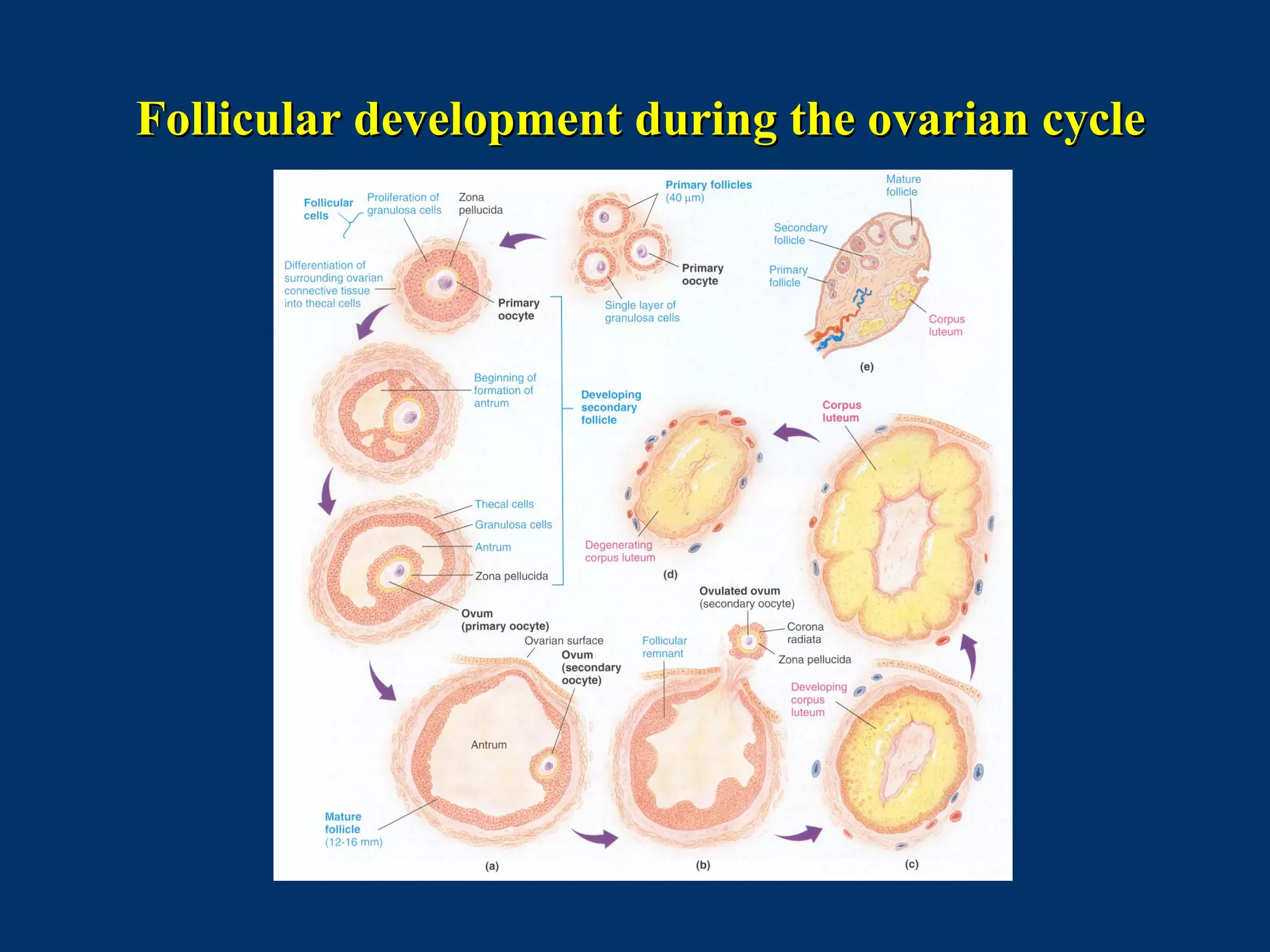
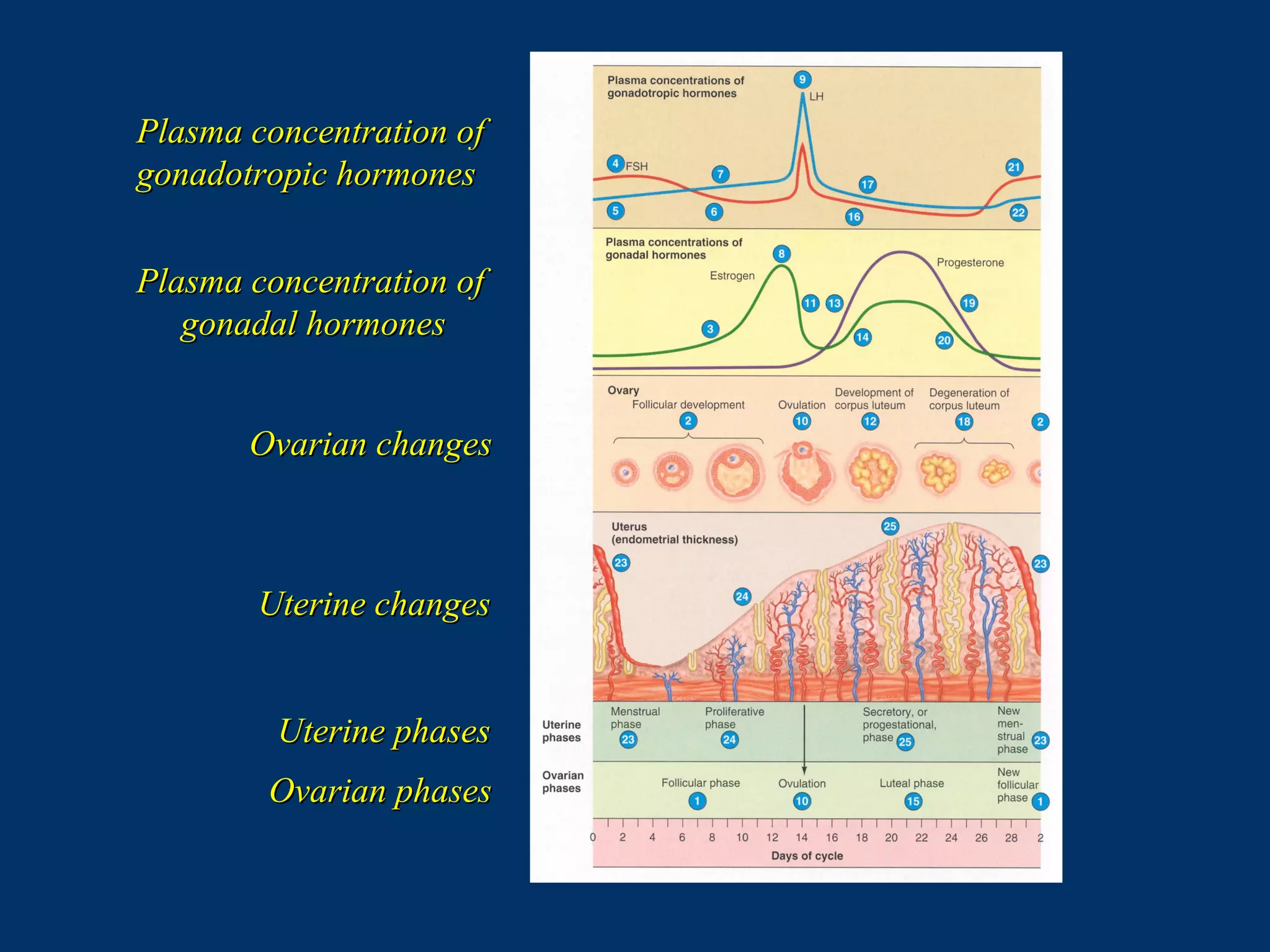
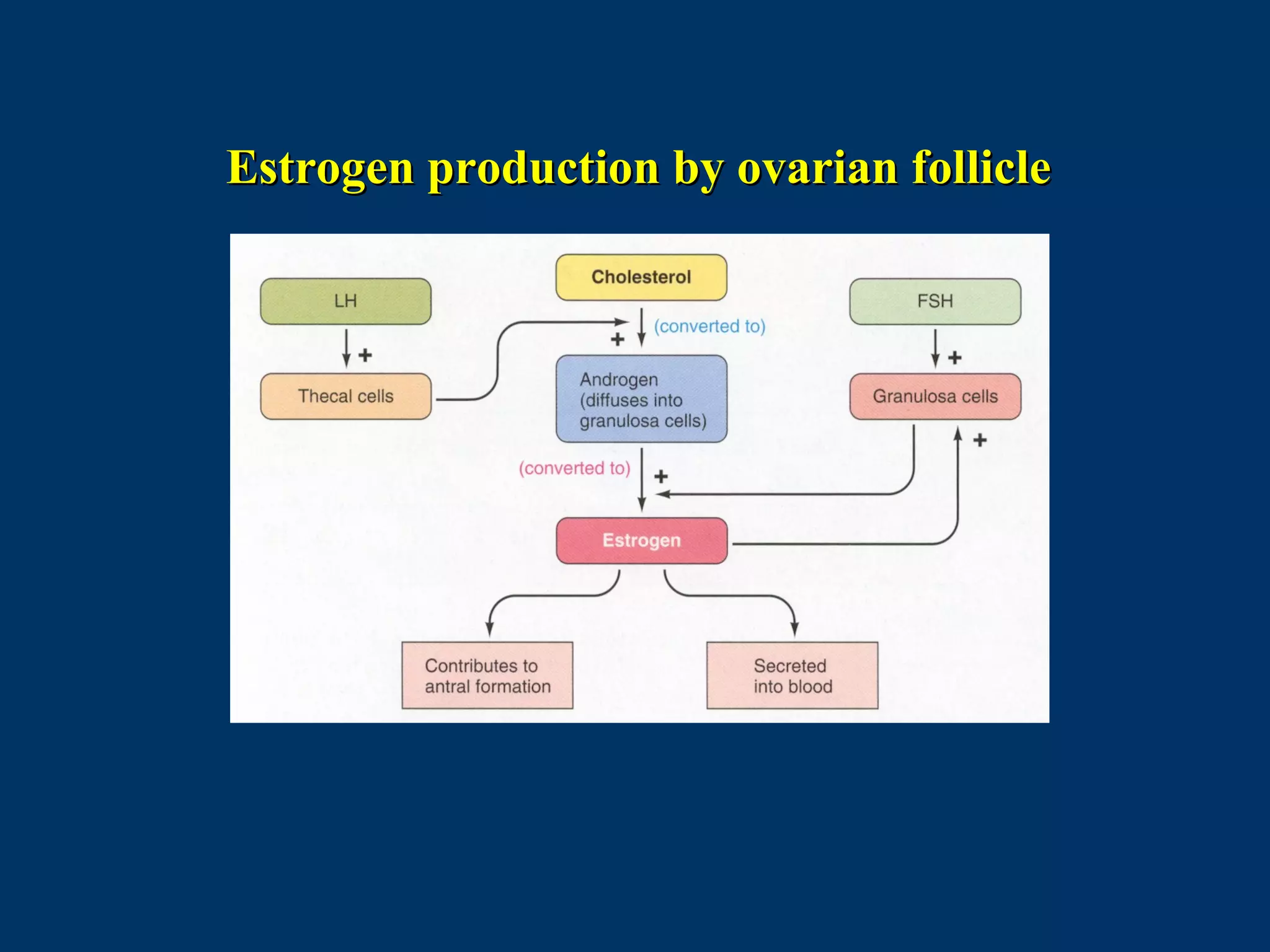
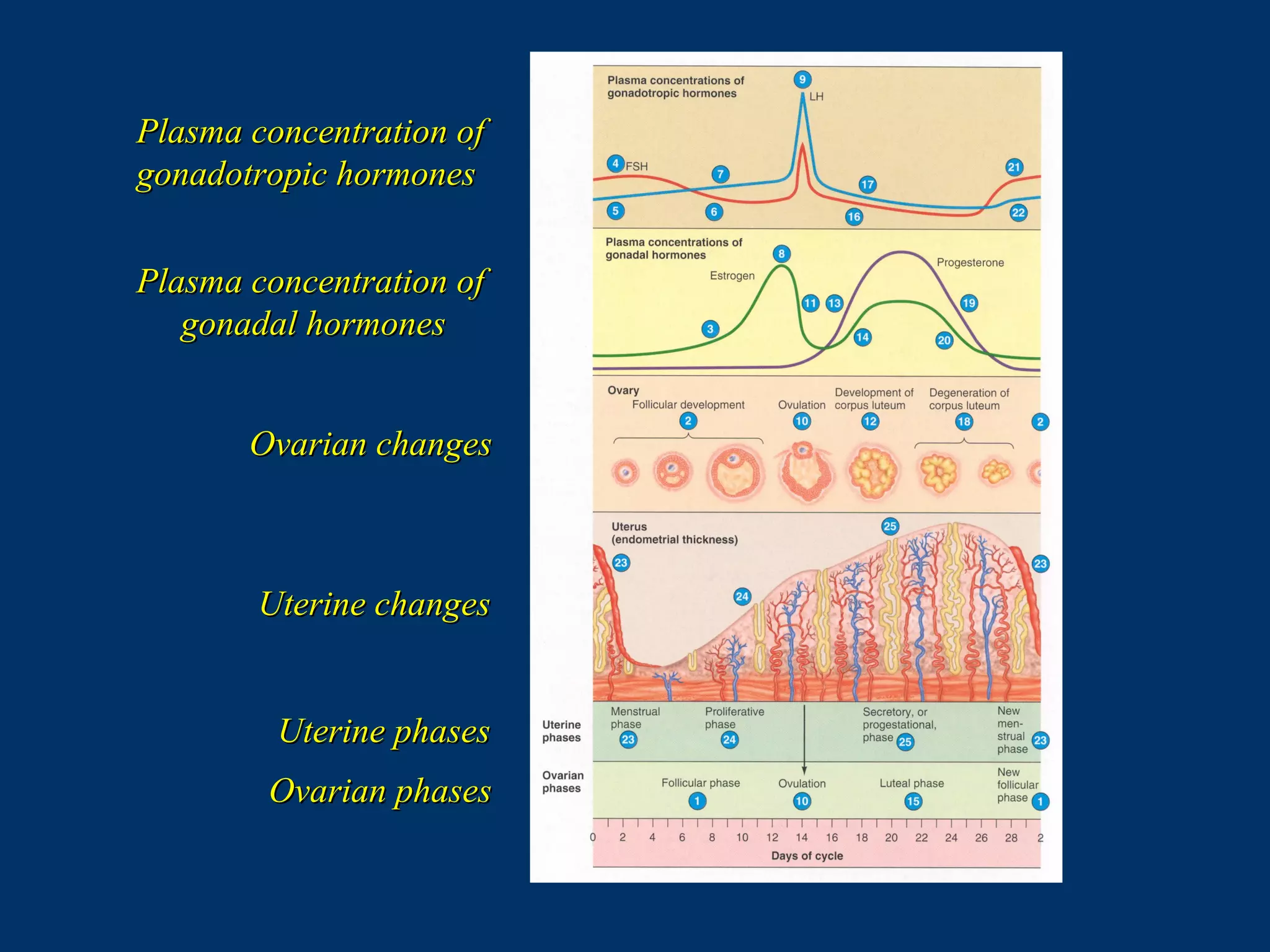
