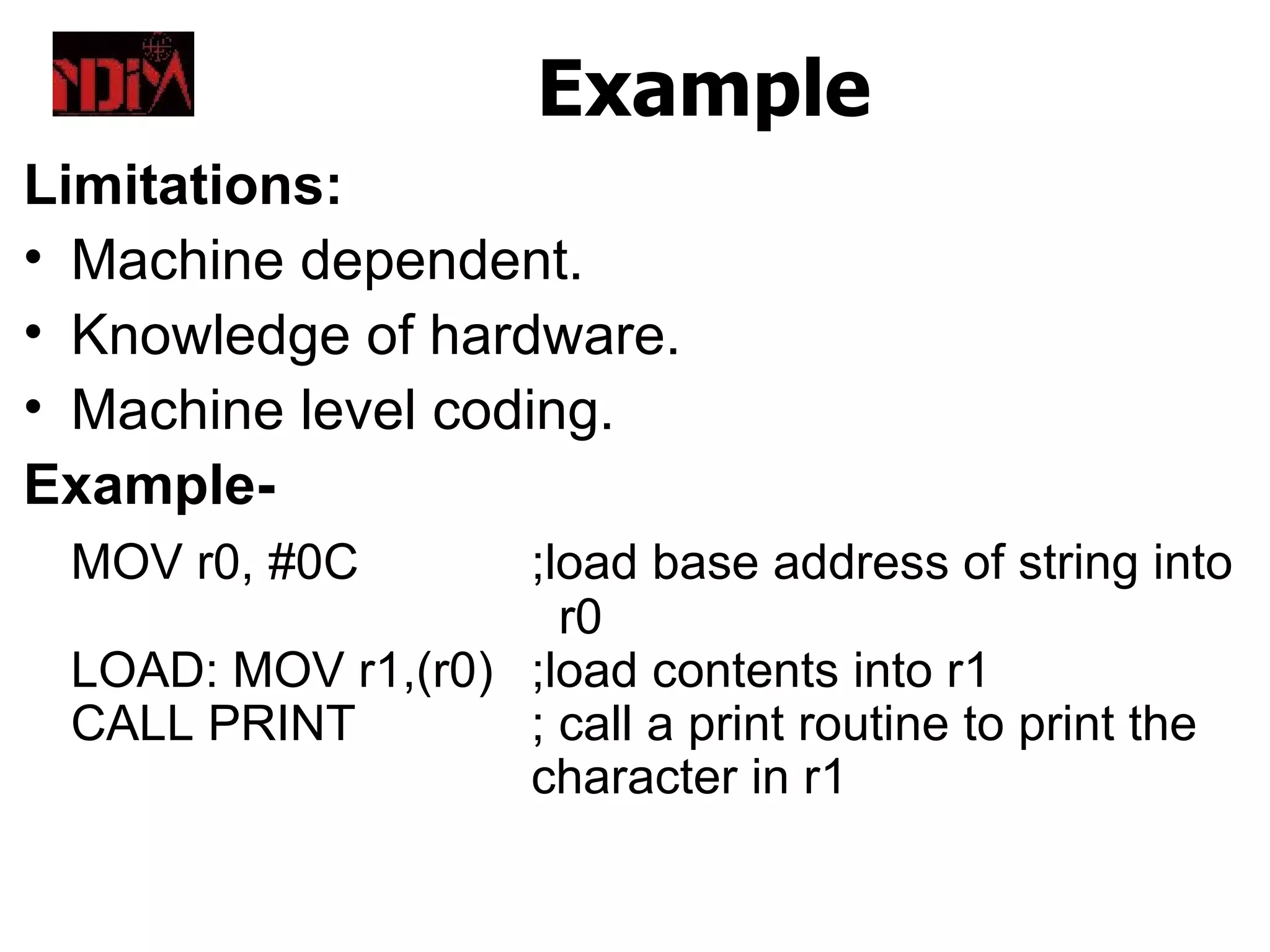
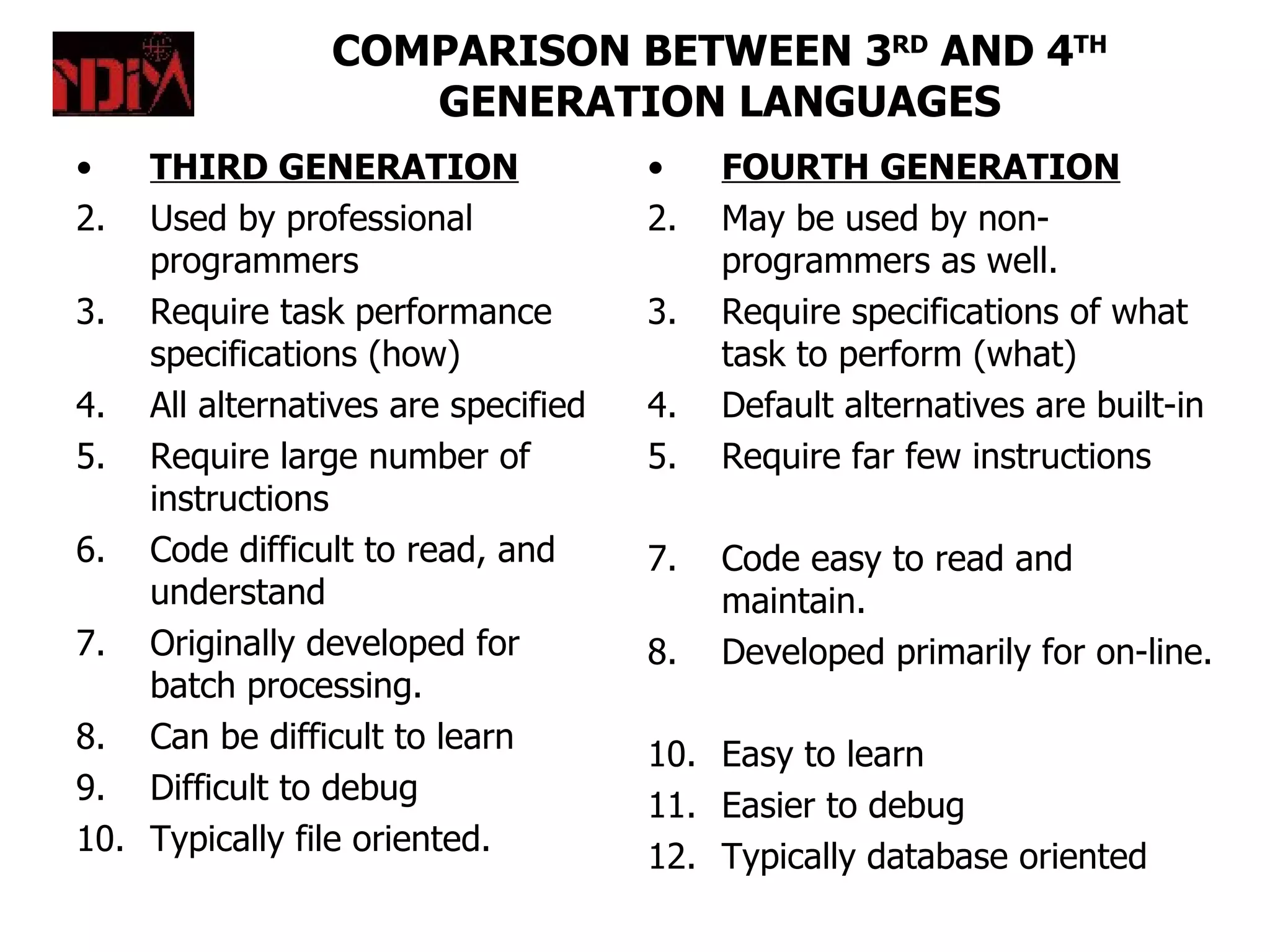
System software includes operating systems and compilers that help utilize hardware resources, while application software performs specific tasks like word processing. Utility programs perform basic functions like formatting disks. High-level languages are easier for humans to read and write than low-level languages like assembly, which are closer to machine code.