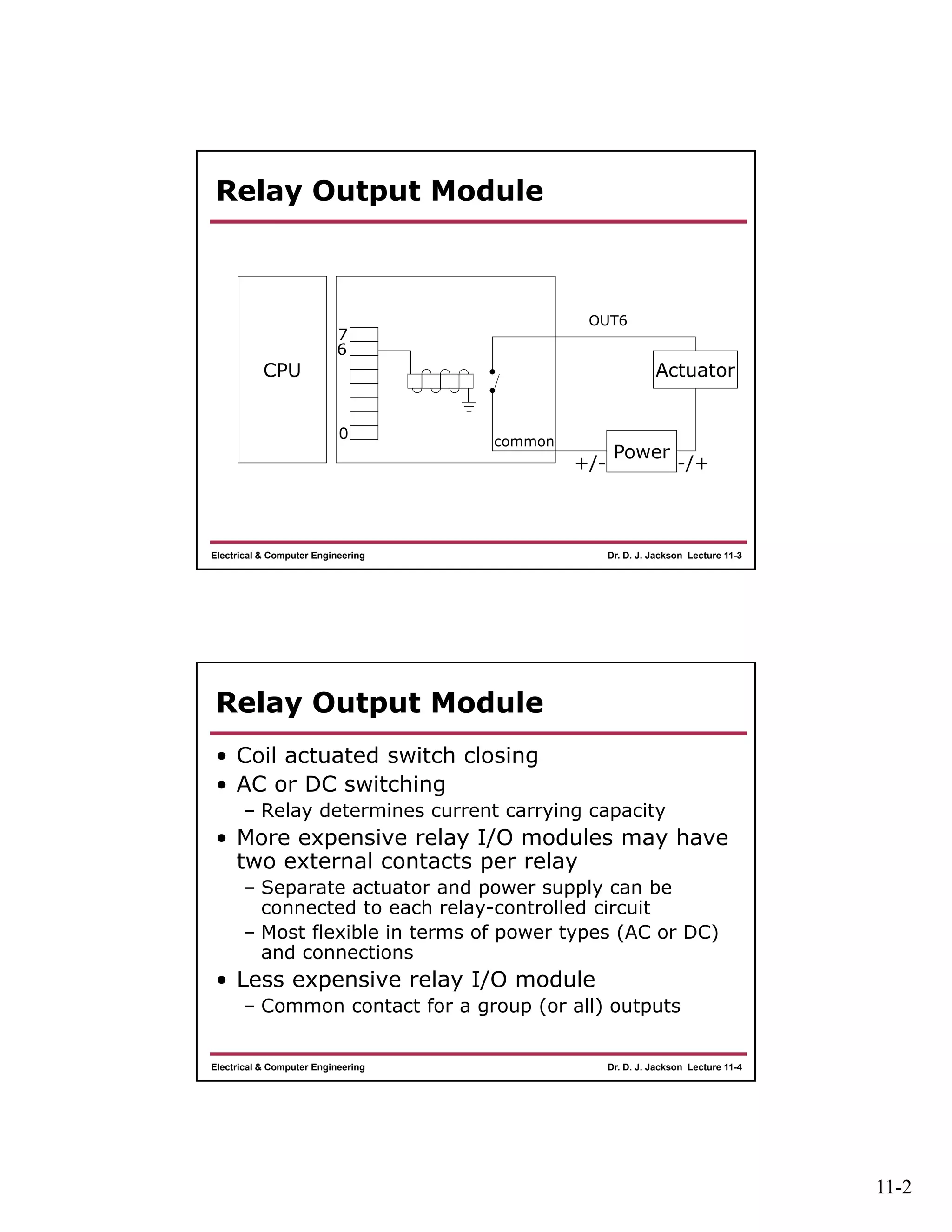
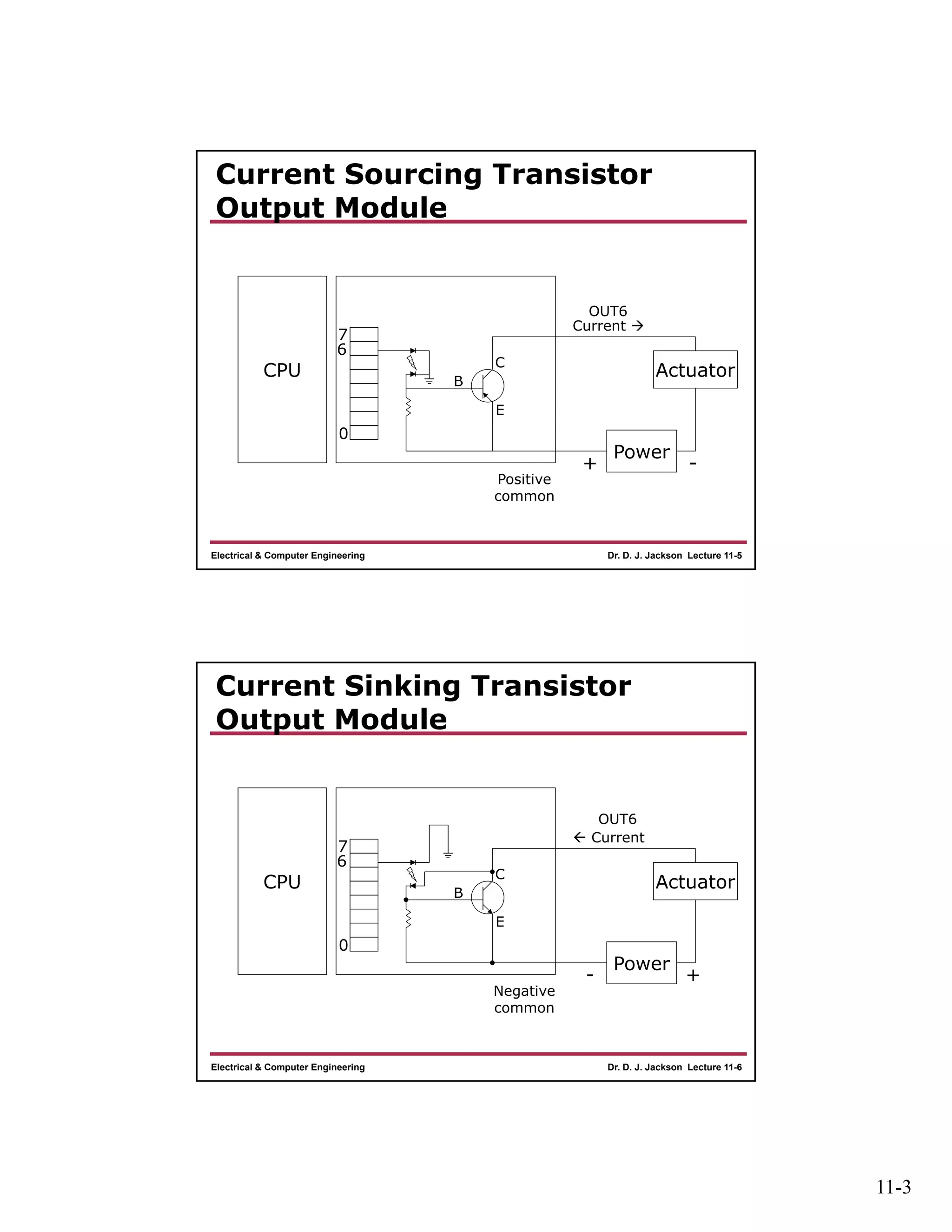
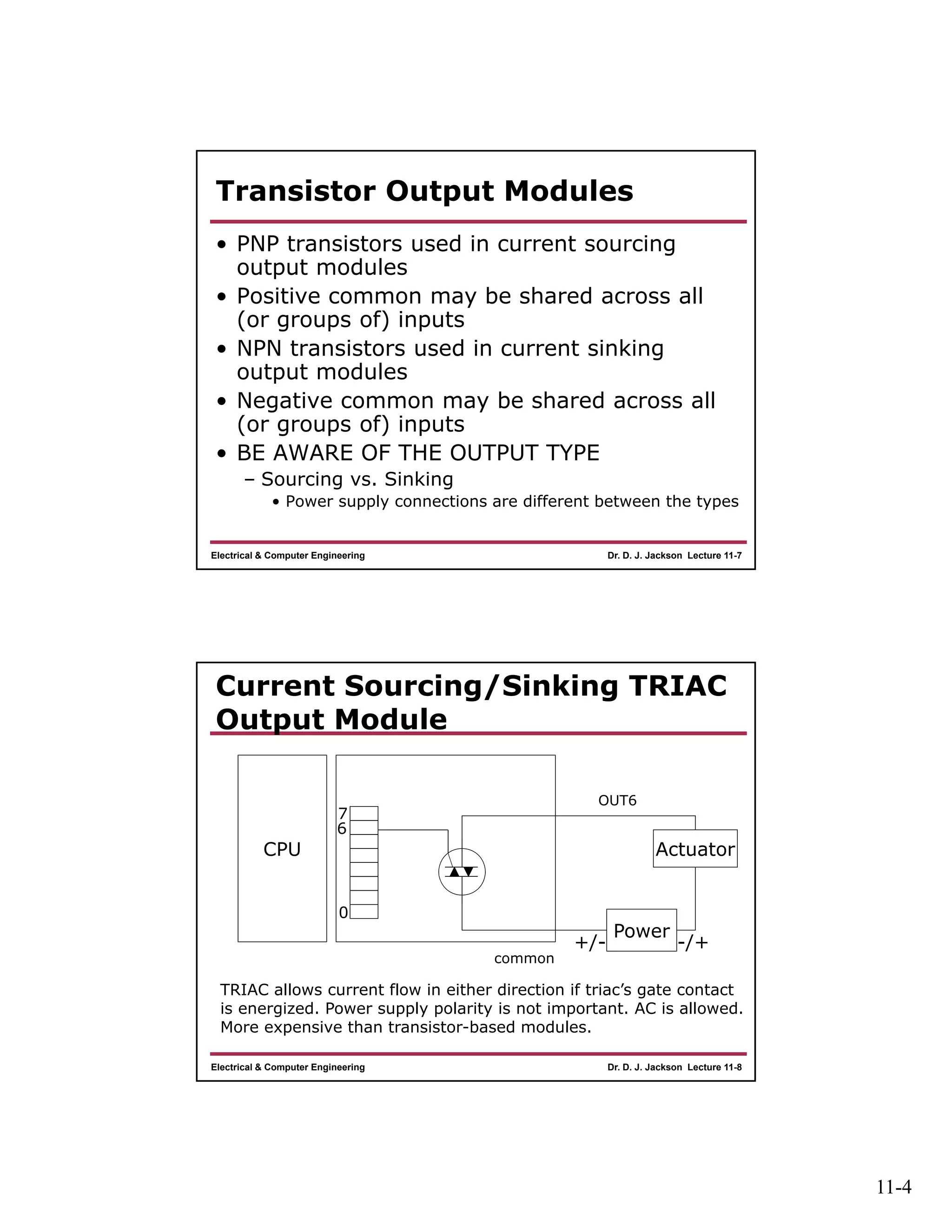