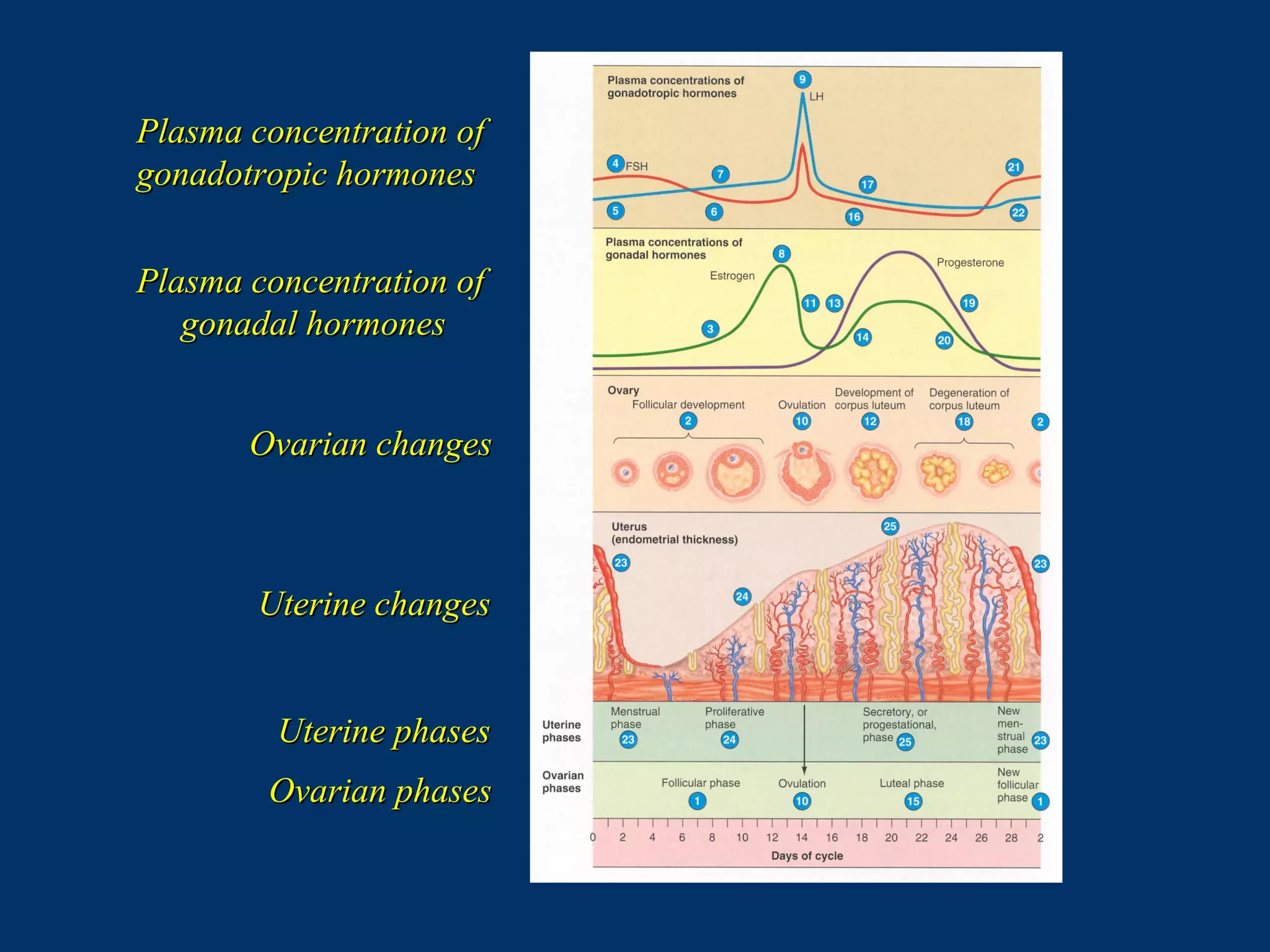
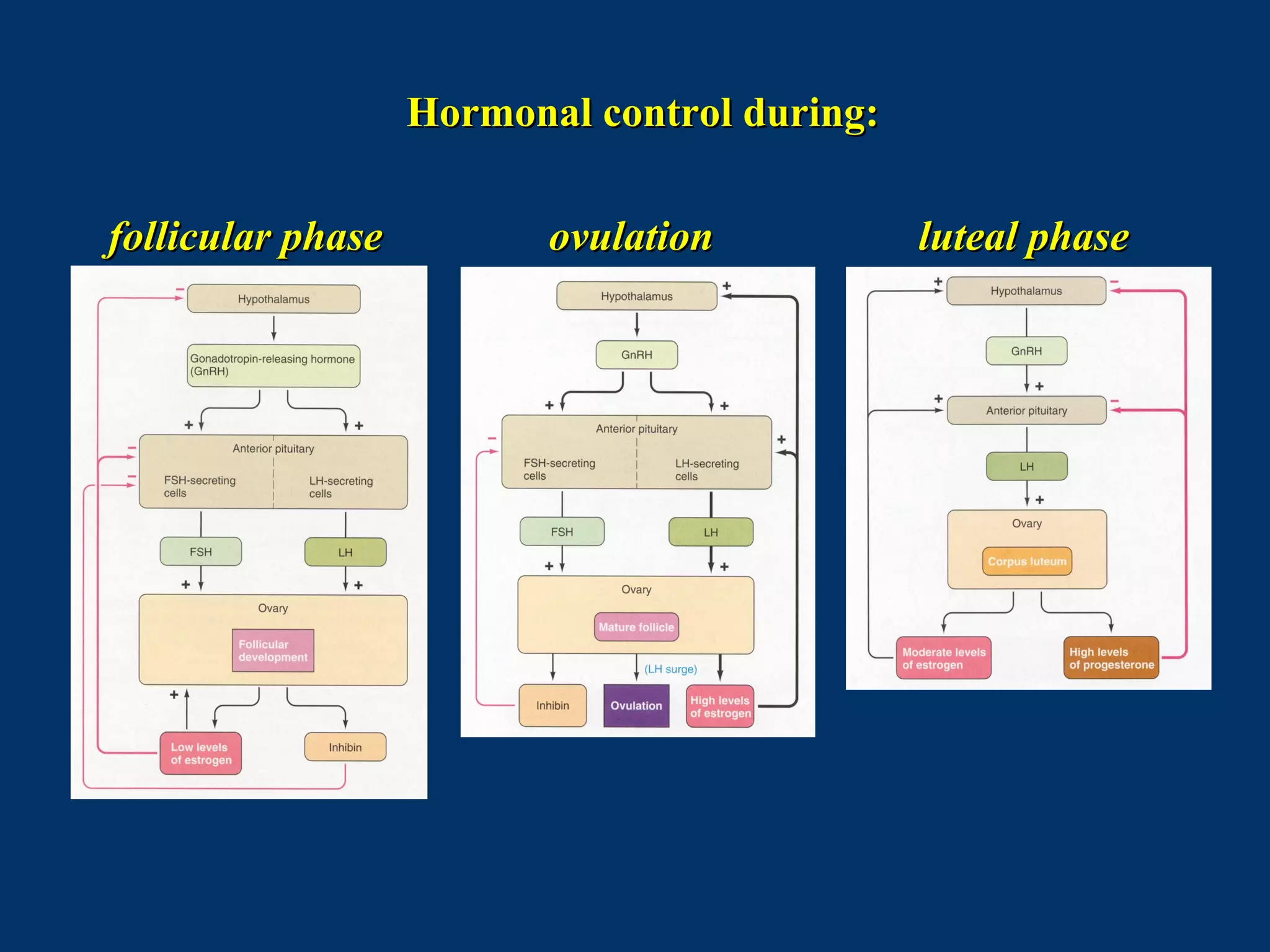
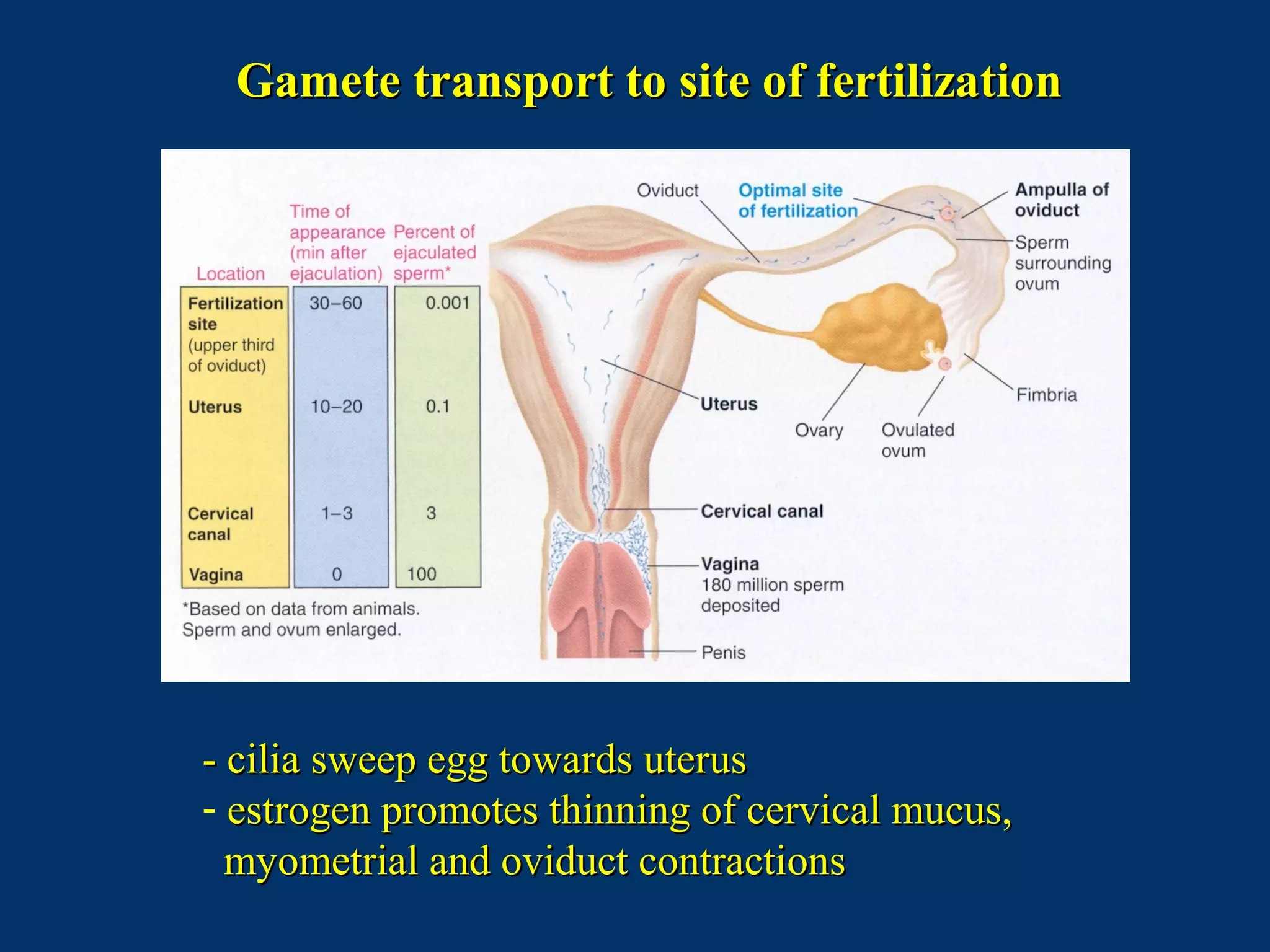
