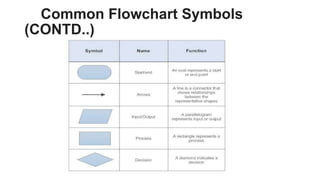
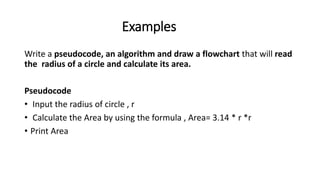
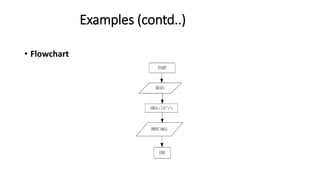
This document discusses algorithms, flowcharts, and pseudocode. It defines algorithms as a set of well-defined steps to solve a problem and notes they should be unambiguous and effective. Flowcharts are described as using shapes and arrows to visually represent algorithmic processes and common symbols are shown. Pseudocode is an informal language similar to English used to develop algorithms. Examples of each are provided, including an algorithm and flowchart to calculate the area of a circle from a radius input.