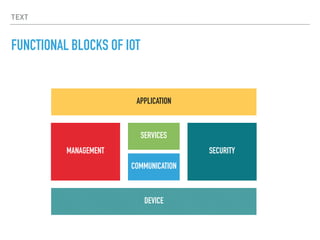
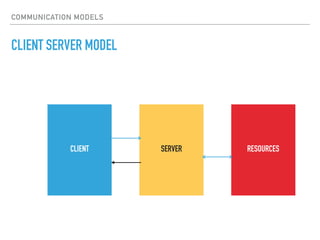
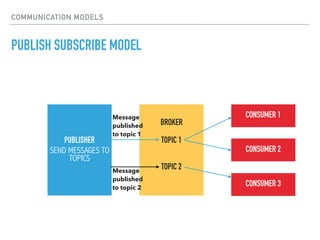
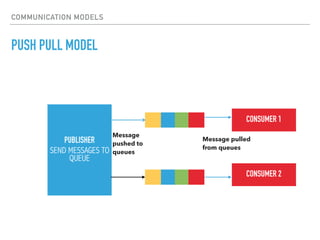
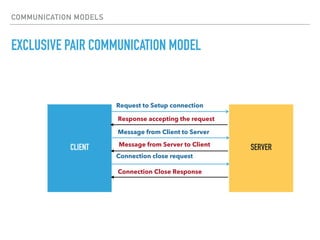
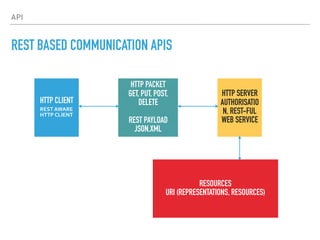
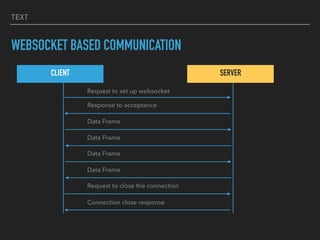
The document provides an overview of various IoT communication protocols categorized into different layers, such as link, network, transport, and application layers. It discusses multiple protocols including Ethernet, WiFi, MQTT, and HTTP, along with their use cases and functionalities. Additionally, the document highlights various communication models and APIs used in IoT, emphasizing the importance of enabling technologies like cloud computing and big data analytics.