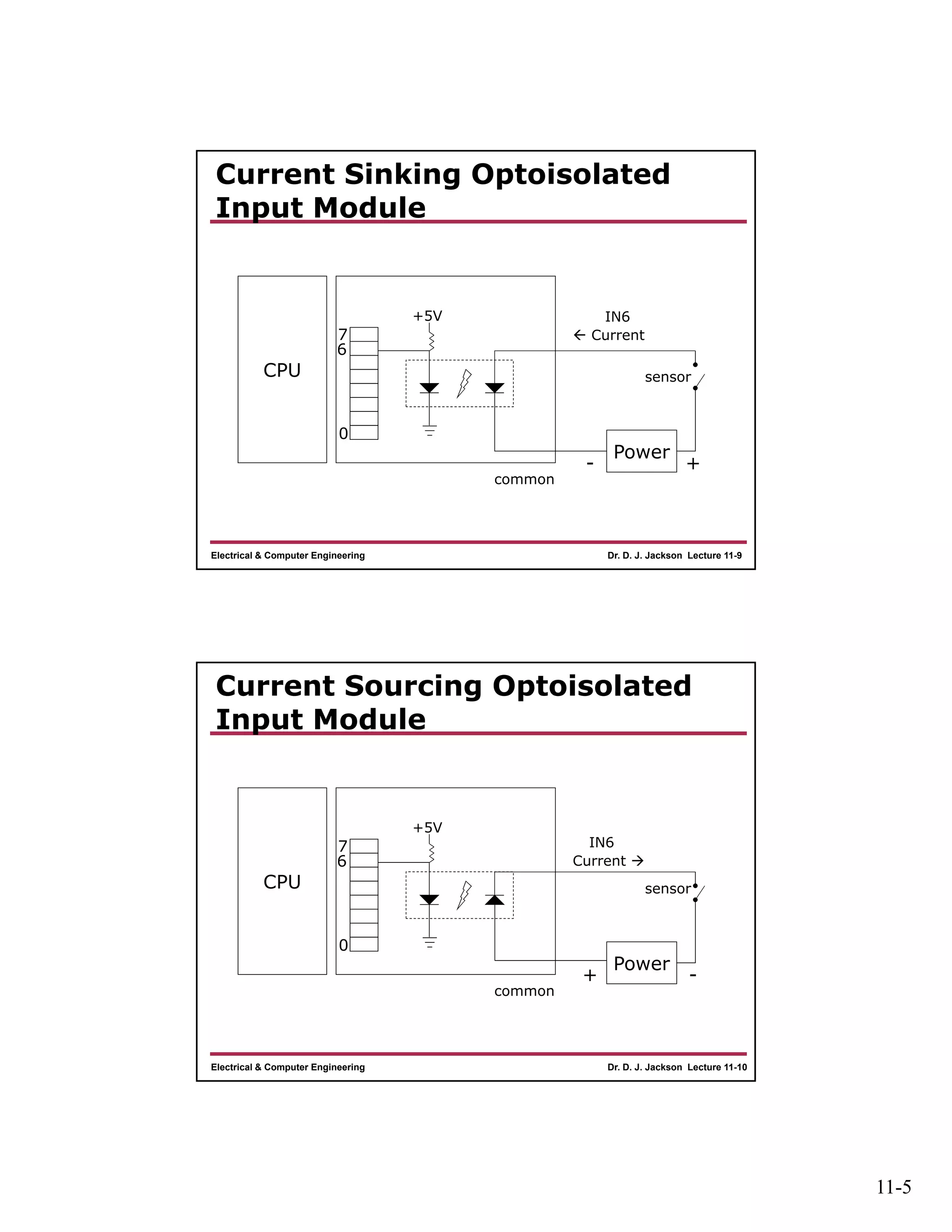
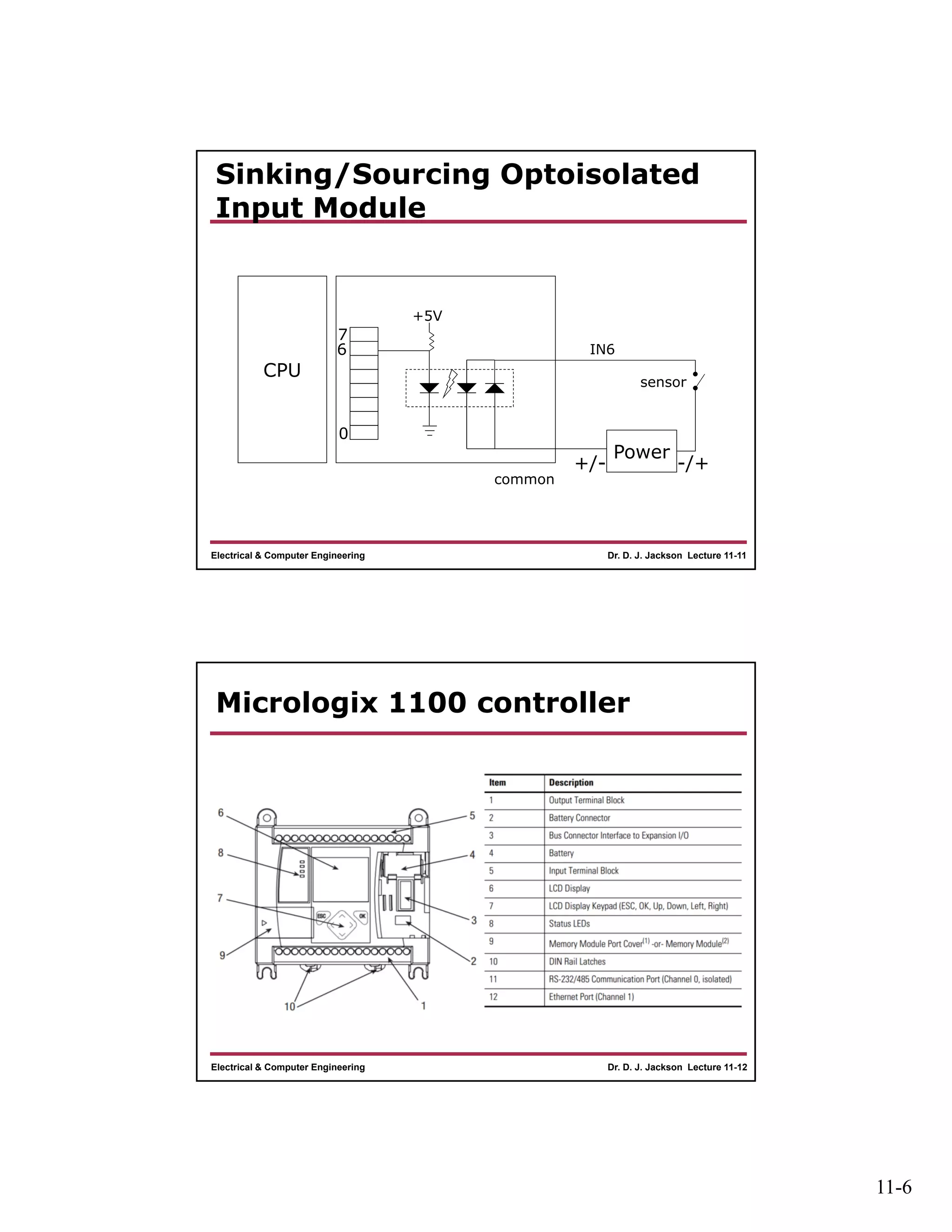
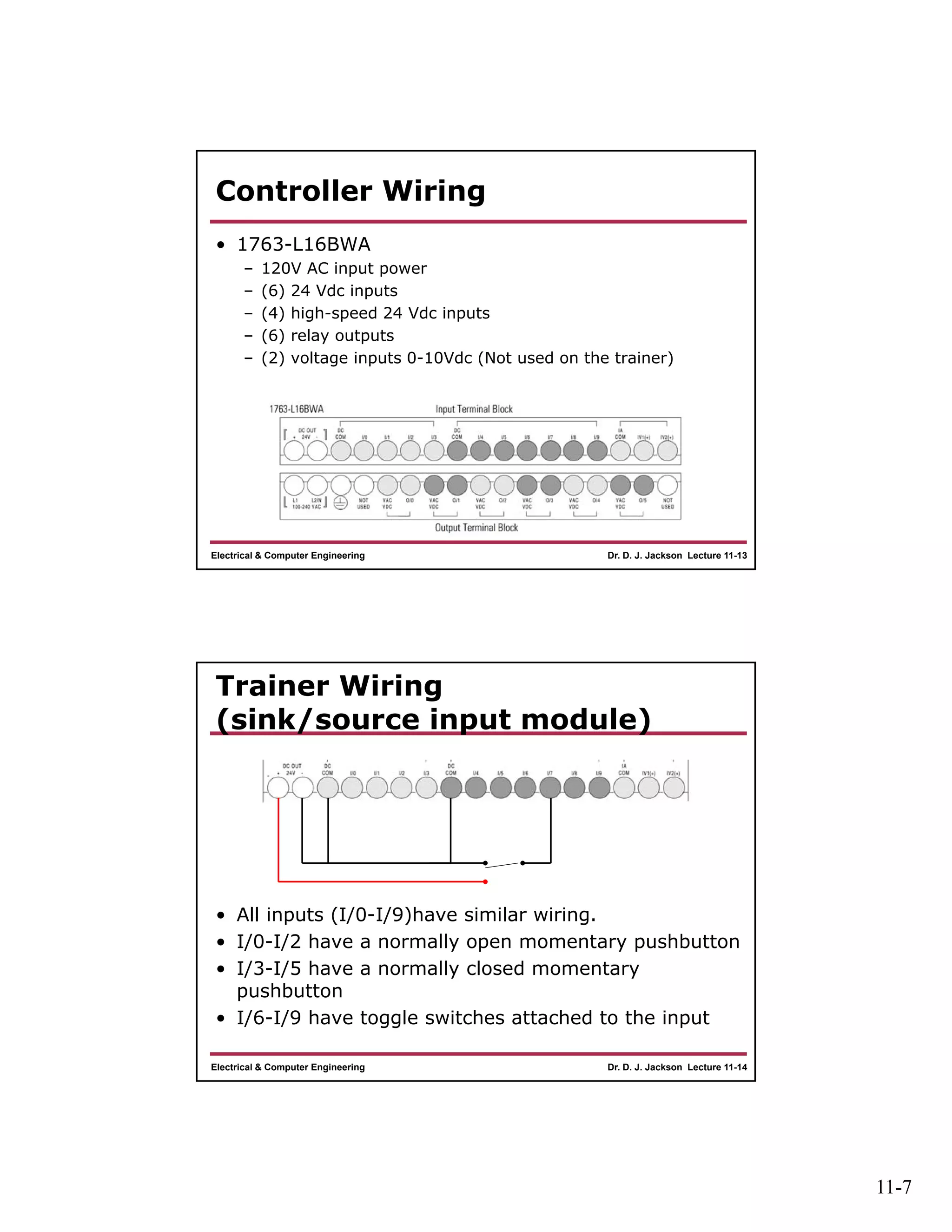
