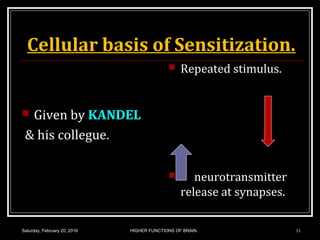
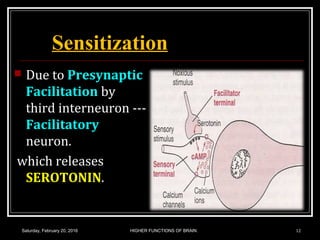
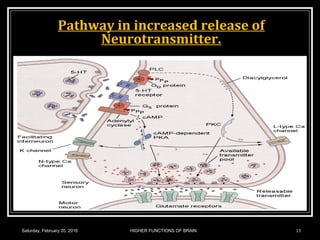
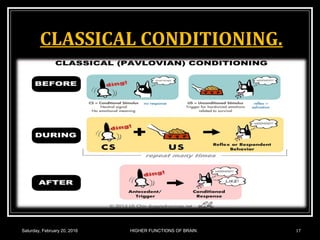
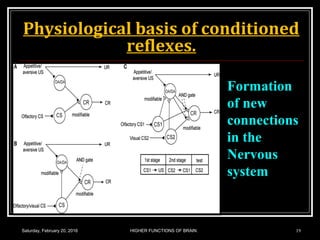
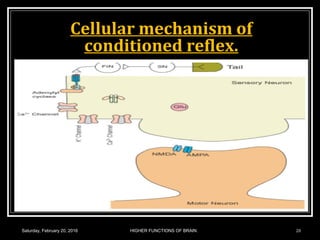
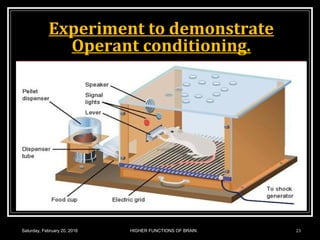
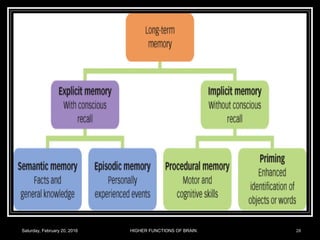
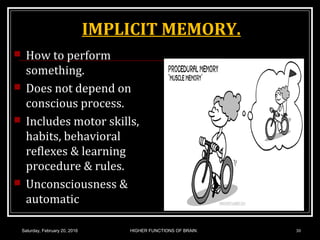
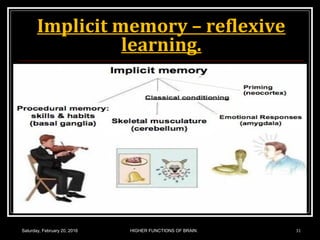
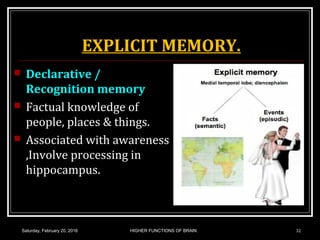
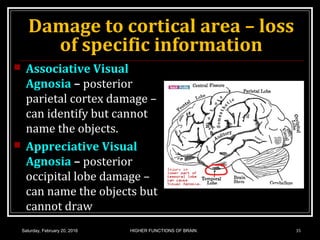
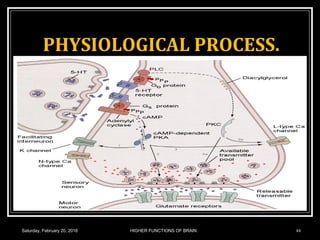
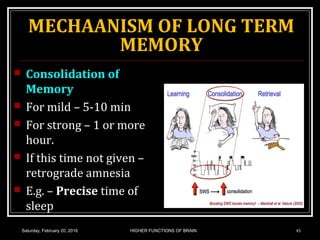
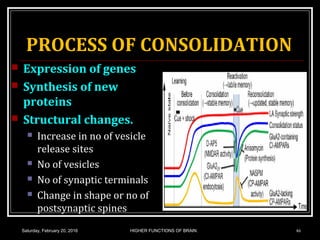
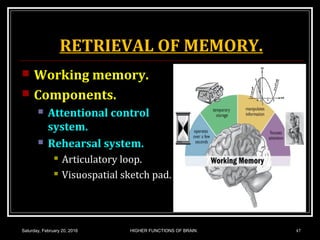
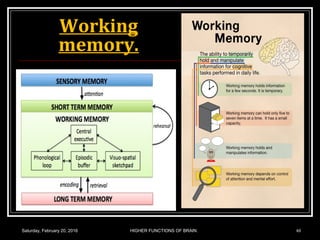
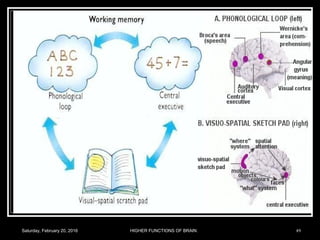
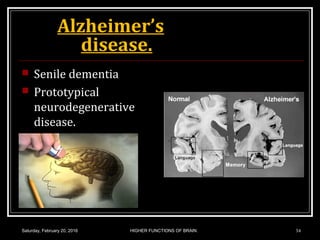
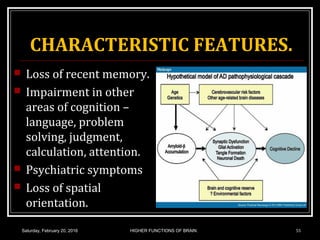
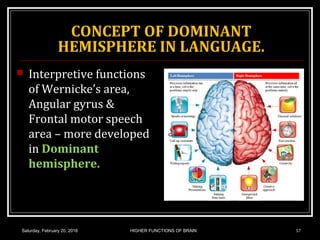
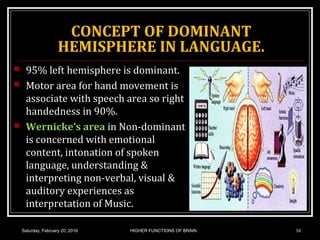
This document discusses learning, memory, and higher brain functions. It covers topics like reflex learning, associative learning through classical and operant conditioning, different types of memory including implicit, explicit, semantic and episodic memory. It discusses the mechanisms of memory formation, consolidation and retrieval. It also covers higher intellectual functions of the prefrontal cortex and disorders of memory like amnesia and Alzheimer's disease.