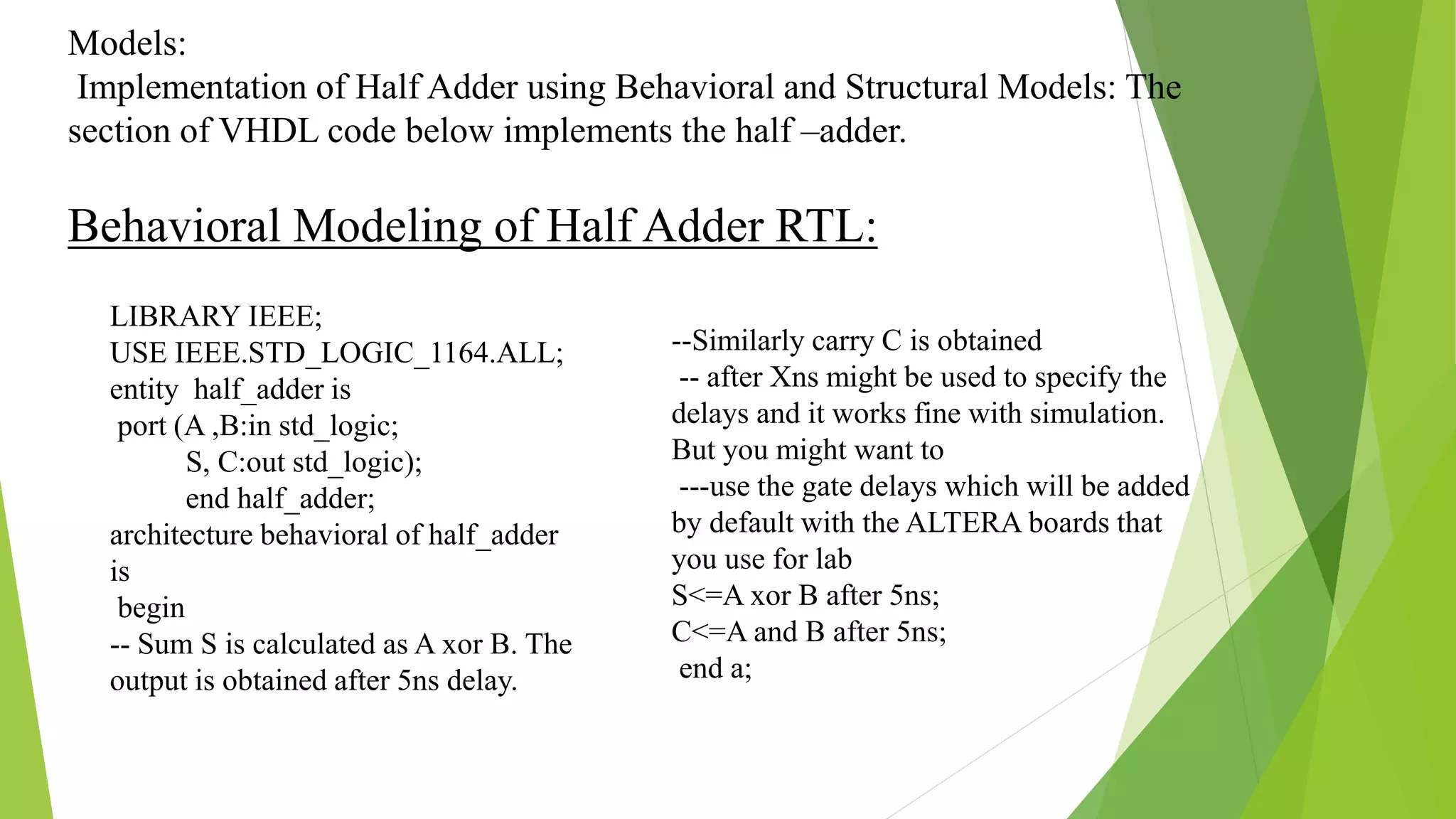
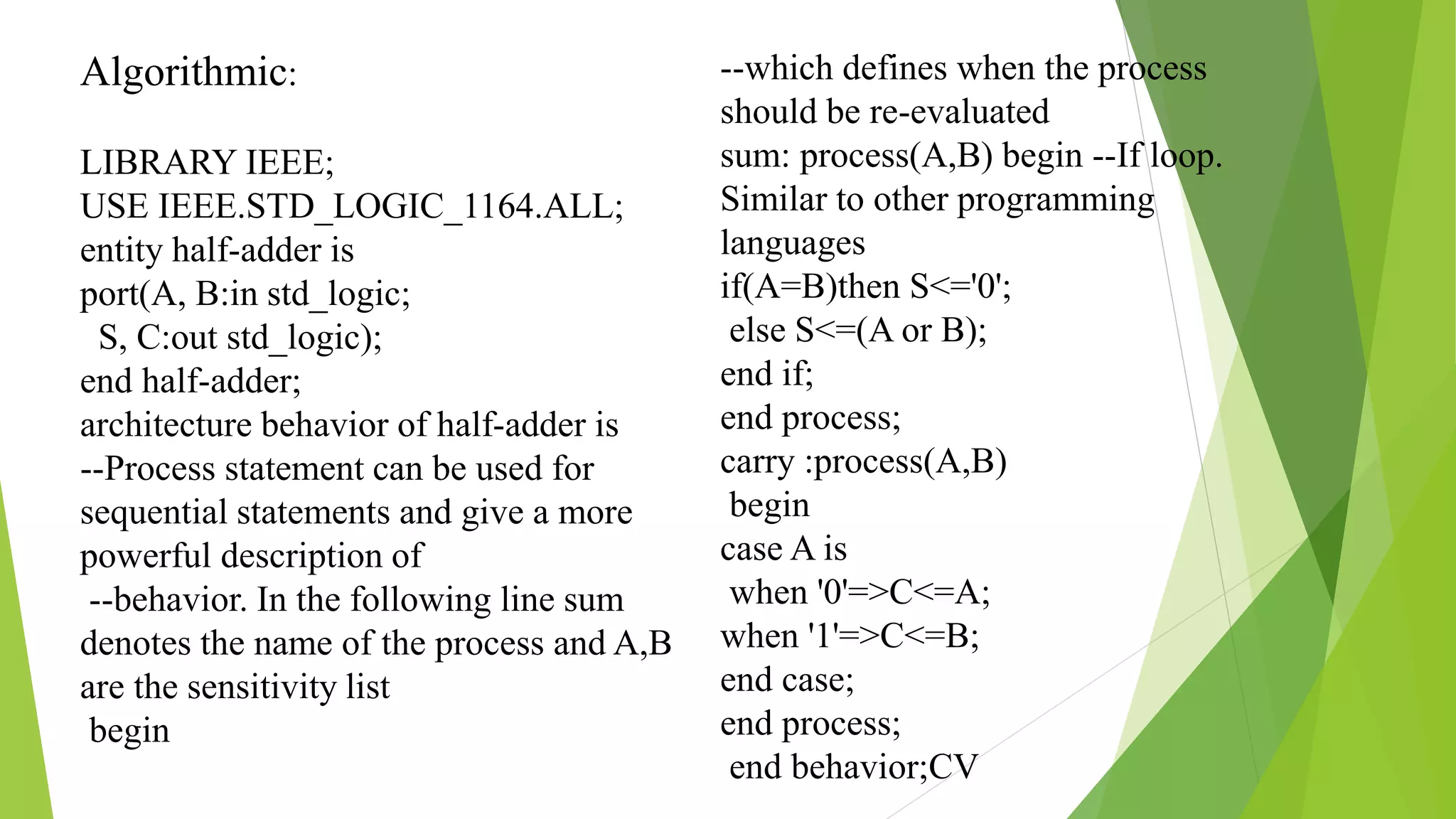
VHDL is a hardware description language used to design digital systems. It allows systems to be modeled at different levels of abstraction like behavioral and structural. The behavioral model describes a system's behavior as inputs and outputs, while the structural model shows how system components are interconnected. VHDL uses entities to define a system's ports and architectures to describe its structure or behavior. Examples show implementing a half adder using behavioral and structural modeling in VHDL.