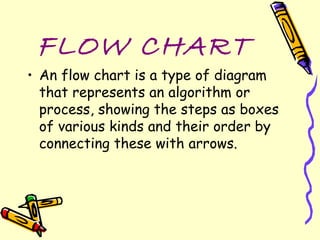
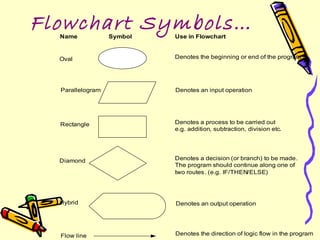
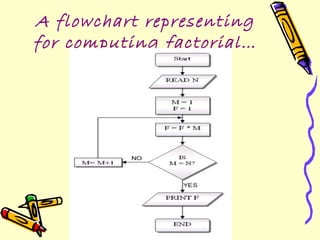
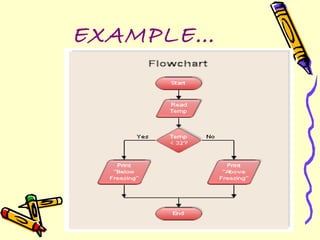
Flowcharts are diagrams that represent algorithms or processes through boxes and arrows. They help visualize processes and aid understanding. There are different types for documenting processes, data flows, systems, and programs. Standard symbols include ovals, rectangles, diamonds, and lines to denote starts/ends, processes, decisions, and logic flow. Flowcharts help with communication, analysis, documentation, coding, and debugging. Limitations include complexity, alterations, and losing the essentials in technical details.