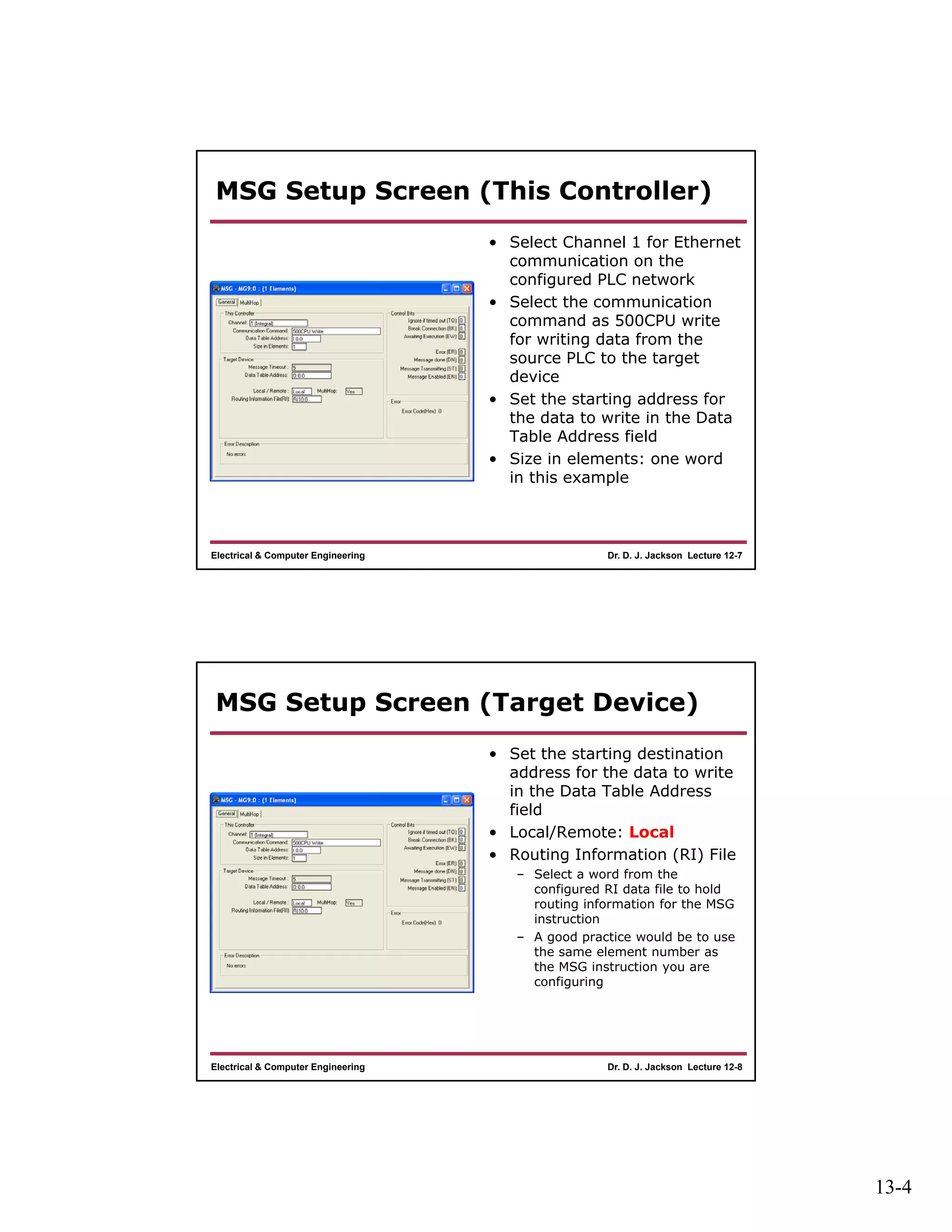
The document discusses setting up programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to communicate over Ethernet using message (MSG) instructions. It explains that two data files need to be created: 1) a MESSAGE data file to hold information for MSG instructions, and 2) a ROUTING INFORMATION data file to hold routing data from MSG instructions. It provides an example program where one PLC writes data from its input file to the output file of a second PLC using a MSG instruction. It outlines the steps to configure the MSG instruction and shows how the routing information is populated in the data file.