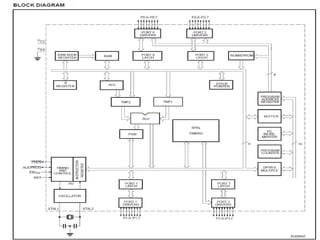
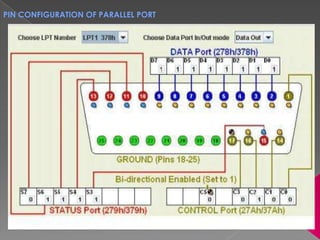
Gopal Dhaker submitted a report about training received at Club First on embedded systems and robotics. Club First is India's largest technical club with over 8,500 members across technical institutes nationwide. The training covered introductions to embedded systems and microcontrollers. Key components of embedded systems like basic electronics, integrated circuits, and the 8051 microcontroller were explained. The report provided details on components like resistors, capacitors, breadboards, LEDs, voltage regulators, timers, motor drivers, and parallel ports. Gopal expressed thanks to Club First for providing a good training to brighten their future.