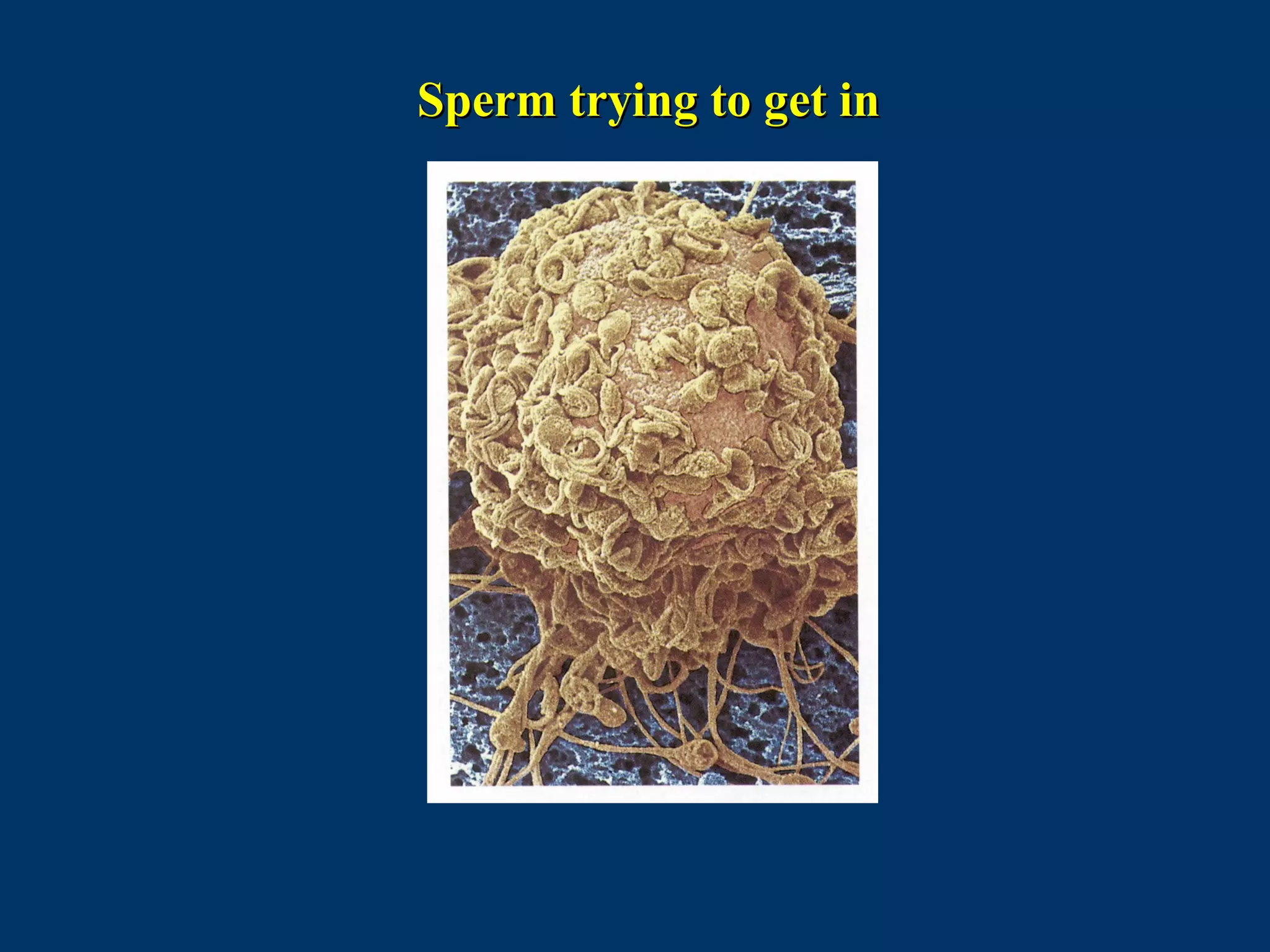
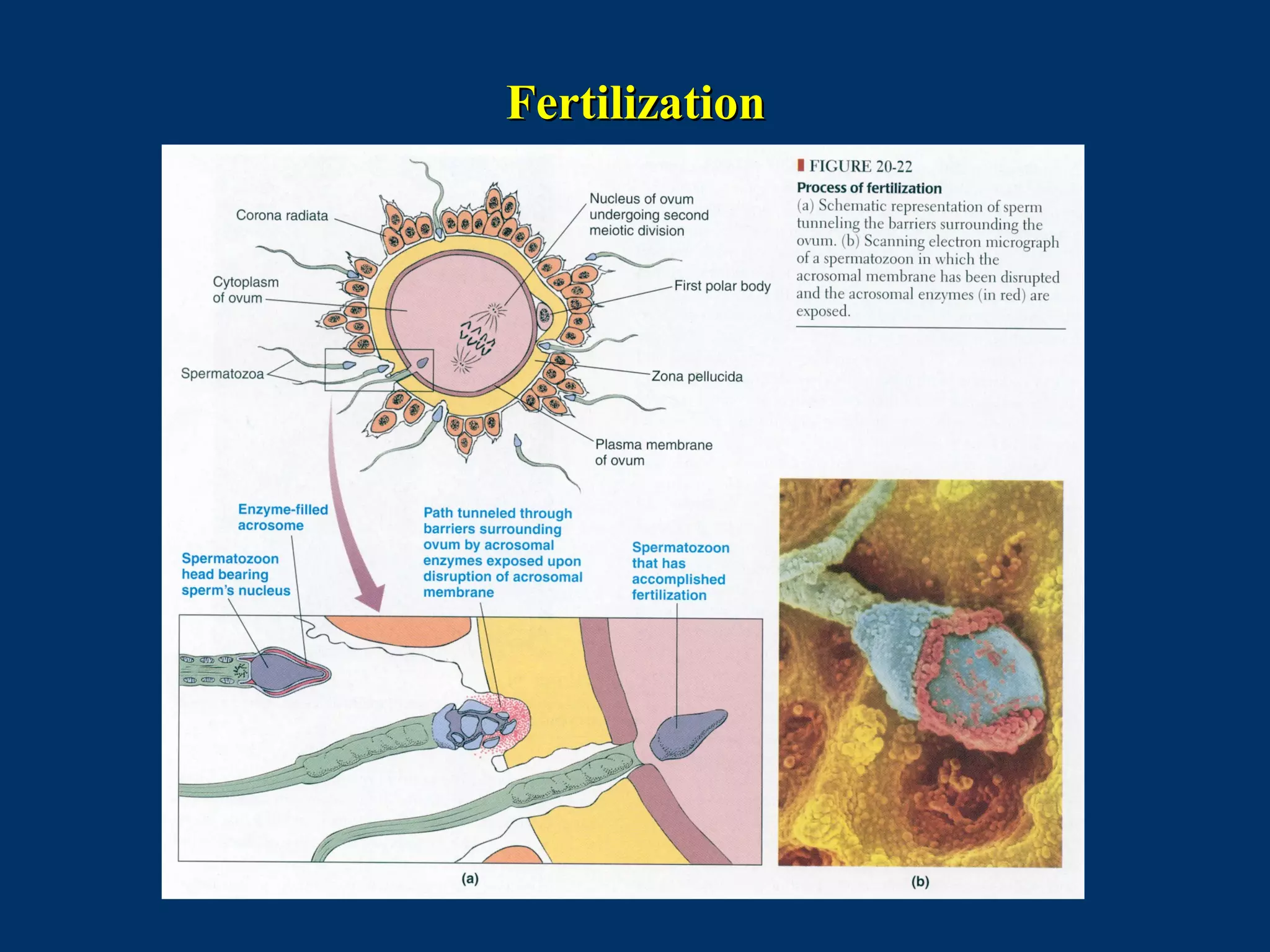
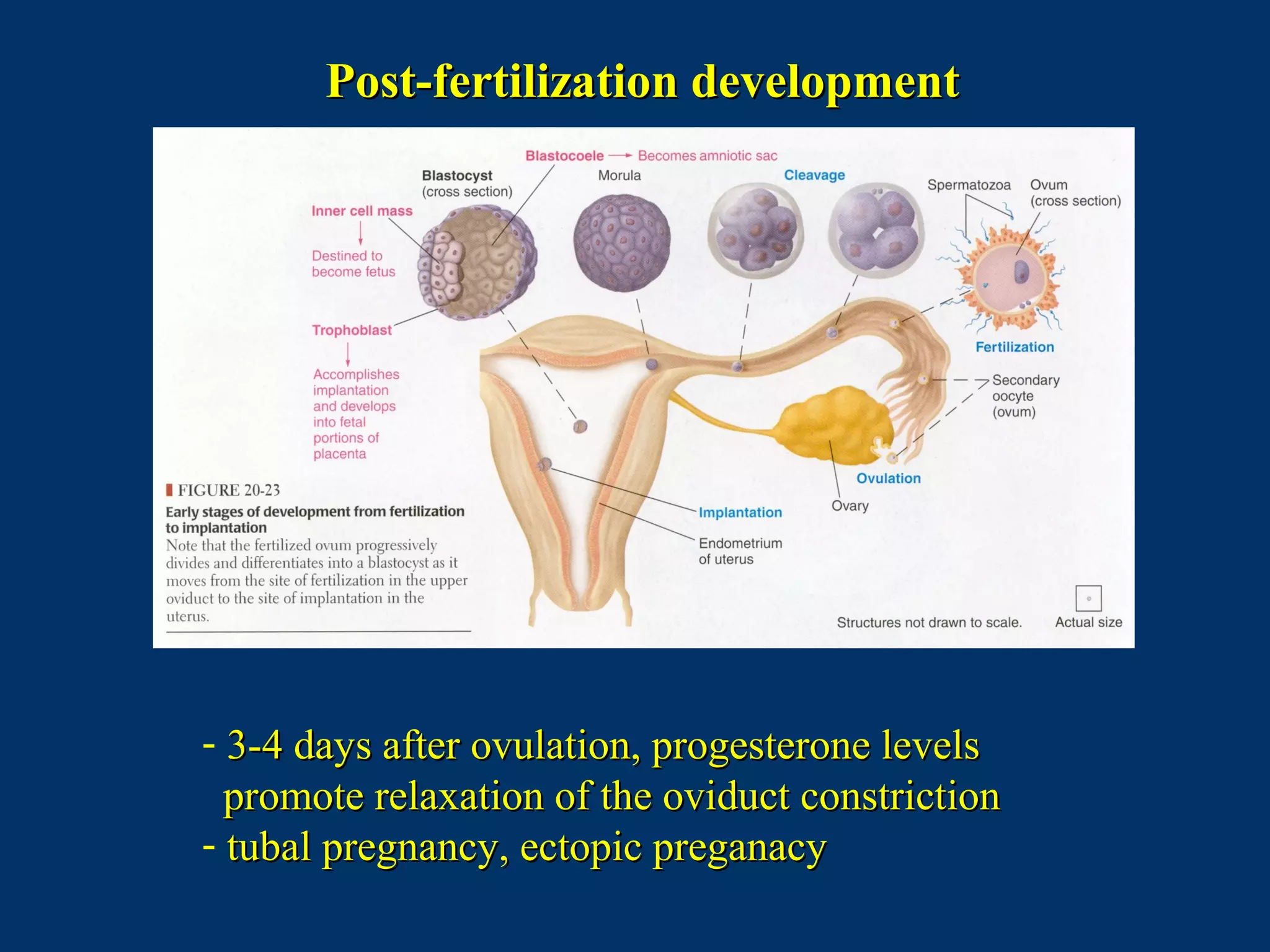
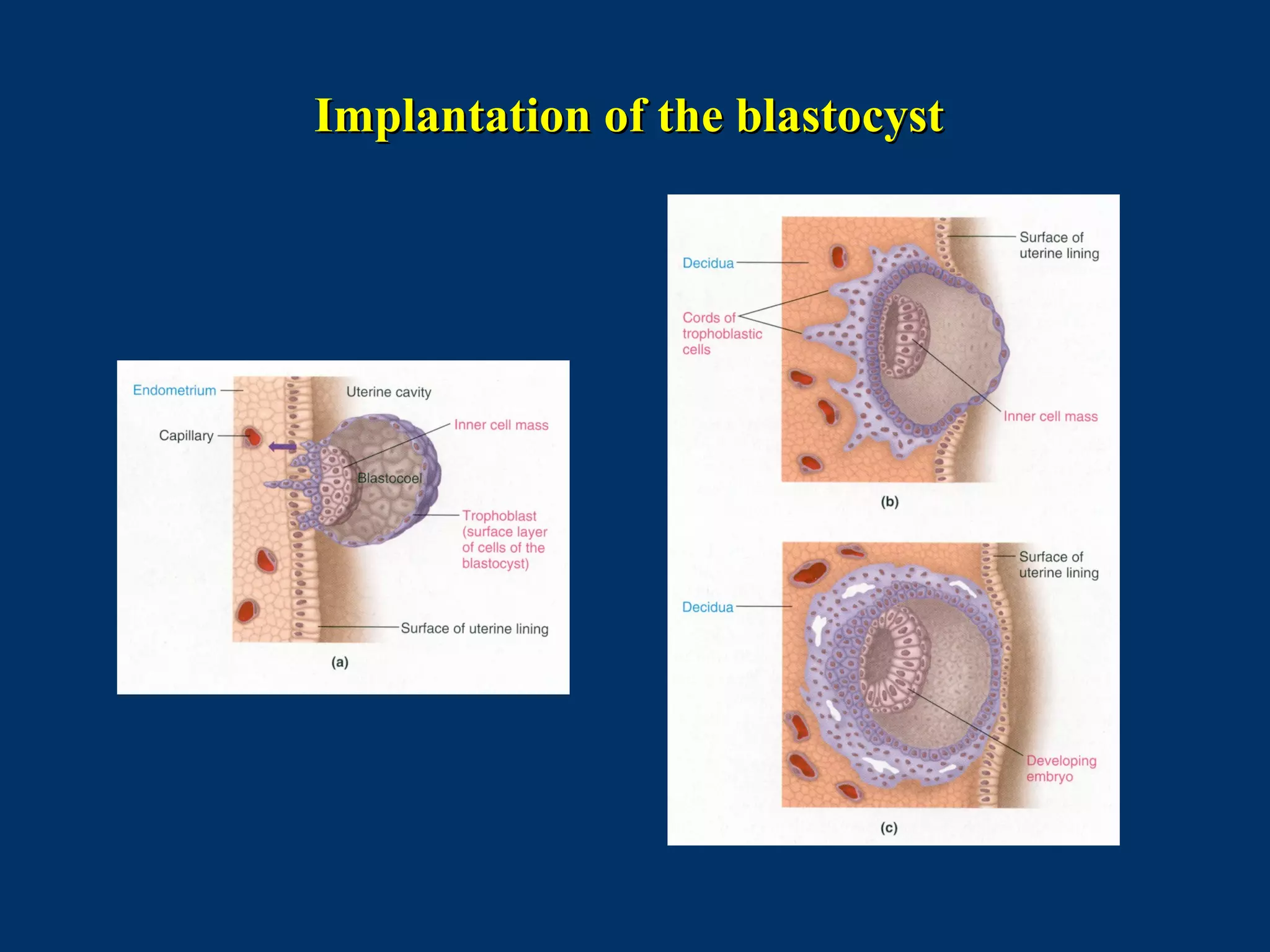