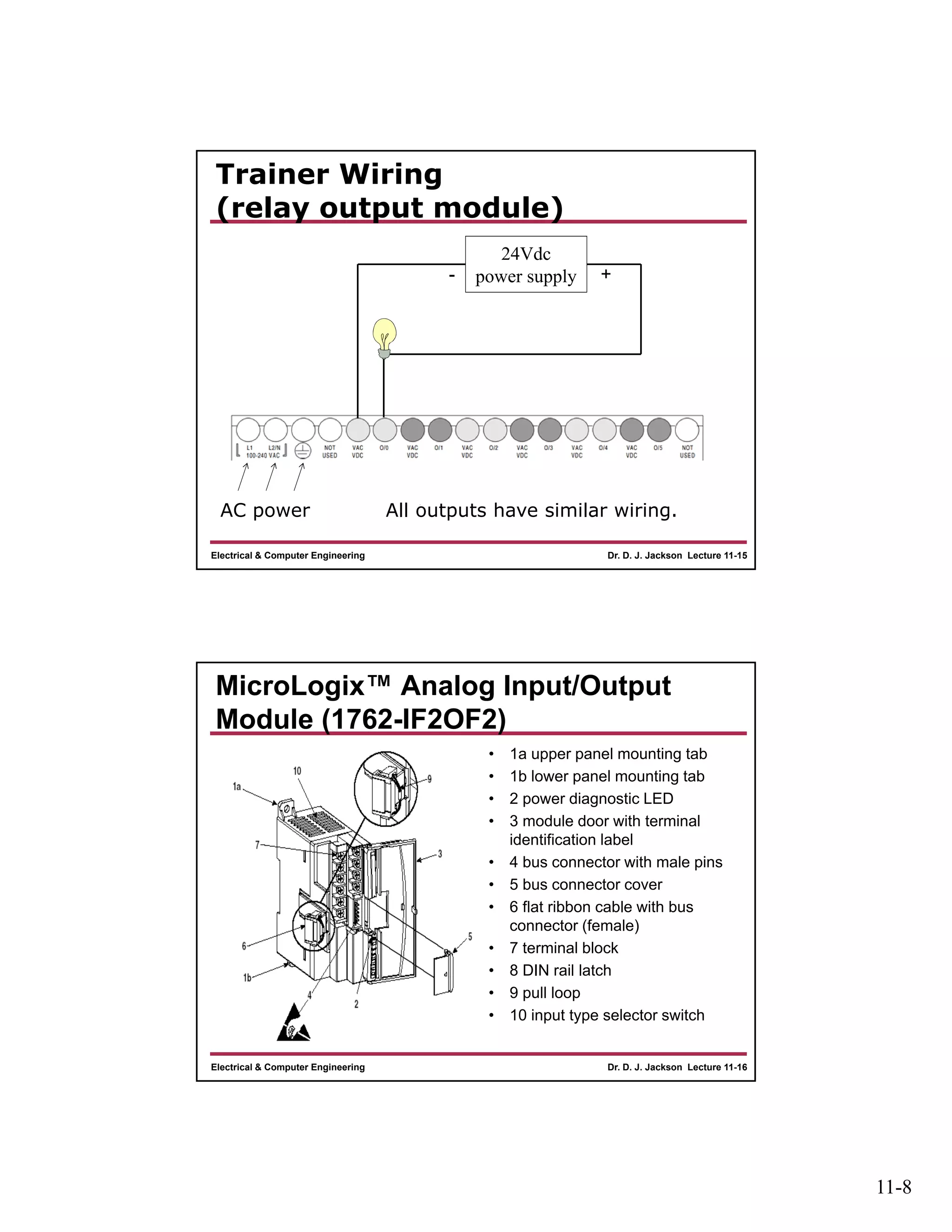
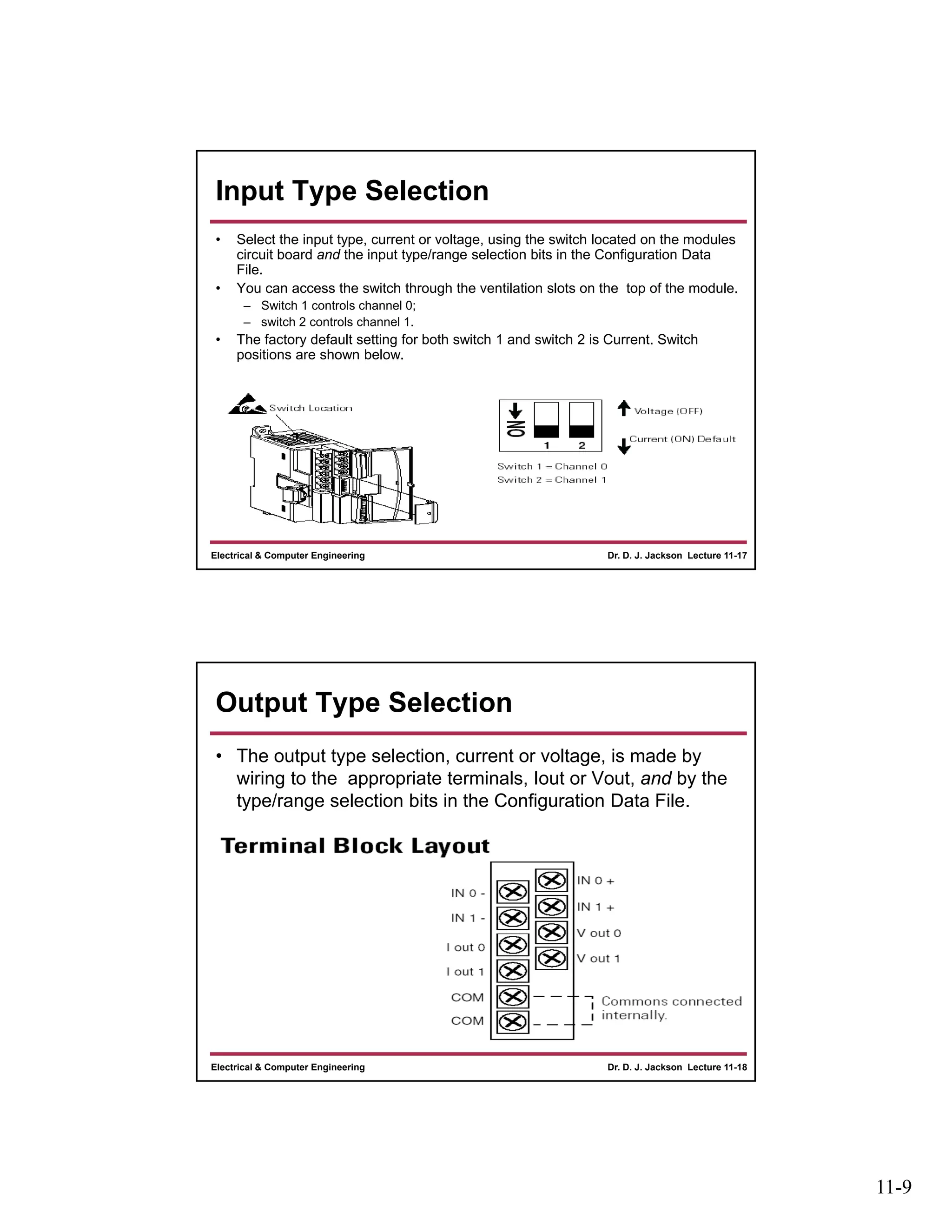
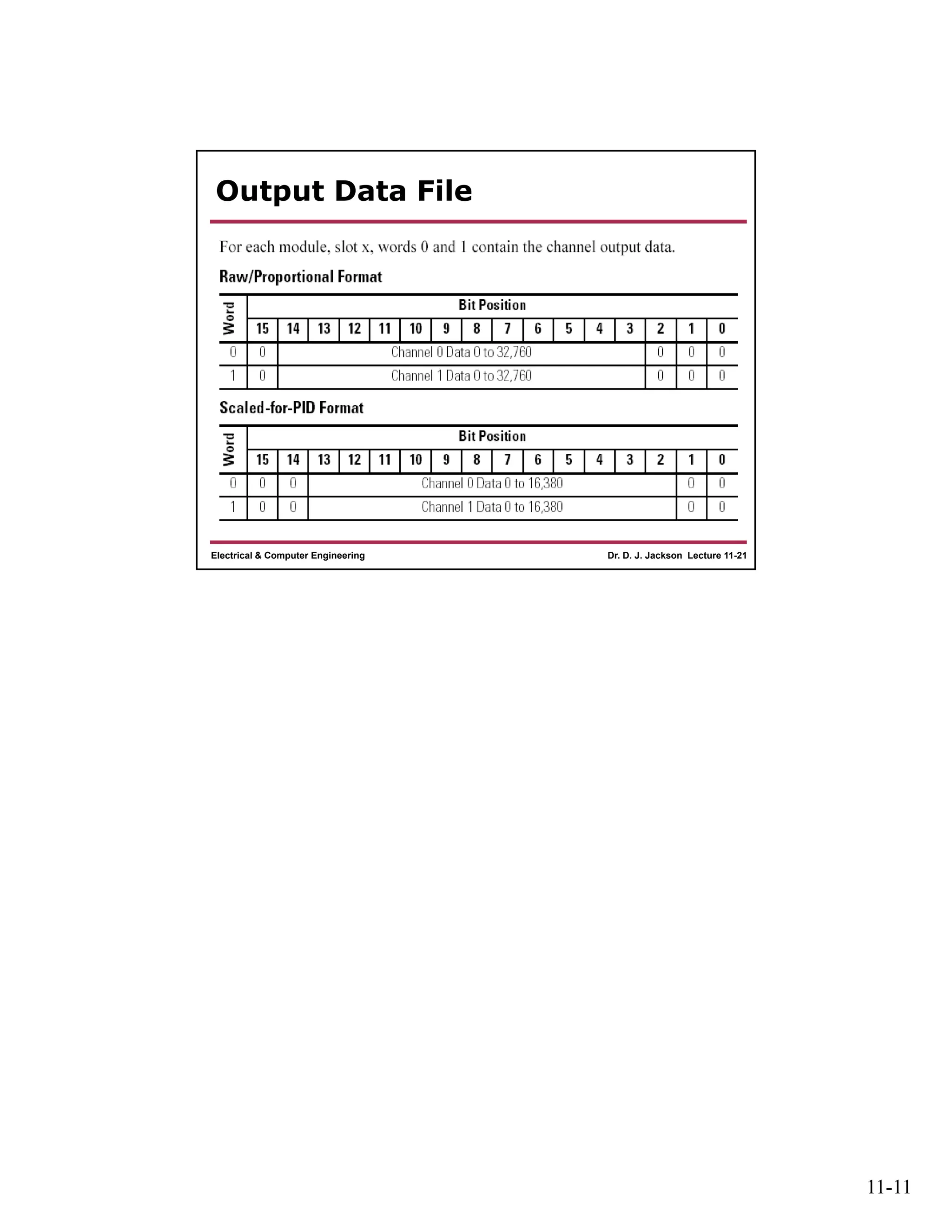
The document discusses different types of input and output modules that can be used in programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It describes relay output modules, transistor-based current sourcing and sinking output modules, and optoisolated current sourcing, sinking, and triac-based input and output modules. It also provides details about configuring and wiring a MicroLogix 1100 PLC trainer, including connection of pushbuttons, toggle switches, and relay outputs. Status and data files for analog input/output modules are also summarized.