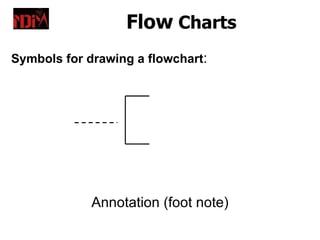
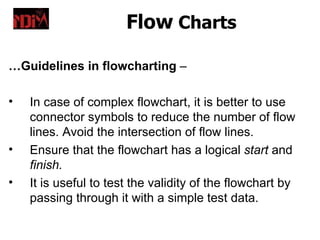
Flow charts are diagrams that represent a sequence of steps to solve a problem. They use standard symbols to visually depict the logic and processes within a program or system. Flow charts facilitate communication between programmers and non-technical stakeholders. Guidelines for effective flow charts include using a logical structure, clear symbols, and ensuring the chart has a defined start and end. Pseudocode and structured English are additional tools to represent programming logic at a higher level before implementation in a specific coding language.