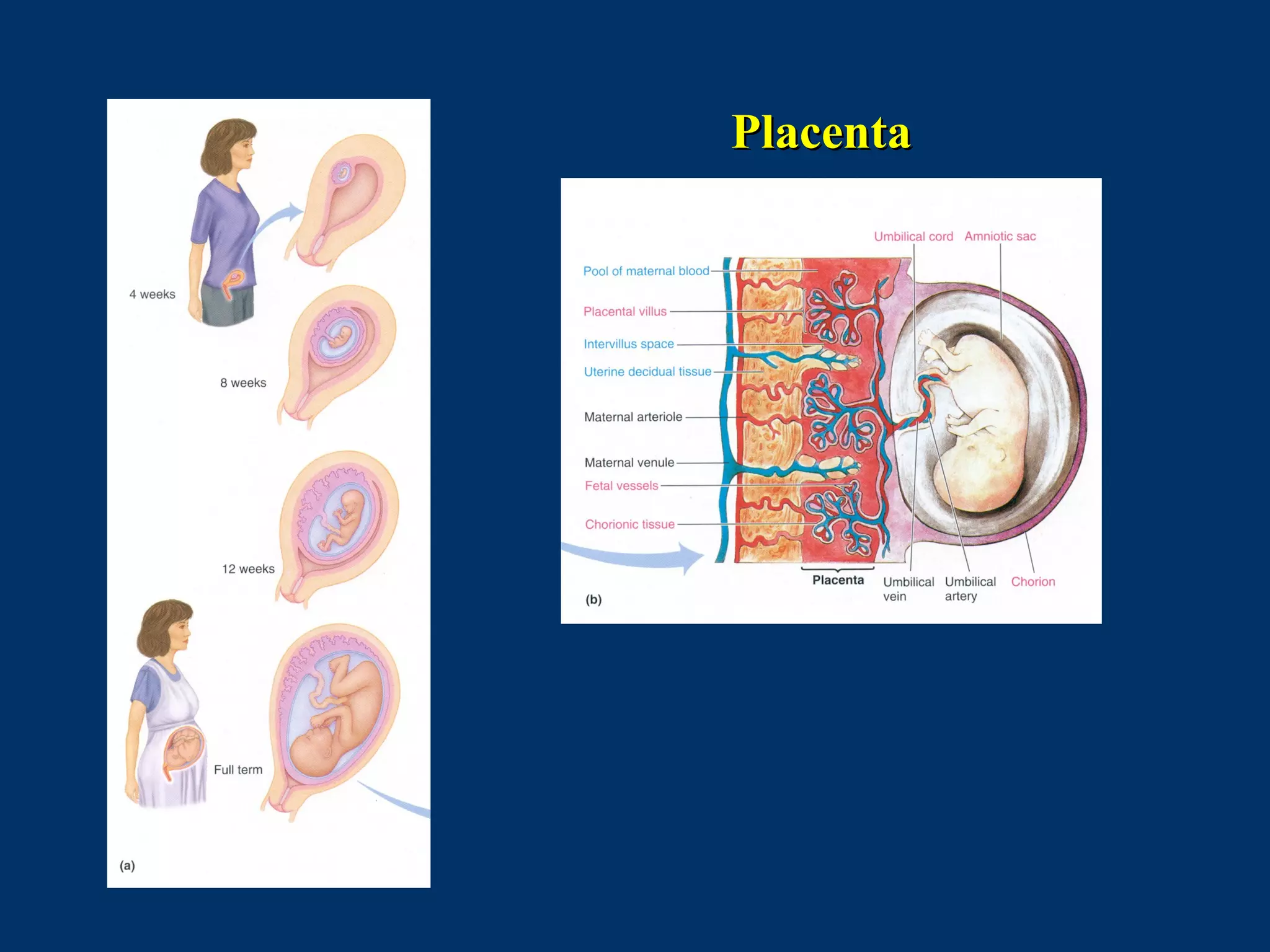
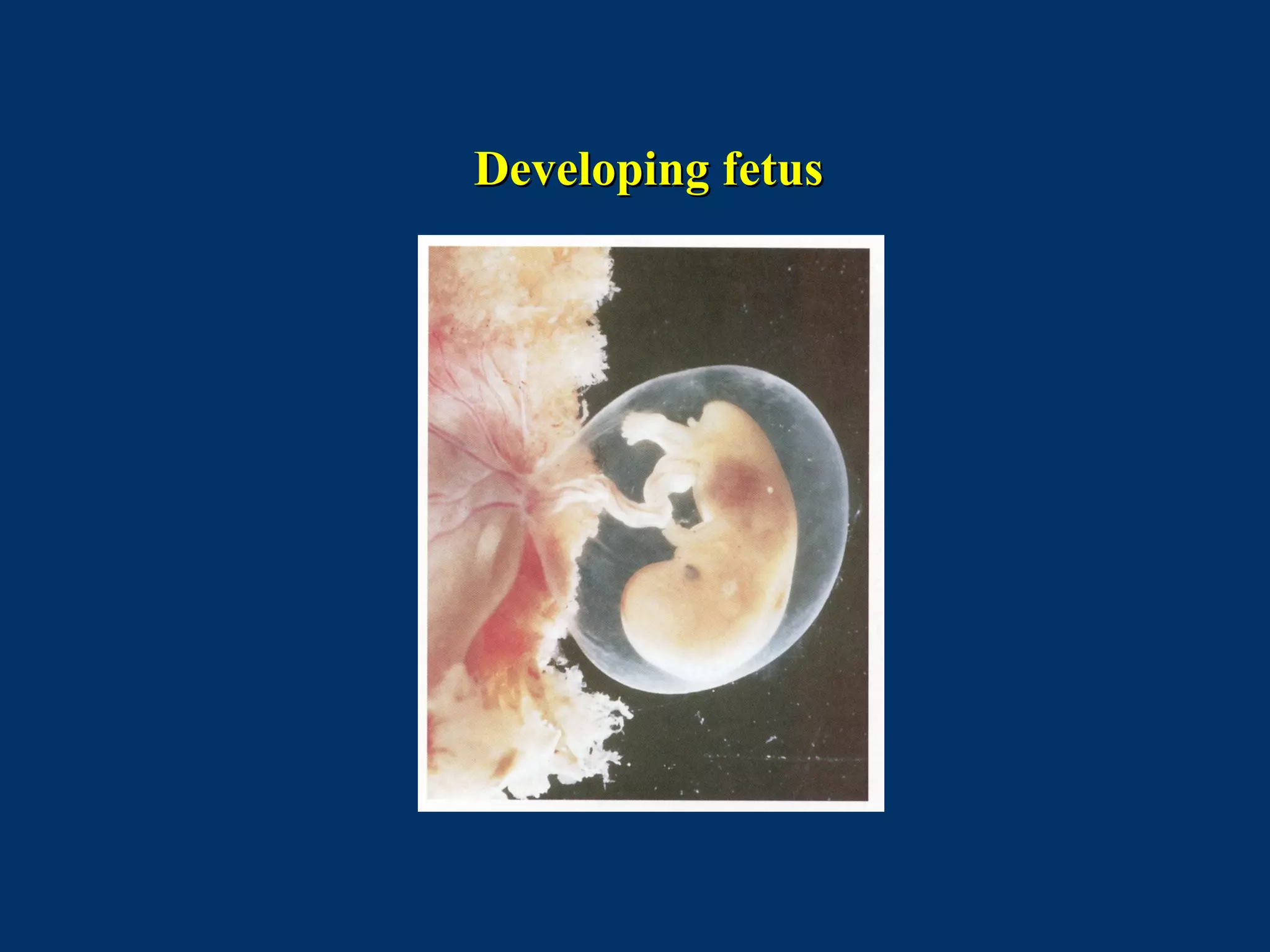
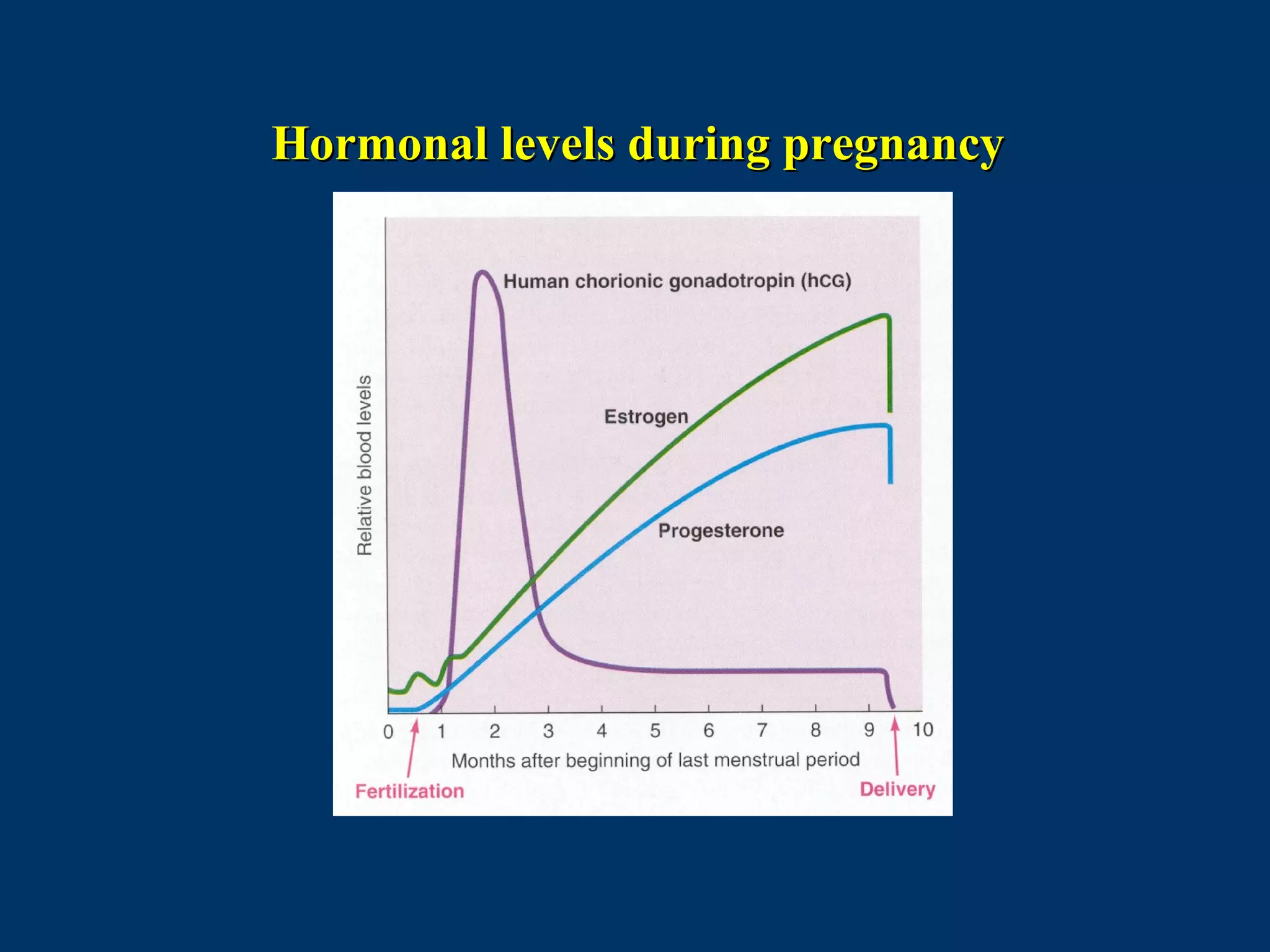
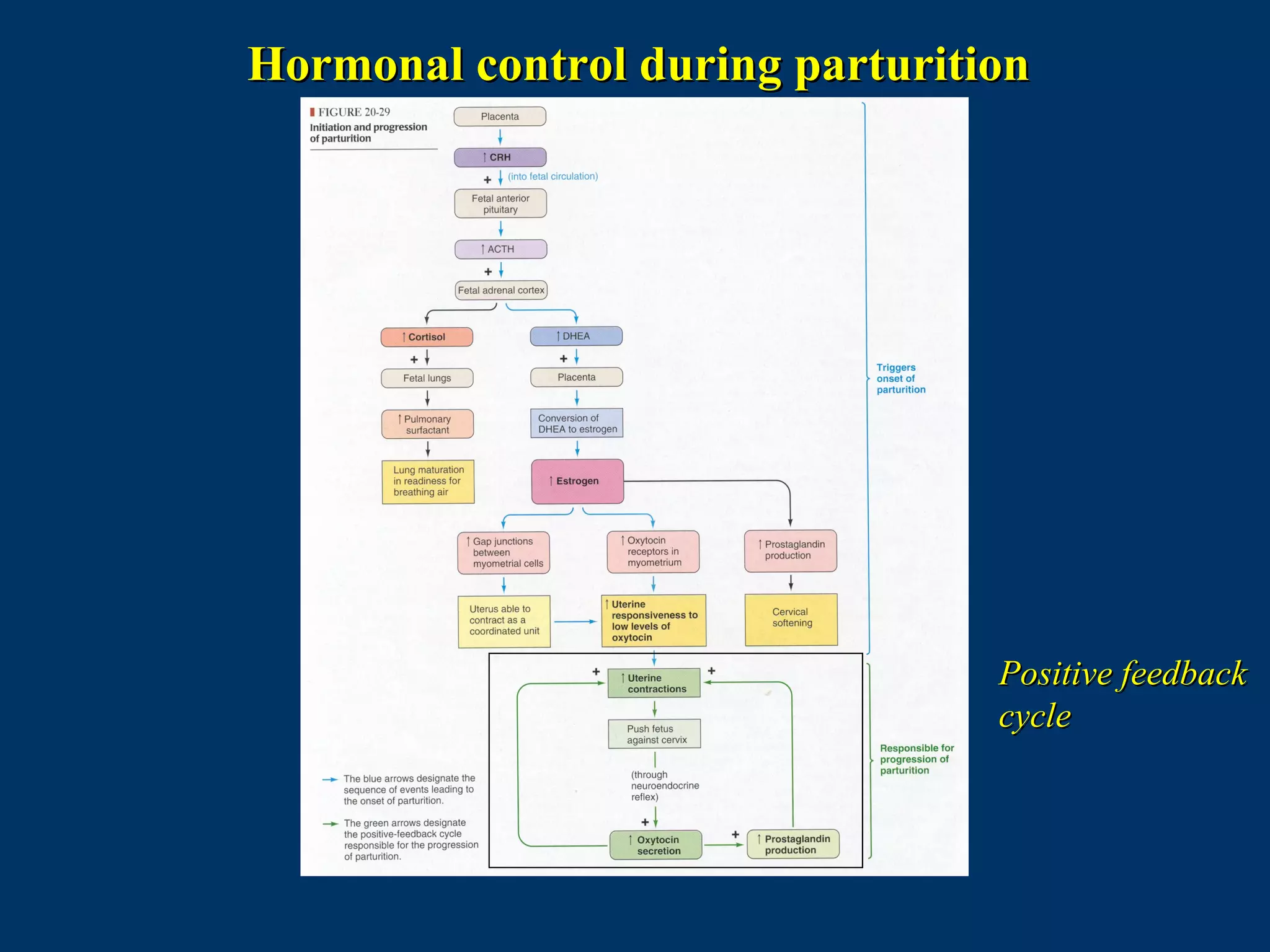
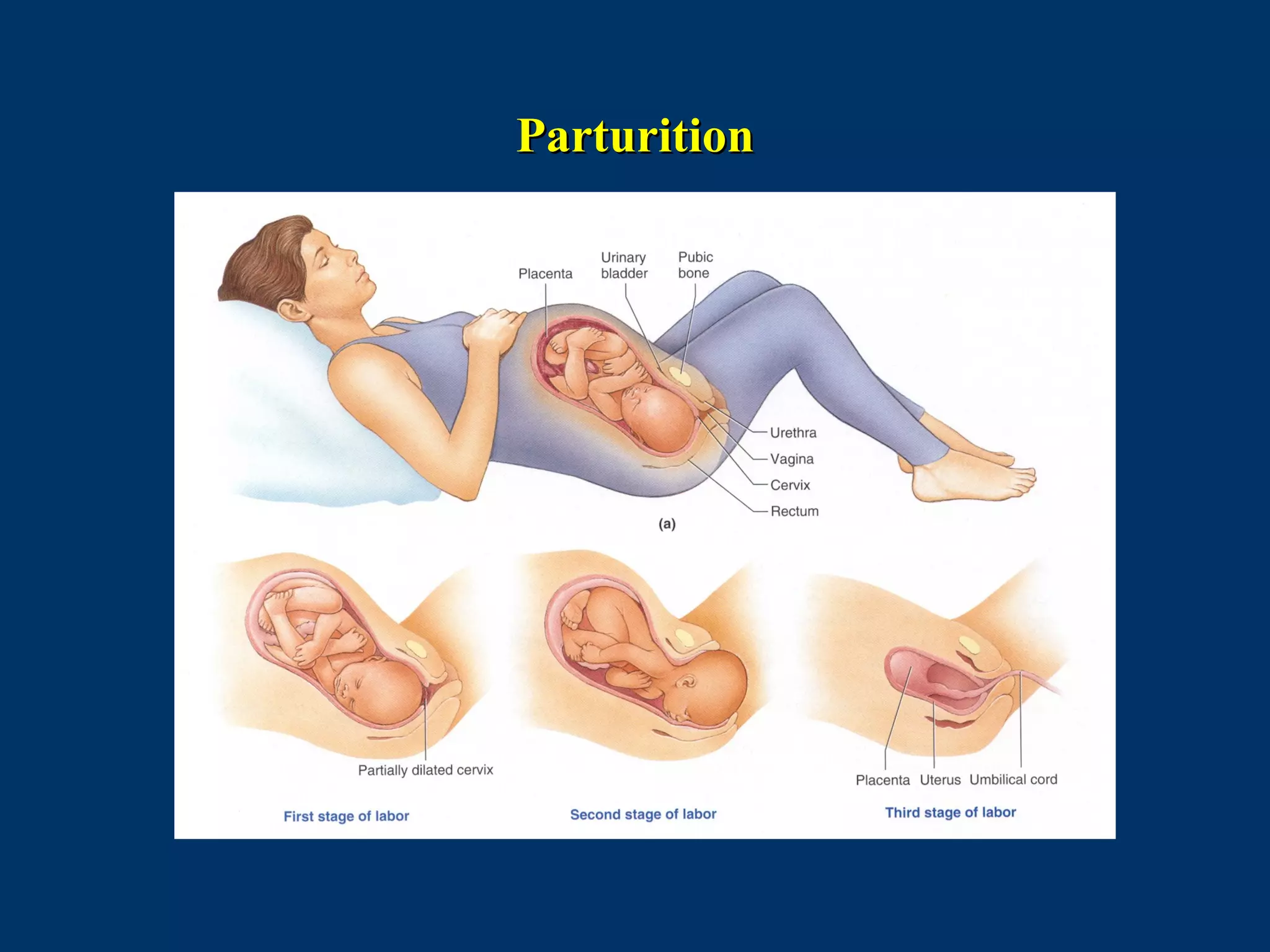
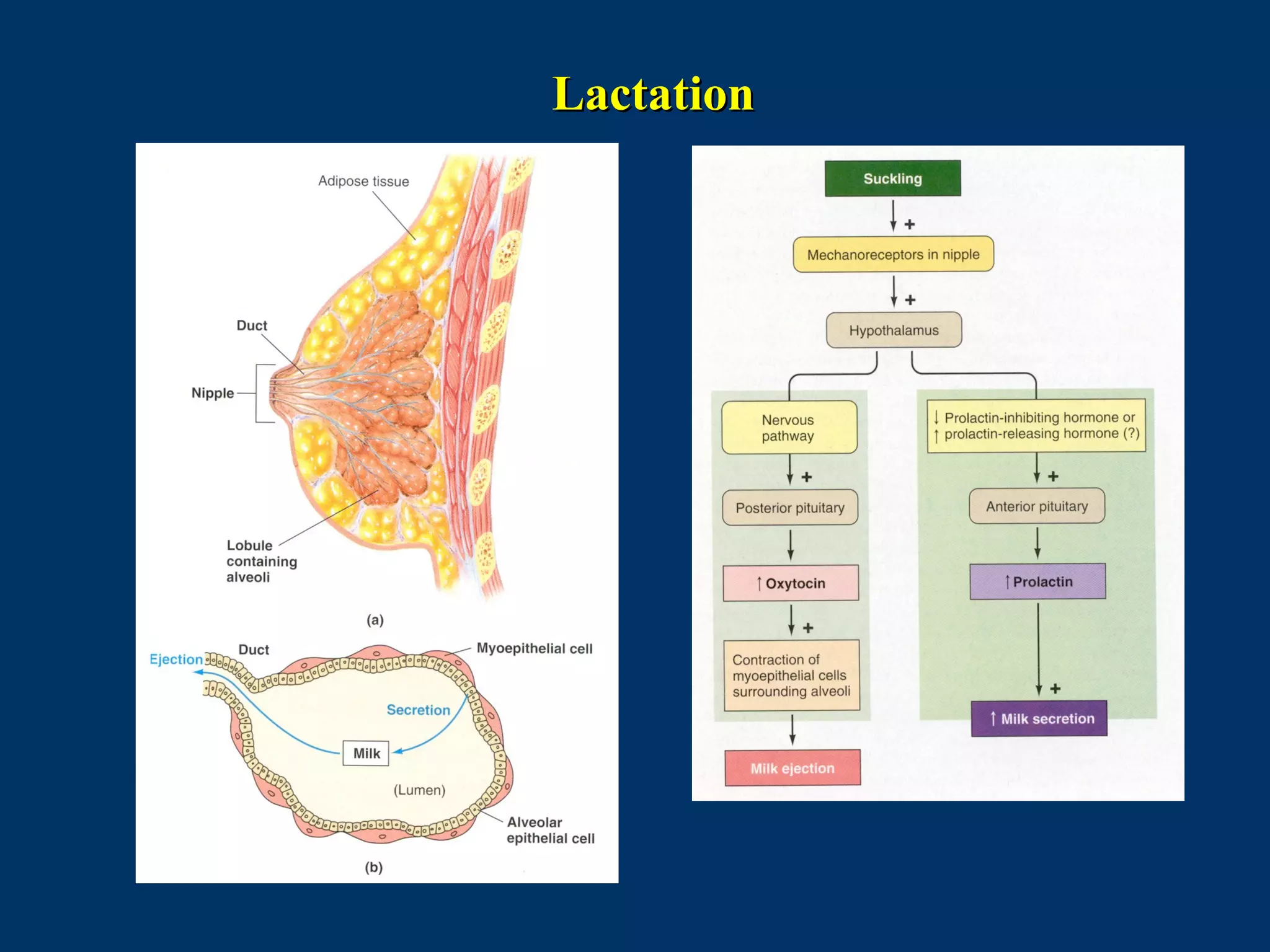
The document discusses reproductive physiology and the male and female reproductive systems. It covers topics like the ovarian and testicular cycles, hormone regulation of spermatogenesis and follicular development, the female menstrual cycle and changes in the ovaries and uterus over the cycle, and the roles of hormones like estrogen and progesterone. Key concepts covered include gamete production, fertilization, pregnancy, and the influences of hormones on sexual differentiation and characteristics.